With the news that U.S. electric vehicle company Rivian is going public through an IPO, Rivian’s partners and electric vehicle-related companies in Korea are also attracting investors' attention. Rivian is an electric vehicle company that has received investments from global companies including Amazon and Ford. Just one week after starting pre-orders for its vehicles at the end of last year, the initial stock was sold out. The market response has been hot, including a contract to supply 100,000 electric vehicles to Amazon by 2030. Expectations are rising that domestic companies related to Rivian will also benefit once Rivian grows through its listing and begins full-scale business expansion. However, if, like the U.S. hydrogen truck company Nikola which went public earlier, Rivian fails to deliver tangible results contrary to market expectations after listing, it could negatively impact related stocks. Therefore, analytical investment that carefully examines the competitiveness, financial soundness, and growth potential of beneficiary companies is necessary in preparation.
[Asia Economy Reporter Jang Hyowon] The market’s attention is focused on the news that secondary battery equipment manufacturer CIS has signed a supply contract with U.S. electric vehicle company Rivian (RIVIAN). CIS, which went public in 2017, is a company steadily growing by supplying equipment to major domestic battery companies.
Secondary Battery Investment Cycle Expected to Benefit
CIS specializes in manufacturing equipment related to electrode production necessary for lithium secondary batteries. The relevant equipment includes Coaters, Calenders, Slitters, and Tape Laminators. These pieces of equipment are used in the electrode process, which is the pre-process in secondary battery manufacturing.
The product with the largest sales share is the Calender, accounting for 69% of sales as of the end of last year. The Calender is used in the rolling process where rotating rollers apply pressure to increase the density per unit area of the coated electrode. The rest are Slitters at 17.4%, Coaters at 6.3%, and others at 7.3%.
CIS succeeded in domestic localization of the Calender for the first time in Korea in 2009 and currently supplies to major domestic conglomerates. Its main customers include LG Energy Solution, Samsung SDI, and Swedish battery manufacturer Northvolt. The production capacity is at a level capable of generating combined sales of 250 billion KRW from its first and second plants.
Previously, CIS entered the KOSDAQ market in January 2017 through a merger with Korea’s third SPAC. At the time of listing, CIS was valued at around 80 billion KRW and has grown into a company with a market capitalization exceeding 1 trillion KRW in about four years. As of the 28th of last month, CIS’s market capitalization was 1.0952 trillion KRW.
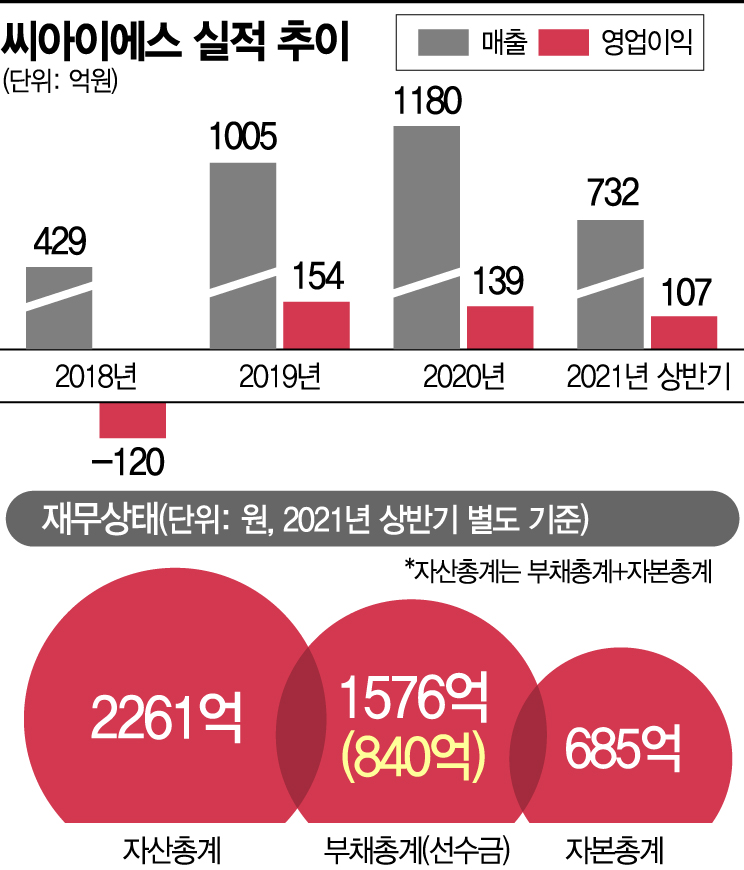
The growth is backed by increased performance. CIS recorded sales of 25.4 billion KRW and an operating loss of 4.5 billion KRW on a separate basis in 2017. Although sales grew to 42.9 billion KRW the following year, the operating loss widened to 12 billion KRW. After two years of sluggish performance post-listing, CIS successfully turned around in 2019. Sales in 2019 surged 134.3% year-on-year to 100.5 billion KRW, and operating profit turned positive at 15.4 billion KRW.
Since then, CIS has maintained steady strong performance and achieved significant growth in the first half of this year. As of the end of the first half, CIS’s sales were 73.2 billion KRW, up 116.6% from 33.8 billion KRW in the same period last year. Operating profit also jumped from 2.8 billion KRW to 10.7 billion KRW. The company had already achieved 77% of last year’s total operating profit in the first half.
The outlook for future performance is also bright. Recently, CIS reportedly signed a purchase contract for battery electrode process manufacturing equipment with Rivian. Rivian plans to invest about 9 trillion KRW by 2025 in building a 100GWh-scale battery factory, expanding electric vehicle production capacity, and establishing a charging network. Additionally, orders from existing battery companies other than Rivian are expected to increase.
Park Chansol, a researcher at SK Securities, analyzed, "Due to the nature of equipment order contracts, orders are expected to start increasing from the fourth quarter of this year to the first quarter of next year. CIS, which possesses material technology in the upcoming secondary battery investment cycle, is expected to benefit as a key equipment company."
High ‘Advance Payments’... Convertible Bonds Are a Burden
From a financial perspective, CIS’s debt ratio was somewhat high at 230.1% as of the end of the first half of this year. However, most of the debt consists of advance payments. Advance payments are amounts received before product sales. They are recorded as liabilities in accounting but are converted to sales after product delivery, so they do not carry the same risk as other debts. Rather, they indicate expected future sales growth.
As of the end of the first half, CIS’s advance payments amounted to 84 billion KRW, accounting for 75.9% of total current liabilities. Due to the high proportion of advance payments, the company’s actual total borrowings are only 23.1 billion KRW. Additionally, CIS holds 40.7 billion KRW in cash equivalents, resulting in net borrowings of negative 17.6 billion KRW.
Although the performance outlook is good and the financial condition is sound, there is expected short-term supply pressure due to the upcoming conversion of 30 billion KRW worth of convertible bonds (CB).
The 30 billion KRW worth of CB issued by CIS to GBI Holdings in October last year was converted on the 18th of last month. The conversion volume is 3,945,810 shares, accounting for 6.86% of the total issued shares. The conversion price is 7,603 KRW, and CB investors are expected to realize about 150% profit based on the current stock price. The listing date for these shares is scheduled for the 5th of this month.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















