Inspection Team Leader Yukukhee, Chairman of the Nuclear Safety Commission Briefing
"On-site Inspection, Significant Progress in Scientific and Technical Aspects"
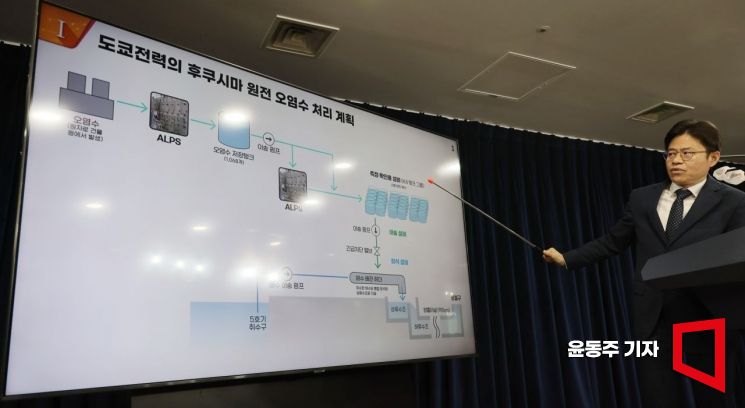
The expert inspection team for the Fukushima nuclear power plant contaminated water conducted an on-site inspection on the 31st, checking the installation status and functionality of the contaminated water storage facility ‘K4 Tank’ and the purification facility ‘Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS).’ The list of all 21 team members was also disclosed. However, since the team stated that further verification is needed regarding performance sustainability and functional suitability, it appears that the safety assessment results of the contaminated water discharge will require more time.
Yu Guk-hee, the head of the inspection team, said at a briefing held at the Government Seoul Office in the morning, “The inspection team focused on key core facilities related to the marine discharge of contaminated water, including ALPS, the K4 tank group, discharge (transfer, dilution, discharge) facilities, the central monitoring and control room, and the chemical analysis building (radioactivity analysis laboratory).”
 Yoo Guk-hee, head of the Japanese Fukushima nuclear power plant government inspection team, is announcing the results of the inspection activities at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant on the 31st at the Government Seoul Office in Jongno-gu, Seoul. Photo by Yoon Dong-joo doso7@
Yoo Guk-hee, head of the Japanese Fukushima nuclear power plant government inspection team, is announcing the results of the inspection activities at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant on the 31st at the Government Seoul Office in Jongno-gu, Seoul. Photo by Yoon Dong-joo doso7@
The inspection team emphasized that this on-site inspection marked a meaningful advancement from scientific and technical perspectives. Specifically, ALPS is a facility that removes radioactive nuclides (excluding tritium) from the Fukushima nuclear power plant contaminated water. They secured data on major failure cases and countermeasures since ALPS operation began. Along with detailed analysis, they plan to additionally secure ALPS maintenance plans to comprehensively verify ALPS performance.
The K4 tank group is a facility that measures the concentration of radioactive nuclides to confirm compliance with discharge standards. The inspection team checked the installation status of circulation pumps that circulate contaminated water between tanks and reviewed test and inspection records to verify the performance of the circulation system.
Regarding the transfer facilities, it was confirmed that the emergency shut-off valves are designed to close automatically upon loss of driving force, and additionally, manual shut-off valves have been installed. For the dilution and discharge facilities, they confirmed whether seawater and contaminated water are being diluted to meet the tritium discharge target (1,500 Bq/L), and whether the seawater transfer pumps are designed with sufficient capacity (7,086 m3/hr per unit) to meet the dilution target.
 Yoo Guk-hee, head of the Japanese Fukushima nuclear power plant government inspection team, is announcing the results of the inspection activities at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant on the 31st at the Government Seoul Office in Jongno-gu, Seoul. Photo by Yoon Dong-joo doso7@
Yoo Guk-hee, head of the Japanese Fukushima nuclear power plant government inspection team, is announcing the results of the inspection activities at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant on the 31st at the Government Seoul Office in Jongno-gu, Seoul. Photo by Yoon Dong-joo doso7@
At the central monitoring and control room, the team focused on inspecting the appropriateness of monitoring and controlling key facilities, as well as whether alarms and emergency shutdowns of contaminated water discharge can be triggered in case of abnormal situations. The inspection team plans to comprehensively verify the adequacy of monitoring and control functions through inspections by the Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) on the transfer, dilution, and discharge facilities in the future.
The inspection team explained, “This inspection represents a meaningful advancement in the scientific and technical review process through direct on-site confirmation and more detailed data acquisition,” adding, “Additional analysis and verification work will be conducted for more precise judgment.”
The team disclosed all 21 members on the day. The disclosed members include Head Yu and the following: ▲ Kang Yu-gyeom, Researcher, Environmental Radioactivity Evaluation Division, Korea Institute of Nuclear Safety (KINS) ▲ Kim Dae-ji, Senior Researcher, Environmental Radioactivity Evaluation Division, KINS ▲ Kim Seok-hyun, Senior Researcher, Marine Environment Research Department, Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology (KIOST) ▲ Kim Sun-hye, Senior Researcher, Mechanical and Materials Evaluation Division, KINS ▲ Kim Sung-il, Senior Researcher, Radiation and Waste Evaluation Division, KINS ▲ Kim Jeong-ho, Senior Researcher, Structural and Site Evaluation Division, KINS ▲ Kim Cheol-soo, Senior Researcher, Environmental Radioactivity Evaluation Division, KINS ▲ Kim Hyun-il, Senior Researcher, Environmental Radioactivity Evaluation Division, KINS ▲ Shin Cheol, Senior Researcher, Overseas Regulatory Technology Support Project, KINS ▲ Shin Ho-cheol, Senior Researcher, Instrumentation, Control and Electrical Evaluation Division, KINS ▲ Jang Jae-kwon, Specialist Senior Researcher, KINS ▲ Jeong Gu-young, Senior Researcher, Nuclear Safety Headquarters, KINS ▲ Jeong Su-jin, Senior Researcher, Regulatory Policy Division, KINS ▲ Jeong Seung-young, Specialist Senior Researcher, KINS ▲ Jeong Yoon-hyung, Appointed Regulator, Education and Operations Division, KINS ▲ Chae Gyu-han, Senior Researcher, Environmental Radioactivity Evaluation Division, KINS ▲ Choi Na-yoon, Researcher, Radiation and Waste Evaluation Division, KINS ▲ Choi Seok-won, Senior Researcher, Environmental Radioactivity Evaluation Division, KINS ▲ Choi Young-sung, Senior Researcher, Innovation Strategy Center, KINS ▲ Han Seung-yeon, Researcher, Environmental Radioactivity Evaluation Division, KINS.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
















