Japanese Companies Play Key Roles in Hydrogen Value Chain
Storage and Transport via Liquefaction, MCH, Ammonia, etc.
South Korea Also Needs Public-Private Joint Hydrogen Production and Technology Development
[Asia Economy Reporter Hwang Yoon-joo] Japanese general trading companies are actively investing in renewable energy sources such as wind power, solar power, and geothermal energy to build a hydrogen value chain. Since securing about 20 million tons of hydrogen by 2050 inevitably requires imports from overseas, the role of general trading companies, which have extensive experience in energy imports, is becoming increasingly important. In Korea, there are calls for joint public-private development of hydrogen production and transportation technologies to revitalize the hydrogen economy.
◆ Japanese Trading Companies Take the Lead in Hydrogen Imports = Since 2017, projects to build a hydrogen value chain have been initiated mainly by Japanese general trading companies. The momentum accelerated last year when Prime Minister Yoshihide Suga declared 'carbon neutrality by 2050.' The Japanese government set targets to consume 3 million tons of hydrogen by 2030 and 20 million tons by 2050 to achieve carbon neutrality. It is limited to produce hydrogen domestically in Japan, making imports from overseas unavoidable. Accordingly, Japanese general trading companies with expertise in importing energy such as oil and gas have launched projects to build a 'hydrogen supply chain' that manufactures hydrogen overseas and imports it into Japan.
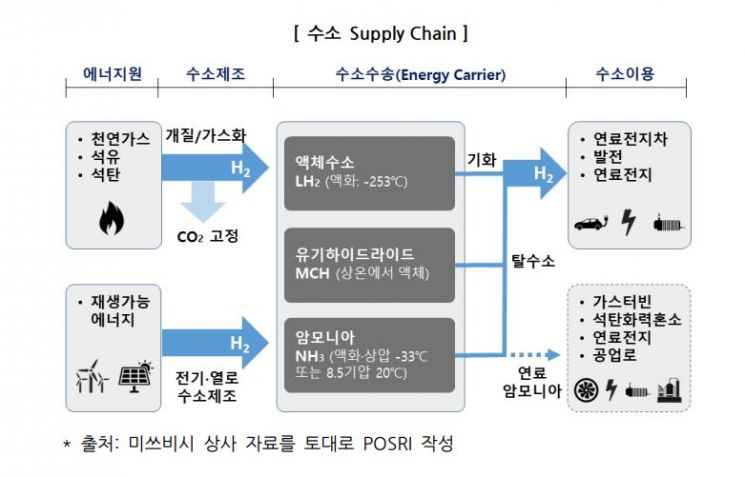
One noteworthy point is the transportation method. To transport hydrogen, gaseous hydrogen must be converted into other forms. Japanese general trading companies have verified and completed demonstration experiments on technologies that store hydrogen not only in liquefied form but also in various forms such as methylcyclohexane (MCH) and ammonia.
◆ Stored as MCH and Liquefied Hydrogen... Plans for Local Sales = Mitsubishi Corporation started its hydrogen project in July 2017 by establishing the business company 'AHEAD' together with Mitsubishi Corporation (overall management), Mitsui & Co. (technical research), Chiyoda Corporation (hydrogen and MCH production), and NYK Line (marine transportation). The method synthesizes hydrogen with toluene to produce MCH, a liquid at room temperature, compressing its volume to 1/500 for transportation. Mitsubishi Corporation completed a demonstration test last year producing hydrogen at an LNG plant in Brunei, storing it as MCH, and transporting it to Japan.
Sumitomo Corporation and Marubeni Corporation chose to store hydrogen in liquefied form. They started hydrogen business in April 2018 and by March this year completed the stage of producing hydrogen at an Australian brown coal mine and storing it as liquefied hydrogen. They will begin demonstration tests for transportation to Japan within the year. Recently, they are reviewing a project to produce hydrogen (green hydrogen) by water electrolysis using hydropower electricity in Malaysia and transport it to Japan in MCH form.
Sumitomo Corporation is also planning a model to produce hydrogen overseas and sell it locally (in Oman and Australia). The plan is to produce hydrogen from by-product gas at an oil refining plant in Oman and use it as fuel for fuel cell vehicles operating within the oil field. The goal is to produce 300 to 400 tons of hydrogen annually starting in 2023. In Australia, in cooperation with the Japanese engineering company JGC, they plan to produce 250 to 300 tons of hydrogen annually by water electrolysis using solar power. The produced hydrogen will be sold locally.
◆ Expectations for Korean Trading Companies’ Role in the Hydrogen Value Chain = Japanese general trading companies are actively engaged in hydrogen business not only because it is a future industry but also because the nature of the projects suits their capabilities. The so-called operational functions of general trading companies (project planning, exploration of key technologies, attracting investors, business development, etc.) and the trade functions of importing products produced overseas into Japan are required in this field. In particular, the experience of Japanese general trading companies in resource development related to LNG, which is used as an energy source for hydrogen production, plays a significant role in commercialization. This is why there are expectations that Korean trading companies will also play a larger role in the hydrogen value chain.
However, for the transition to green hydrogen, reducing the cost of renewable energy electricity is important, but securing large-scale energy sources like LNG through renewable energy is also a challenge. It is pointed out that Korea needs to consider actively investing in renewable energy such as wind power, solar power, and geothermal energy and linking these investments with hydrogen business.
[Reference = POSCO Research Institute]
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.