Starting from March next year, the financial burden for blood sugar management for pediatric and adolescent patients with type 1 diabetes, including insulin pumps, will be significantly reduced.
On the afternoon of the 28th, the Ministry of Health and Welfare held the 30th Health Insurance Policy Deliberation Committee meeting of 2023 to discuss plans to expand support for insulin pumps (precision insulin automatic injectors) for pediatric and adolescent patients with type 1 diabetes.
Diabetes is generally considered a "lifestyle disease" occurring in adults over 40 years old, but this mainly applies to type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an intractable disease caused by immunological and environmental factors, where immune cells attack and destroy pancreatic beta (β) cells, leading to insulin deficiency. It often develops during childhood and adolescence, hence it is sometimes called "pediatric diabetes." As of June, among 400,000 registered type 2 diabetes patients, only 0.67% (2,681) are under 19 years old, whereas among 30,000 type 1 diabetes patients, 9.9% (3,013) are under 19, showing a significant difference in proportion.
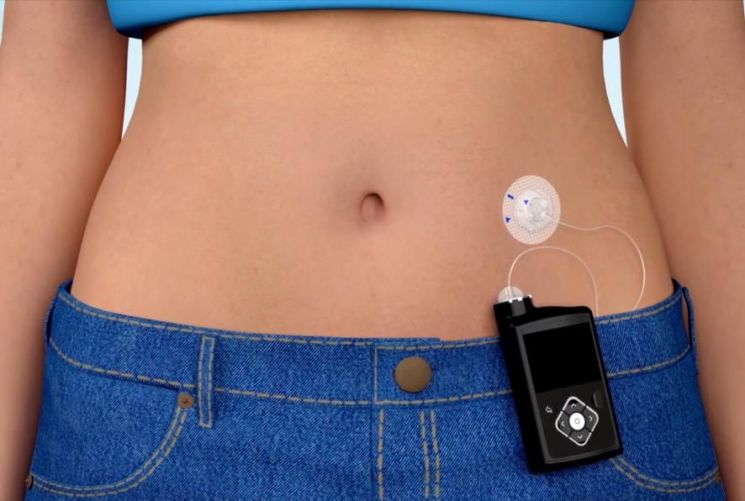
Type 1 diabetes currently has no cure, and patients must receive daily insulin injections for life. However, many young children have difficulty administering injections themselves, so pediatric patients and their families are known to rely heavily on insulin pumps, which allow easy adjustment of insulin supply.
Through this Health Insurance Policy Deliberation Committee discussion, the Ministry of Health and Welfare plans to subdivide diabetes management devices into insulin pumps, electrodes, and consumable materials by function, establish and increase reimbursement standard amounts, and reduce the patient co-payment rate for insulin pumps and electrodes from the current 30% to 10%.
Currently, insulin pumps, which have a replacement cycle of five years, are supported with a reimbursement standard amount of 1.7 million KRW for the basic model upon replacement. Considering the 30% co-payment rate, patients pay 510,000 KRW to purchase an insulin pump. However, if a patient wants the latest "hybrid closed-loop" insulin pump, which costs around 5 million KRW, the difference from the reimbursement standard amount, about 3.3 million KRW, is fully borne by the patient, resulting in a total cost of approximately 3.8 million KRW.
However, from March next year, as the sales price of the hybrid closed-loop model is expected to decrease to around 4.5 million KRW in the long term, the reimbursement standard amount will be set at this level, and the co-payment rate for pediatric and adolescent patients will be lowered to 10%, reducing the patient’s financial burden to about 450,000 KRW. The sensor-integrated insulin pump will also have a standard amount set at 2.5 million KRW (patient burden 250,000 KRW). Additionally, new reimbursement standard amounts will be established for electrodes and other consumable materials, which must be replaced daily, for the sensor-integrated and hybrid closed-loop models, and these will be supported by insurance.
An official from the Ministry of Health and Welfare stated, "By using precision diabetes management devices, caregivers of pediatric and adolescent type 1 diabetes patients, who have been anxious due to the risk of hypoglycemia inherent to type 1 diabetes requiring insulin use, will be able to live with peace of mind," adding, "This will greatly contribute to the management of pediatric and adolescent type 1 diabetes."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![User Who Sold Erroneously Deposited Bitcoins to Repay Debt and Fund Entertainment... What Did the Supreme Court Decide in 2021? [Legal Issue Check]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026020910431234020_1770601391.png)














