[Battery Material Supergap]③
The Key to All-Solid-State Commercialization: 'Solid Electrolyte'
Sulfide Electrolyte Technology Leads the Way
Active Development of Safe Wet and Ceramic-Coated Separators Underway
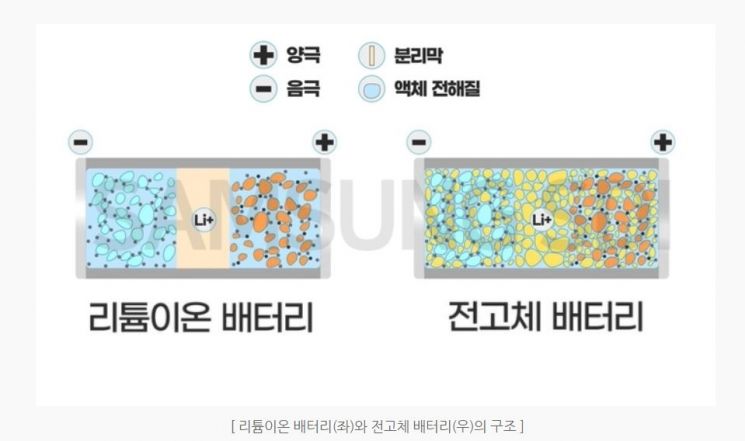
The key to the commercialization of all-solid-state batteries, known as the "dream battery," lies in the core material called the "solid electrolyte." An all-solid-state battery replaces the conventional flammable liquid electrolyte between the cathode and anode with a solid electrolyte. Since the electrolyte serves as the "means of transport" for lithium ions moving between the cathode and anode, it must have high "conductivity" to allow lithium ions to move smoothly.
However, current technology cannot produce solid electrolytes with high ionic conductivity. Additionally, because it is solid, it has high resistance, resulting in slow charging speeds and shortened battery life. Technologies to overcome these drawbacks are under development.
Solid electrolyte materials are broadly categorized into ▲oxide-based ▲sulfide-based ▲polymer-based types. Oxide-based electrolytes have high resistance and are unsuitable for electric vehicles that require fast charging, so they are mainly used in small batteries. Polymer-based electrolytes are similar to conventional liquid electrolyte technology and have similar manufacturing processes, providing cost competitiveness. However, they have low lithium-ion conductivity and can only be used in high-temperature environments.
Among these, the most technologically advanced field is sulfide-based electrolytes. Sulfide-based electrolytes exhibit the highest ionic conductivity. They also enable implementation with a high energy density exceeding 900Wh/ℓ, making them a focus of active research.
All-solid-state battery technology is expected to be a "game changer" in the future electric vehicle market. SNE Research forecasts that global all-solid-state battery production capacity will gradually increase from 0.06GWh last year to 1GWh in 2025, 149GWh in 2030, and 950GWh in 2035. LG Energy Solution has set goals to commercialize polymer-based batteries by 2026 and sulfide-based batteries by 2030. Samsung SDI plans to commercialize sulfide-based batteries by 2027, and SK On aims for 2030. Since last year, Samsung SDI has been constructing a pilot line for all-solid-state batteries at its research center in Suwon, Gyeonggi Province. Sample production is planned to begin in the second half of this year.
Separators, which serve as pathways for lithium-ion movement, must prioritize safety. Separators physically prevent contact between cathode and anode materials and help prevent explosions and fires. To address electric vehicle battery fire issues, development of wet separators and ceramic-coated separator technologies is underway.
Wet separators are thinner than dry separators. This allows more batteries to be packed per unit volume. Wet separators are dry separators coated with ceramic powder, reducing thermal shrinkage and enhancing stability. Wet separators are used in high-end electric vehicle models. Leading companies are pursuing various technological developments such as thinning to less than 9μm, ceramic coating (high strength and heat resistance), and more.
In 2021, LG Chem acquired the battery materials business division, including separator coating, from LG Electronics' Business Solutions (BS) division. Additionally, it entered the market by establishing a joint venture (JV) with Japan's Toray for separators. SK IE Technology (SKIET), the global leader in wet separators, internalized its separator business through a "sequential stretching" technology that stretches the material horizontally once and vertically once more. Typical separator production processes stretch the material simultaneously in all directions, making it difficult to change the fabric specifications once the equipment is set. Based on sequential stretching technology, SKIET rose to the top of the wet separator market. It can currently produce separators as thin as 4 micrometers (μm), which is 1/25th the thickness of a human hair.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















