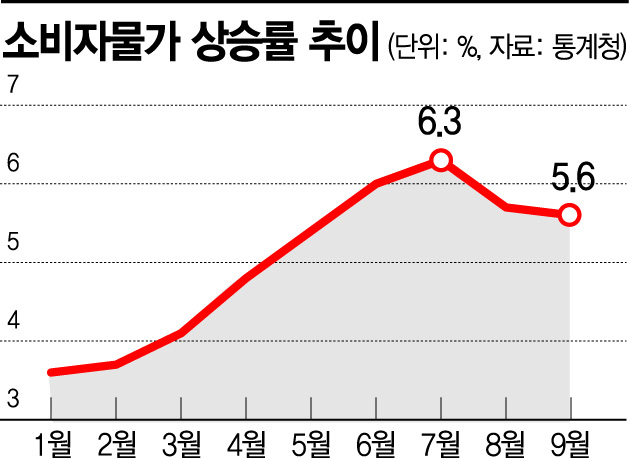
Eojogisu, Leading Consumer Price Inflation Rate from Q1 to Q2
[Asia Economy Reporter Seo So-jeong] The Bank of Korea measured the tone of inflation reflected in news articles and estimated an index, revealing that the inflation tone index for the third quarter of this year was 0.303, lower than the record high of 0.561 in the second quarter. On a monthly basis, the inflation tone index for September was 0.286, lower than the highest level this year in June (0.587), but slightly higher than August (0.281).
The Bank of Korea noted that considering the tone index leads the consumer price inflation rate by 1 to 2 quarters, there is a possibility that the inflation rate in the fourth quarter may decline somewhat, but it is difficult to say that the peak has passed.
In its report titled "Development and Implications of Inflation Tone Index Using Artificial Intelligence Language Model" released on the 17th, the Bank of Korea stated that the inflation tone index is judged to contain unique information related to consumer price changes and is also useful for inflation forecasting.
Kim Tae-wan, head of the Digital New Technology Division at the Bank of Korea’s Digital Innovation Office, explained, "The inflation tone index was highest in the second quarter of this year and slightly declined in the third quarter. When the tone index passes an inflection point, the consumer price inflation rate is expected to pass its peak, but data through September and October show a slight increase, so the consumer price inflation rate based on the current tone index remains highly uncertain."
The Bank of Korea collected 64.06 million sentences from a total of 1.88 million news articles retrieved by searching price-related keywords on internet portal sites over the past 20 years (February 2002 to June 2022). Among these, 5,000 news article sentences were randomly extracted and classified for their current and future inflation tone as rising, neutral, or falling.
Analysis showed a high correlation between the inflation tone index and major price indices such as the consumer price index and producer price index. Overall, the current tone index showed a clearer correlation than the future tone index. The current inflation tone index had the highest positive correlation with the consumer price inflation rate (year-on-year) five months later.
By averaging the inflation tone of each news article sentence measured using this model, the inflation tone index was estimated, and inflection points were analyzed. The inflection points of the inflation tone index generally led the inflection points of the consumer price inflation rate by 1 to 2 quarters.
According to the Bank of Korea, among the eight inflection points of the tone index from the second quarter of 2002 to the second quarter of 2022, seven led or coincided with the inflection points of the consumer price inflation rate within two quarters. Notably, in the second quarter of 2020, when economic uncertainty expanded due to the pandemic, both the tone index and inflation rate recorded lows and then increased at an unprecedented pace.
Furthermore, when the tone index was applied as a predictor variable in an inflation forecasting model, it generally showed better forecasting performance than the benchmark model.
The Bank of Korea stated, "We plan to utilize text data for various economic analyses through artificial intelligence language models and internally improve work productivity such as document summarization and classification. We also plan to develop AI language models specialized in the economic and financial fields to improve the accuracy of text analysis. Once the model’s performance is verified, we are considering making it publicly available for general researchers outside the Bank of Korea to use."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.