Ministry of Science and ICT Announces Telecom Quality Evaluation Results
LTE Subscribers Still High
SKT Leads in Speed... LGU+ Shows Significant Improvement
[Asia Economy Reporter Cha Min-young] As the proportion of LTE (4G) subscribers in South Korea reaches the 60% range, it has been revealed that efforts to improve LTE speeds by some telecom companies, including KT, are insufficient. Although the speed and coverage of 5G services have improved for all three major telecom companies this year, there are concerns that quality improvement efforts should not be neglected for LTE services, which are used by more than half of users.
LTE speeds slightly improved compared to last year... LG U+ shows larger improvement
On the 29th, the Ministry of Science and ICT announced the results of the 2022 telecommunications service quality evaluation reflecting these details. The Ministry, together with the National Information Society Agency (NIA), conducts coverage inspections and quality evaluations of wired and wireless communication services to provide coverage and quality information and to promote telecom companies' network investment expansion.
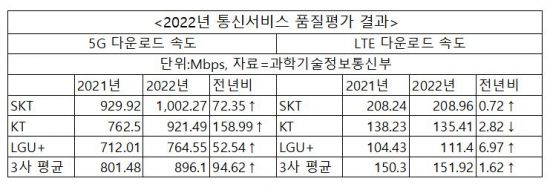
The average LTE download speed among the three companies was 151.92 Mbps, which is 1.62 Mbps faster than the previous year. Upload speed was 39.39 Mbps, down 0.37 Mbps from the previous year. By telecom company, SK Telecom's download speed was 208.96 Mbps, up 0.72 Mbps from last year; LG U+ was 111.40 Mbps, up 6.97 Mbps, showing a significant improvement. In contrast, KT's speed decreased by 2.82 Mbps to 135.41 Mbps, the only one among the three major telecom companies to experience a speed decline.
Among a total of 311,210 download speed measurements, 37.85% were in the 100 Mbps to 200 Mbps range, the largest portion. For speeds below 100 Mbps, 21.98% were between 50 Mbps and 100 Mbps, and 14.81% were below 50 Mbps, totaling 36.79%. Measurements below 6 Mbps accounted for 1.52%.
Download speeds notably dropped in transportation infrastructure. Inside subway cars, the speed was 196.39 Mbps, down from 217.92 Mbps the previous year. High-speed trains such as KTX and SRT recorded 108.32 Mbps, down from 118.63 Mbps last year, and highways showed a slight decrease to 135.76 Mbps from 134.00 Mbps the previous year.
By city type, large cities recorded 181.48 Mbps, small and medium cities 151.12 Mbps, and rural fishing villages 127.32 Mbps. In rural LTE download speeds by telecom company, SK Telecom led with 186.34 Mbps, followed by KT at 115.47 Mbps, and LG U+ at 80.14 Mbps. The LTE download speed gap between urban and rural areas averaged 38.98 Mbps, a 20% reduction from the previous year.
5G download speeds increased for all three companies
The average 5G download speed among the three companies was 896.10 Mbps, an 11.8% increase from 801.48 Mbps the previous year. By company, SK Telecom improved by 72.35 Mbps to 1002.27 Mbps; KT increased by 158.99 Mbps to 921.49 Mbps; and LG U+ rose by 52.54 Mbps to 764.55 Mbps. The average 5G upload speed improved by 12% to 93.16 Mbps.
Among 410,655 download speed measurements, 41.18% were between 600 Mbps and 1 Gbps, the largest share. Speeds below 600 Mbps accounted for 21.33% between 200 Mbps and 600 Mbps, and 3.67% below 200 Mbps, totaling 25.00%. Measurements below 50 Mbps accounted for 0.95%.
Download speeds improved across outdoor areas, multi-use facilities, transportation infrastructure, and residential areas. Outdoor administrative districts saw a 14% increase to 890.33 Mbps; multi-use facilities such as amusement parks and hospitals, and transportation infrastructure like subways, improved by 10% to 901.38 Mbps; residential areas improved by 3% to 890.46 Mbps.
By city size, large cities recorded 929.64 Mbps and small to medium cities 898.95 Mbps, reflecting improvements of 10.6% and 14.7% respectively from the previous year. The speed gap narrowed by 45.8% to 30.69 Mbps.
The '5G→LTE handover rate,' indicating 5G network stability, averaged 1.34% for the three companies, improving by 0.54 percentage points from 1.88% the previous year. By company, SK Telecom was lowest at 0.98%, followed by LG U+ at 1.32%, and KT at 1.72%.
Latency averaged 17.89 ms for the three companies, a 3.86% improvement from 18.61 ms the previous year. By company, SK Telecom recorded 15.75 ms, KT 17.21 ms, and LG U+ 20.70 ms.
The coverage area indicating 5G service availability also expanded. For outdoor areas, the 5G coverage area in 85 cities publicly disclosed by telecom companies reached an average of 33,212.50 km² as of October, 1.7 times the 19,044.04 km² recorded in the same month last year. By company, SK Telecom covered 34,241.58 km², KT 33,185.10 km², and LG U+ 32,210.82 km². It was confirmed that 5G networks have been established in almost all administrative districts and major towns and townships in all 85 cities nationwide.
For indoor facilities such as department stores, large hospitals, and cinemas, among 4,505 major multi-use facilities in the 85 cities, an average of 4,492 facilities (99%) had 5G available, a 1.6% increase from the previous year. By company, KT and LG U+ each covered 4,505 facilities, and SK Telecom covered 4,466.
The 5G connection availability rate in major multi-use facilities, based on sample inspections by the Ministry of Science and ICT, was 96.54%, improving by 1.18 percentage points from the previous year. Among transportation infrastructure, the three telecom companies installed 5G in 1,041 of 1,063 subway stations, accounting for 98%. However, the Shinbundang Line and Seohae Line had lower coverage rates of 58.82% and 6.63%, respectively. For KTX and SRT, 5G was installed in 67 of 69 stations (97%). On highways, 5G was established in 223 of 228 sections across 41 highways nationwide, accounting for 98% coverage.
Open Wi-Fi speeds decline... Wired internet shows mixed trends
Wi-Fi speeds declined across both commercial and open Wi-Fi. Commercial Wi-Fi download speeds dropped to 338.56 Mbps from 400.85 Mbps the previous year, and open Wi-Fi speeds decreased to 353.30 Mbps from 420.20 Mbps. Public Wi-Fi speeds, a key policy focus for the Ministry of Science and ICT next year, slightly improved. Public Wi-Fi download speeds rose to 336.21 Mbps from 328.04 Mbps. Newly measured bus Wi-Fi speeds averaged 104.10 Mbps this year.
Wired internet speed improvements varied by segment. According to continuous user evaluations, the average download speed for 1 Gbps plans was 980.86 Mbps, slightly slower than 962.62 Mbps the previous year. The 500 Mbps plan's average download speed improved to 493.34 Mbps from 470.08 Mbps. Newly measured this year, the average download speeds for 10 Gbps, 5 Gbps, and 2.5 Gbps plans were 8.52 Gbps, 4.14 Gbps, and 2.19 Gbps, respectively.
The average video quality rating for major mobile video services such as YouTube, Naver TV, Kakao TV, Netflix, and Wavve was 4.19 out of 5, higher than 4.08 the previous year.
The Ministry of Science and ICT stated, "Although 5G coverage and quality have improved, active network investment expansion by the three telecom companies is crucial to enhance the perceived quality for 5G users. Continuous quality management investment is also necessary for LTE, which is still used by many users."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















