International Oil Prices and KRW-USD Exchange Rate Fall, Leading to Decline in Import Prices
Decline in Import Prices Positively Affects Consumer Prices
Last month, international oil prices and the won-dollar exchange rate fell sharply, causing import prices to decline for the second consecutive month. As the leading indicator of import prices decreases, a downward stabilization of consumer prices is expected in the future.
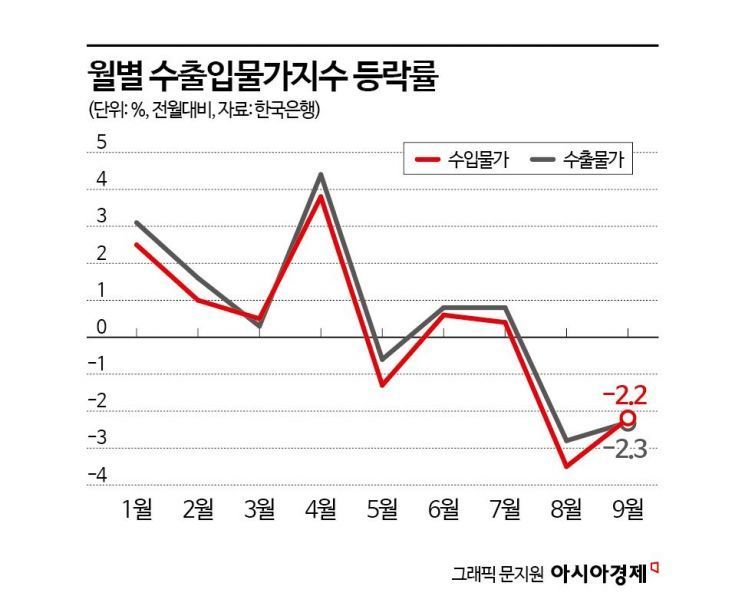
According to the "September Export and Import Price Index and Trade Index (Provisional)" released by the Bank of Korea on the 15th, import prices in September fell by 2.2% compared to the previous month. This marks the second consecutive month of decline following a 3.5% drop in the previous month.
The Bank of Korea explained that import prices fell due to the sharp decline in international oil prices and the won-dollar exchange rate last month. The average Dubai crude oil price in September was $73.52 per barrel, down 5.3% from $77.60 in the previous month. The average won-dollar exchange rate in September was 1,334.82 won, down 1.4% from 1,354.15 won in August.
With the decline in oil prices and exchange rates, the import prices of major mineral products fell, leading to a decrease in import prices overall, according to the Bank of Korea. By item, the decline rates were -3.7% for coal and petroleum products, -1.9% for chemical products, -3.5% for computers, electronics, and optical devices, -6.6% for crude oil, and -4.0% for mineral products. Since import prices tend to lead consumer prices by one to two months, this is expected to help reduce domestic consumer prices in the future.
Lee Moon-hee, head of the Price Statistics Team at the Bank of Korea's Economic Statistics Bureau, said, "Import prices fell mainly for mineral products such as crude oil due to the decline in international oil prices and exchange rates."
Export prices also fell by 2.3% in September compared to August, influenced by exchange rates and oil prices. By item, the decline rates were -7.8% for coal and petroleum products, -2.5% for chemical products, -1.3% for textiles and leather products, and -2.3% for manufactured goods.
Excluding the exchange rate effect, on a contract currency basis, import prices in September fell by 1.0% compared to the previous month, and export prices dropped by 1.1%.
The September export volume index, which shows the fluctuation in exports and imports, rose 3.9% year-on-year due to increases in computers, electronics, optical devices, coal, and petroleum products, while the export value index increased by 5.0%. The import volume index rose 2.4% due to increases in computers, electronics, optical devices, machinery, and equipment, and the import value index increased by 2.1%.
Last month, the net barter terms of trade index rose 1.4% as import prices fell by 0.4% and export prices rose by 1.0%. The net barter terms of trade index measures the quantity of goods that can be imported with one unit of export revenue.
The income terms of trade index increased by 5.3%, influenced by the rise in both the export volume index (3.9%) and the net barter terms of trade index (1.4%). The income terms of trade index measures the quantity of goods that can be imported with total export revenue.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.