Announcement of Four Major Policy Directions This Year to Prepare for Supply Chain Risks
Participation in China-led RCEP Alongside CPTPP
Concurrent Promotion of Mega FTAs with Developed Countries and Bilateral FTAs with Emerging Countries
Cambodia and Israel FTAs to Be Ratified in the First Half
Establishment of Stabilization Plans for 180 Key Items by Ministries in Q1
Strengthening Technology Protection... Top 10 Essential Technology R&D Roadmap in the First Half
Targeting MSCI Developed Markets Index Candidate Registration in June
Government "Domestic Forex Market Trading Hours Extension"
 Hong Nam-ki, Deputy Prime Minister for Economy and Minister of Economy and Finance. / Photo by Moon Ho-nam munonam@
Hong Nam-ki, Deputy Prime Minister for Economy and Minister of Economy and Finance. / Photo by Moon Ho-nam munonam@
[Sejong=Asia Economy Reporter Moon Chaeseok] The government announced that it will submit an application to join the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), which includes 11 countries such as Japan, Australia, and Singapore, in April. In the first quarter, it will prepare supply stabilization measures for 180 major items to prepare for risks related to supply chain restructuring.
Hong Nam-ki, Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Economy and Finance, held the 227th Foreign Economic Ministers' Meeting (Daegyeongjang) and the 140th Foreign Economic Cooperation Fund Management Committee on the morning of the 25th to discuss these matters.
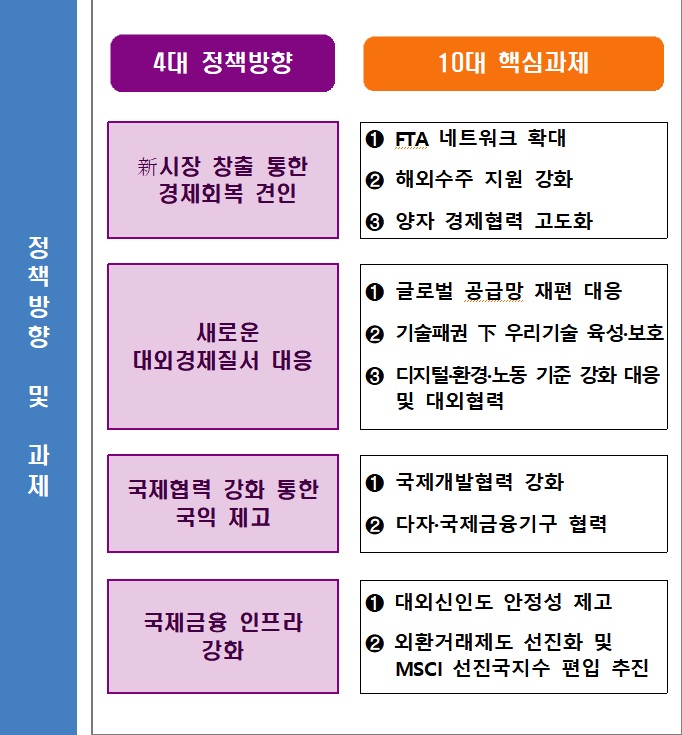
The government forecasted that the growth rate of the external economy will slow down this year. Although the recovery trend will continue, it is expected to be affected by the spread of the Omicron variant, supply chain bottlenecks, and shifts in fiscal and monetary policies of various countries. According to the World Bank, the growth forecast for advanced economies this year is 3.8%, which is 1.2 percentage points (p) lower than last year's 5%. Developing countries are also expected to slow down by 1.7%p from 6.3% to 4.6%. Concerns also exist regarding supply chain restructuring and the regionalization and bloc formation of economies. For South Korea, which has a high dependence on external factors, this poses a considerable burden. Accordingly, the government has set four major policy directions for external economic policy this year: creating new markets, responding to the new external economic order, strengthening international cooperation, and enhancing international financial infrastructure, along with establishing 10 core tasks and 10 performance goals.
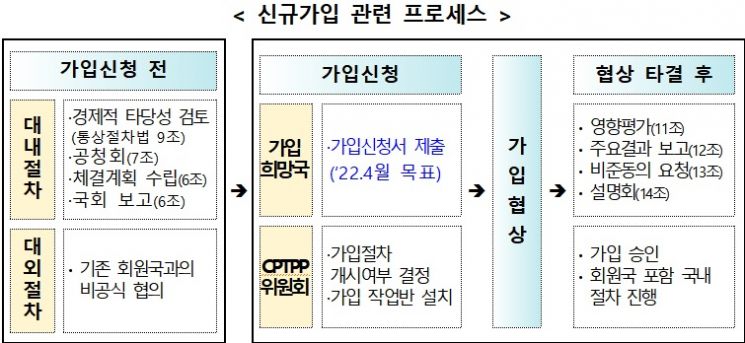
First, as Deputy Prime Minister Hong announced at the end of last year’s Foreign Economic Security Strategy (Daegyeongan) meeting, the government officially stated that it will "submit the CPTPP membership application in April." It will continue discussions on membership with key countries such as the chair countries Singapore and New Zealand, while reviewing supplementary measures for sensitive sectors such as agriculture, fisheries, and small and medium manufacturing industries. The government will accelerate social discussions through sectoral councils and regional roundtable meetings. Regarding the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), the world's largest mega free trade agreement (FTA) expected to take effect this month, the government plans to increase utilization by Korean industries through joint public-private briefings and attend the RCEP joint committee scheduled for the first quarter to explore areas of joint cooperation. RCEP, led by China, is an agreement involving five countries including South Korea, China, Japan, Australia, and New Zealand, as well as 10 ASEAN countries.
Along with mega FTAs with advanced countries, the government plans to expand bilateral FTAs with emerging countries. The government expects the FTA network to cover 90% of the global gross domestic product (GDP) in the future. It will accelerate negotiations with emerging countries worldwide, including the New Southern Policy (Shin-Nambang), New Northern Policy (Shin-Bukbang), Latin America, and the Middle East. In particular, it plans to ratify FTAs with Cambodia in the New Southern region and Israel in the Middle East in the first half of this year.
Having reduced supply chain risks through the so-called "AdBlue crisis," the government announced it will present supply stabilization measures for 180 major items within the first quarter. Previously, the government announced 200 core economic security items considering external dependence and plans to manage supply accordingly. Regarding this, the 180 core items will have supply stabilization measures prepared and announced by the relevant ministries within the first half of the year. For the 20 priority management items closely related to key industries, the government plans to implement already prepared supply stabilization measures such as expanding stockpiles and securing long-term supply sources. The government stated, "Based on the experience of responding to the AdBlue incident, we will prepare crisis management manuals for core items and proactively establish response systems in case of supply instability."
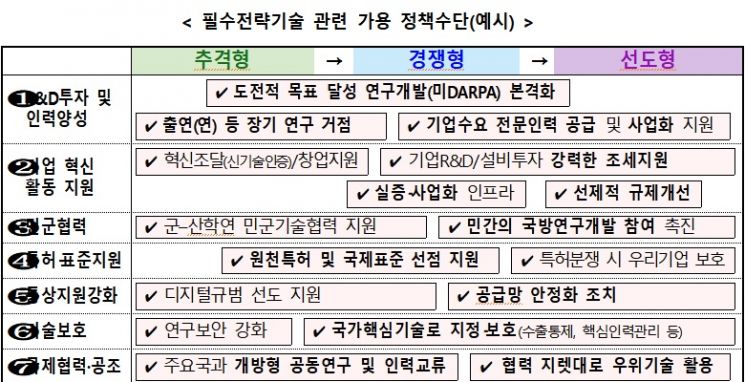
The government will also actively protect technology. With the 'National Advanced Strategic Industry Act' set to be enforced in the second half of this year, it plans to select detailed key technologies for 10 national essential strategic technology fields such as semiconductors, displays, and secondary batteries, and prepare R&D roadmaps for each technology in the first half of the year. The 10 technologies include semiconductors, displays, secondary batteries, 5G/6G, artificial intelligence (AI), advanced robotics and manufacturing, hydrogen, cybersecurity, quantum, space and aerospace, and advanced bio.
In the financial market, the government plans to ease regulations to be recognized as a genuine advanced market. Last December, Deputy Prime Minister Hong held a Korea investment roadshow (IR) in London, UK, and declared to major institutional investors that Korea would begin its challenge to join the Morgan Stanley Capital International (MSCI) advanced market index. The goal is to be included in the MSCI advanced market index watchlist (promotion review target) by June.
To this end, the government plans to review improvements to the foreign exchange market, such as extending domestic foreign exchange market trading hours. Issues related to the securities market, such as the foreign investor registration system, will be reviewed by the Financial Services Commission, and full-scale consultations with MSCI will begin next month. The government also plans to prepare a comprehensive revision bill for foreign exchange transaction laws centered on a 'reporting system' by the end of the year. Through the 'Foreign Exchange System Improvement Task Force (TF),' composed of the Bank of Korea, Financial Supervisory Service, Korea Customs Service, and Korea Institute of Finance, the government will gather market opinions, establish a comprehensive reform plan in the first half of the year, and prepare the bill by year-end.
A government official said, "The progress of policy implementation in each sector will be reviewed through the Daegyeongjang meeting and the Daegyeongan security strategy meeting this year," adding, "We will check the first half performance in July."
Additionally, at the Daegyeongjang meeting, the government discussed detailed plans such as the 2022 FTA promotion plan and the 2022 bilateral economic cooperation promotion direction, while at the fund committee, it discussed the 2022-2024 mid-term operation direction of the Economic Development Cooperation Fund (EDCF), plans to expand non-binding support of the EDCF, and ways to strengthen domestic and international partnerships of the EDCF.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.