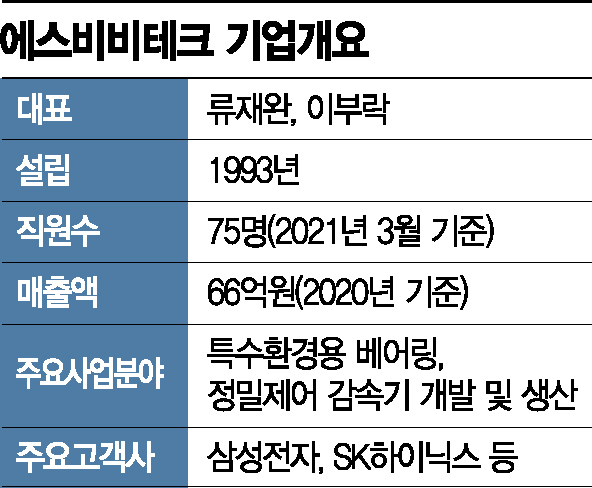
SBV Tech has Mass-Produced Gearboxes Since 2017...Core Robot Components
Over 10 Years of Technology Development Since 2005...Reduced Average Unit Cost
Sales Share Still Only 20%...Government Support Secures Large Enterprise Market Access
Robot Market Growing 32% Annually..."Will Grow as Company's Main Production Component"
[Asia Economy Reporter Junhyung Lee] Precision control reducers are called ‘Harmonic Drive’ in the industry. It has become a generic term as it was virtually monopolized by the Japanese company Harmonic Drive Systems (HDS). This is similar to how vinyl tape is called ‘Scotch Tape’ and adhesive bandages are called ‘Daeil Band.’ According to market research firm QY Research, HDS’s market share exceeds 70%. Including the market share of Nidec Shimpo, another Japanese company in the same industry, Japanese companies occupy about 85% of the market.
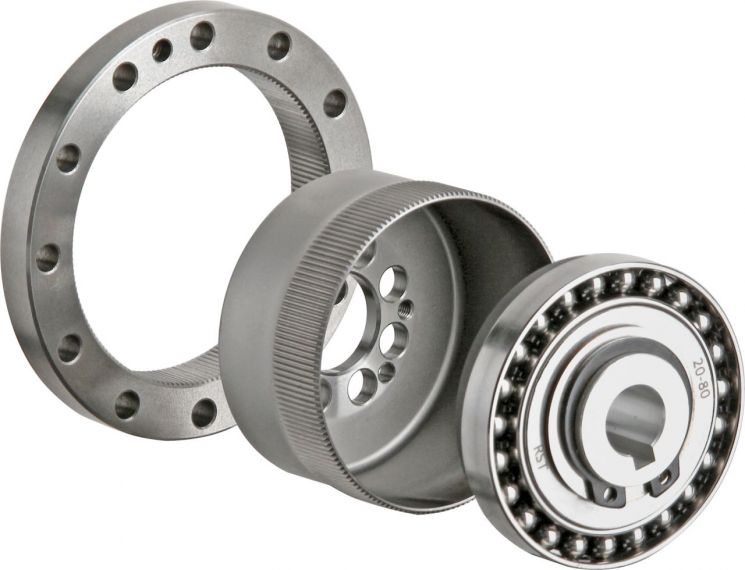
This component controls the rotational speed of the motor at the robot’s joint. It reduces the rotational speed and increases driving force to control the robot’s movement. It is a key component for robots that require fine movements. Due to the high level of technology required, it accounts for about 40% of the robot production cost, making it a high-priced part.
Localization through 10 years of technology development... Bearing unit price reduced by 50%
Machine and robot parts manufacturer SBV Tech began mass production of precision control reducers in 2017. This is the result of over 10 years of technology development investment since 2005. The unit price was reduced by about 30%. CEO Jaewan Ryu of SBV Tech said, “Japanese parts companies were like ‘masters over servants.’ Since Japan had monopolized the market for nearly 50 years, the supply price was practically whatever they asked for.”
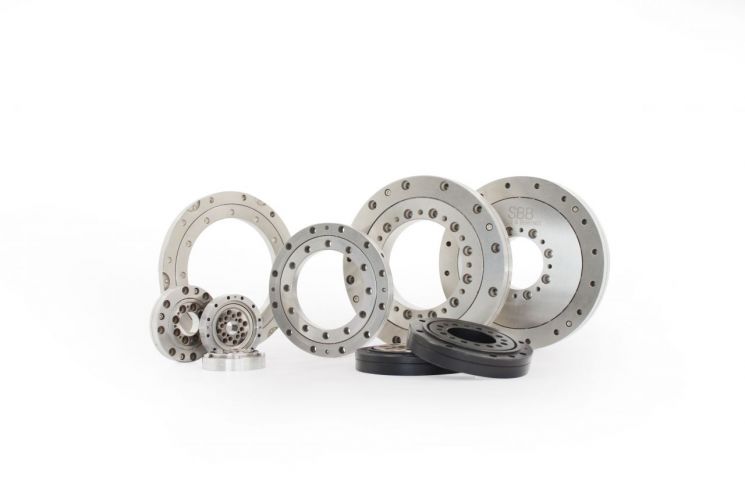
SBV Tech is recognized for reducing overseas dependence on robot parts. The company also localized special environment bearings that were monopolized by an American company. These bearings support the joints of semiconductor process robots and maintain rotational precision. Semiconductor robots operate in high-temperature vacuum conditions, requiring high durability even for small parts. CEO Ryu said, “Semiconductor processes are extreme working environments. Bearings are mainly used in wafer (thin discs used as semiconductor materials) processes, so particle generation must be avoided, and lubrication is difficult due to the vacuum state.”
Through localization, the bearing price was lowered to less than half. One American bearing with a diameter of about 15cm costs over 2 million won. SBV Tech’s bearing costs just under 1 million won. CEO Ryu said, “Although technology development costs money, the actual production cost of bearings is not high. American companies took advantage of their monopoly position to charge excessive prices.”
The company supplies bearings to Samsung Electronics, SK Hynix, and others. Most semiconductor process robots are imported, so foreign parts are used when bringing in robots, but their lifespan is short. Semiconductor equipment operates in extreme environments, requiring parts replacement every 1 to 1.5 years. Domestic companies prefer relatively cheaper domestic parts when replacing parts. Foreign parts suppliers often fail to meet delivery deadlines precisely, but domestic parts have the advantage of smooth supply.
Reducer accounts for only 20% yet... Government supports market expansion
Bearings supplied to large companies are the company’s cash cow products. On the other hand, the sales proportion of precision control reducers is less than 20%. The cause is difficulty in securing sales channels. CEO Ryu said, “Even if small and medium-sized enterprises succeed in localizing parts, it is not easy to find large-scale suppliers. Semiconductor companies tend to use verified foreign parts because they must take responsibility if problems occur with new parts.” This industry atmosphere is a hardship shared by small and medium manufacturers who contributed to the localization of materials, parts, and equipment (SoBuJang). According to the ‘2019 Robot Industry Status Survey Report’ recently published by the Korea Robot Industry Association, domestic robot companies cited ‘difficulty in developing sales channels’ (31.4%) as the biggest challenge in sales and export fields.
Fortunately, with government support, the company has laid the groundwork for supplying large companies. Last year, the company was selected for a technology demonstration project that connects robot parts companies, large demand companies, and national research institutes. This project supports market expansion for small and medium manufacturers with independent technology. The Korea Institute of Technology conducted tests on dozens of robots to secure data proving the reliability of the parts. CEO Ryu said, “This year, the technology demonstration will expand to hundreds of robots. With the newly secured reliability, we expect to supply large companies starting in the second half of this year.”
CEO Ryu sees reducers as the company’s future growth engine. He believes the growth potential of reducers is high according to the robot market outlook. According to Hyundai Motor Group, the global robot market will grow at an average annual rate of 32% until 2025. The market size will increase from 50 trillion won last year to 200 trillion won in five years. Considering that reducers account for about one-third of the robot cost, the reducer market will also grow to a considerable size. CEO Ryu said, “Reducers can become the main parts the company produces in the future. The investments made so far are like sowing seeds.”
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.


!["I'd Rather Live as a Glamorous Fake Than as a Poor Real Me"...A Grotesque Success Story Shaking the Korean Psyche [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















