Statistics Korea Announces August Industrial Activity Trends
Manufacturing Production Up 5.5%... Highest in 38 Months
Semiconductors Shift to Growth from -2.5% in July
Memory Prices Rebound Mainly in Next-Generation Products
"Semiconductor Production Increasing Compared to Early This Year"
Industrial production in August increased the most in 30 months. This was due to a significant rise in semiconductor production. As the analysis that Korea's key industry, semiconductors, is stabilizing and passing the bottom gains traction, a green light has been turned on for economic recovery.
 On the 27th, cargo containers are stacked at Pyeongtaek Port as seen from the air. [Aerial photography cooperation = Seoul Metropolitan Police Agency Aviation Unit, Pilots: Inspector Shin Seung-ho - Inspector Park Ji-hwan, Crew: Inspector Park Sang-jin] Photo by Kang Jin-hyung aymsdream@
On the 27th, cargo containers are stacked at Pyeongtaek Port as seen from the air. [Aerial photography cooperation = Seoul Metropolitan Police Agency Aviation Unit, Pilots: Inspector Shin Seung-ho - Inspector Park Ji-hwan, Crew: Inspector Park Sang-jin] Photo by Kang Jin-hyung aymsdream@
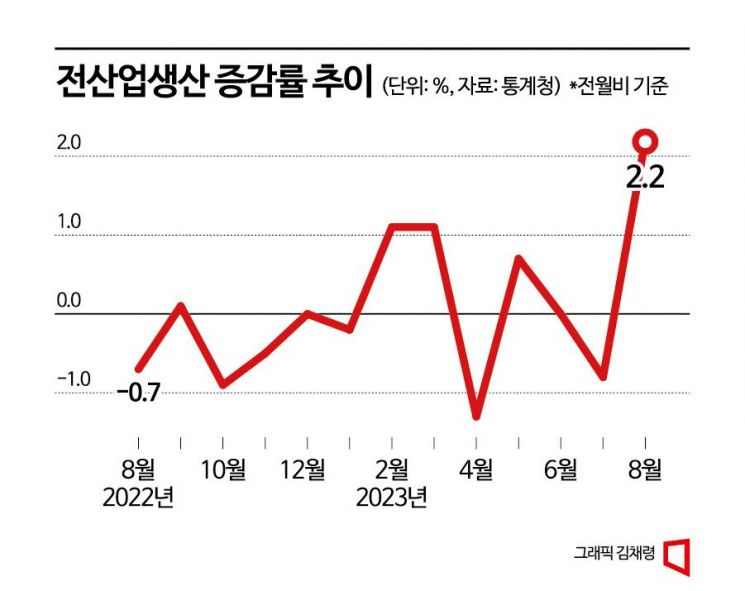
According to the 'August Industrial Activity Trend' announced by Statistics Korea on the 4th, total industrial production increased by 2.2% compared to the previous month. Industrial production showed sluggish performance in June (0%) and July (-0.8%) but returned to an upward trend. The increase was the largest since February 2021, when it rose by 2.3%.
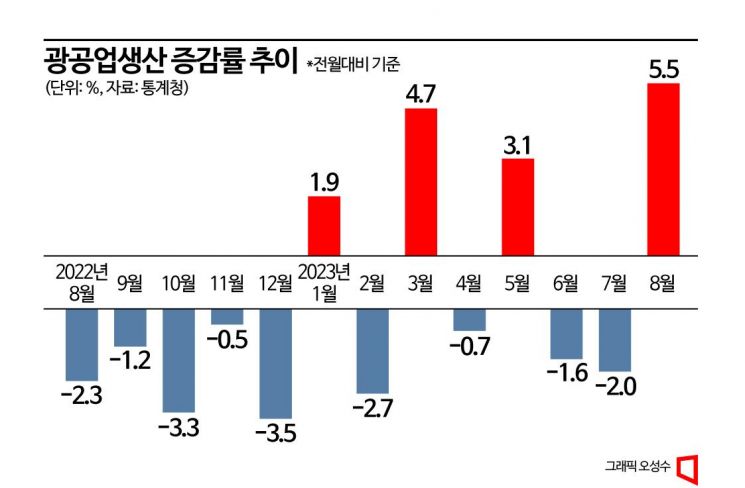
Manufacturing production rose by 5.5%, marking the largest increase in 38 months since June 2020, when it grew by 6.4%. Although production decreased in electronic components (-3.8%), semiconductors (13.4%) and machinery equipment (9.7%) showed strong performance. Increases were also recorded in arts, sports, and leisure (6.2%), as well as accommodation and restaurants (3.0%).
Growth Led by Semiconductors: "Increase in High-Performance Memory Demand"
The production sector's growth was also led by semiconductors. Semiconductor production showed single-digit growth after large fluctuations in February (-15.5%) and March (30.9%). In July, it even decreased by -2.5%. However, production surged again as memory semiconductors such as DRAM and flash memory increased, along with related equipment production including other semiconductor equipment and semiconductor assembly equipment.
Semiconductors also posted favorable results in the manufacturing shipment sector. Semiconductor shipments increased by 3.5% compared to the previous month and by 6.8% compared to the same month last year. Notably, despite a 6.9% decrease in domestic shipments, export shipments rose by 4.4%. Consequently, manufacturing shipments increased by 3.8% compared to July. Kim Bo-kyung, Economic Trend Statistics Officer at Statistics Korea, analyzed, “Production has increased compared to earlier this year due to rising demand for high-performance memory.”
Semiconductor exports continued their recovery in the month following August. According to the 'September Export-Import Trend' announced by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy on the 1st, semiconductor export value last month reached $9.9 billion, the highest since October last year. Quarterly average semiconductor exports increased from $6.86 billion in Q1, $7.55 billion in Q2, to $8.6 billion in Q3 this year. The ministry analyzed, “The reduction in memory production has led to higher spot prices, and demand for high-performance products is showing signs of recovery.”
Memory semiconductor prices are showing signs of rebound, centered on next-generation products. According to market research firm DRAMeXchange, the average fixed transaction price of PC DDR5 16-gigabit (Gb) products in August was $3.40, up 7.26% from $3.17 in the previous month. Another market research firm, Gartner, forecasts that global DRAM prices will rise nearly 18% in Q4 compared to Q3 due to supply shortages.
Industry analysts also suggest that the semiconductor market has passed its bottom. This is because the effects of production cuts by major semiconductor companies are likely to become more apparent. Typically, the effects of semiconductor production cuts take 3 to 6 months to fully manifest. SK Hynix and Micron began production cuts earlier this year, and Samsung Electronics started in April. If there are no additional external shocks and China's economic recovery occurs, the recovery trend is expected to gain momentum.
However, semiconductor inventory increased by 15.3%. This is because the increase in shipments was smaller compared to the significant rise in production. Officer Kim explained, “Semiconductor shipments increase significantly at the end of the quarter,” adding, “Until then, production and inventory tend to increase.”
Investment Up 3.6%, Consumption Down 0.3%
In August, facility investment rose by 3.6% compared to the previous month, driven by increased investment in transportation equipment (13.1%). However, compared to the same period last year, it decreased by 14.9%. This was due to reduced investment in machinery such as special industrial machinery (-17.3%) and transportation equipment like automobiles (-7.3%). Construction performance increased by 4.4% compared to the previous month, with both civil engineering (13.8%) and architecture (1.8%) showing growth.
Retail sales, an indicator of consumption, decreased by 0.3%. Sales increased in non-durable goods such as food (0.2%), but decreased in durable goods like passenger cars and furniture (-1.1%) and semi-durable goods such as clothing (-0.6%). Retail sales have been rebounding this year. After a decrease of -1.8% in January, sales rose by 5.2% in February and 0.1% in March. They declined again by -2.6% in April but increased for two consecutive months in May (0.6%) and June (0.9%), before falling by -3.3% in July.
The coincident composite index, which reflects the current economic situation, stood at 99.4, down 0.2 points from the previous month. The leading composite index, which forecasts future economic conditions, remained unchanged at 99.3 compared to the previous month.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.