Shock to Economic Activity Participation Rate... Between the Asian Financial Crisis and the Global Financial Crisis
Although the number of employed persons has been recovering since COVID-19, the economic activity participation rate is still significantly below the pre-COVID-19 level.
According to an analysis by the Employment Analysis Team of the Research Department at the Bank of Korea on the 26th, the magnitude of cyclical fluctuations in the economic activity participation rate due to COVID-19 was -1.2 percentage points, which is between the levels seen during the financial crisis (-0.7 percentage points) and the foreign exchange crisis (-1.8 percentage points).
The cyclical fluctuation of the economic activity participation rate represents the deviation from the long-term trend. It usually shows an amplitude of around 0.5 percentage points, but during economic crises, the fluctuation expands to about 1 to 2 percentage points.
In particular, unlike past economic crises, the COVID-19 situation caused a significant shock to the economic activity participation rate, increasing the importance of the recovery path.
By gender and age group, the economic activity participation rate shock was found to be large among women and young to middle-aged adults after COVID-19.
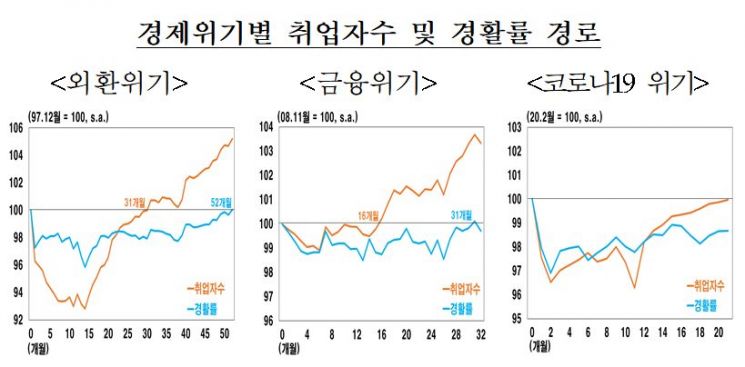
Looking at the recovery paths by economic crisis, the economic activity participation rate generally recovered more slowly than the number of employed persons during crises. During the foreign exchange crisis, the number of employed persons recovered to pre-crisis levels in 31 months, whereas the economic activity participation rate showed signs of recovery only after 52 months. During the financial crisis, the number of employed persons recovered after 16 months, and the economic activity participation rate after 31 months.
Regarding the factors affecting the economic activity participation rate after COVID-19, in 2020, inflow and outflow factors had a significant impact on the downturn, but last year, the contribution of cyclical factors expanded to the level of inflow and outflow factors.
To evaluate the overall employment situation in the labor market, when decomposing the cyclical factors of the employment rate into economic activity participation rate and unemployment rate factors, it was assessed that the unemployment rate recovered its trend after COVID-19, but the trend recovery of the economic activity participation rate is still insufficient.
The cyclical factor of the employment rate is considered to be the sum of the cyclical factors of the economic activity participation rate and the unemployment rate.
Hwang Subin, head of the Employment Analysis Team at the Bank of Korea’s Research Department, explained, "Based on past economic crisis patterns, it is expected that it will take more time for the employment rate to recover to the pre-crisis trend," adding, "During economic crises, the economic activity participation rate tends to recover its trend later than the unemployment rate, delaying employment recovery, and the United States shows a similar pattern."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.