AI Interpretation Including Video Analysis
Accuracy Improved by About 20%
Expected to Aid Rapid and Accurate Patient Diagnosis
Also Helps Reduce Doctors' Burden
[Asia Economy Reporter Lee Gwan-ju] Artificial intelligence (AI) has surpassed specialists. Research continues to show that AI's judgments are more accurate than those of doctors in interpreting various tests. Given AI's ability to instantly learn from numerous cases through machine learning techniques, its accuracy is expected to improve over time as more data accumulates.
On the 28th, according to the medical community, an intriguing paper was published in the first half of this year in 'Scientific Reports,' a sister journal of the globally prestigious journal 'Nature.' The paper reported that AI applying machine learning demonstrated superior accuracy compared to five specialists in analyzing X-ray images.
This study, conducted by the University of Bath in the UK to verify machine learning accuracy, assessed the diagnostic accuracy of hip fracture presence in 2,364 X-ray images. The results showed that the specialists' cross-diagnosis accuracy was only 77.5%, whereas AI achieved 92%, 19 percentage points higher. Despite verification by up to five specialists, AI showed significantly better accuracy.
Similar research results are emerging in Korea as well. Professor Hwang Ho-sik's research team at Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital Ophthalmology developed a technology to interpret eyelid meibomian gland images using AI and demonstrated its accuracy. The meibomian gland is a type of sebaceous gland in the eyelid, and meibomian gland dysfunction is a representative cause of dry eye syndrome. After training the AI, the team compared its interpretation results with those of two dry eye specialists. In verifying the degree of meibomian gland loss, AI showed 73.01% accuracy, outperforming the specialists at 53.44%. For reproducibility verification, when comparing AI trained on 600 meibomian gland images taken at Korea University Ansan Hospital with specialists' evaluations of gland loss, AI again showed higher accuracy.
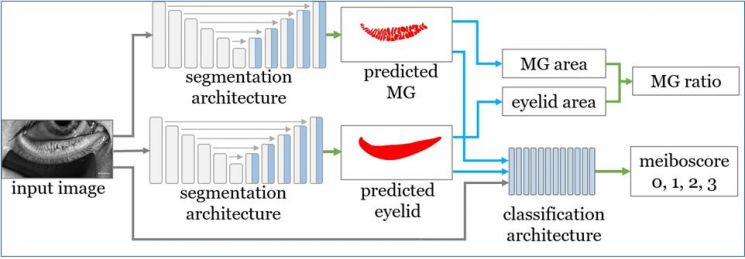 Infrared Meibomian Gland Imaging Analysis Artificial Intelligence Deep Learning Model. [Source=Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital]
Infrared Meibomian Gland Imaging Analysis Artificial Intelligence Deep Learning Model. [Source=Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital]
Additionally, Professor Yoo Il-han's neurology research team at Nowon Eulji University Hospital recently announced research results showing that AI's interpretation of electromyography (EMG) tests is more accurate than that of specialists. The team applied AI to analyze data from 57 patients suspected of muscular disease who underwent EMG tests between 2015 and 2020. The AI's accuracy was 88%, sensitivity 82%, and positive predictive value 86%. In contrast, six doctors interpreting the same EMG tests under identical conditions showed an accuracy of 69%, sensitivity of 54%, and positive predictive value of 60%. Notably, AI took only one second to provide a final diagnosis, whereas doctors took an average of 30 to 40 minutes. Professor Yoo stated, “AI-based EMG interpretation was fast and accurate,” adding, “If AI interpretation is applied to EMG, it will play an important role in diagnosing neuromuscular patients more accurately and quickly.”
The advancement in AI's interpretation accuracy is ultimately expected to assist doctors' readings, reduce their workload, and enable rapid and accurate diagnoses, leading to overall improvement in the quality of medical services. The medical community particularly anticipates its valuable use in medically underserved areas lacking specialists in image interpretation.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















