10x Faster COVID-19 Screening and 12-Hour Early Sepsis Prediction
AI-Based Medical Startup Technology Gains Spotlight
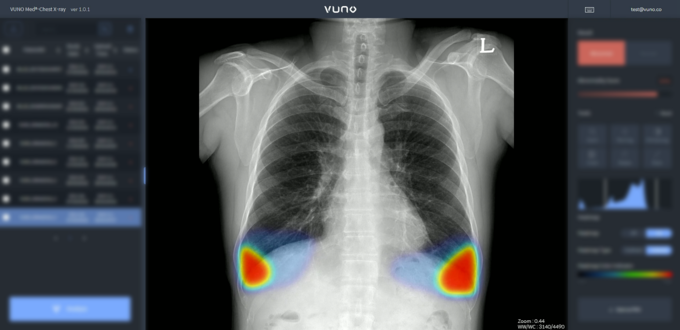 Usage of VunoMed Chest X-ray developed by Vuno, a medical artificial intelligence (AI) startup. Photo by Vuno
Usage of VunoMed Chest X-ray developed by Vuno, a medical artificial intelligence (AI) startup. Photo by Vuno
[Asia Economy Reporter Kim Heeyoon] Amid the normalization of social distancing across various sectors due to the impact of the novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19), medical startups supporting non-face-to-face medical services are gaining attention.
According to the industry on the 3rd, artificial intelligence (AI) medical technology is being utilized in various ways on-site, such as assisting with examination and diagnosis during non-face-to-face consultations.
The lung diagnosis assistance AI technology developed by the medical startup Lunit has recently been used to screen suspected COVID-19 patients. Since February, Seoul National University Hospital has been applying Lunit's lung diagnosis assistance AI technology (Lunit Insight CXR) to interpret images of suspected COVID-19 patients.
A Lunit official explained that it can classify patients more than 10 times faster than general chest X-ray interpretation, greatly aiding the screening process. Currently, Lunit's solutions are being used in more than 10 countries worldwide.
Seobeomseok, CEO of Lunit, stated, “In May, a study showing that Lunit Insight CXR’s classification method can classify patients 10 times faster compared to the standard diagnostic method (PCR test) was published in an international journal issued by the Korean Society of Radiology. This is a meaningful case proving the clinical value of combining chest X-rays and AI in the field.”
Medical AI solution startup VUNO introduced a deep learning algorithm that predicts the occurrence of sepsis up to 12 hours in advance with high accuracy. The research paper on the self-developed deep learning algorithm, published on the 28th of last month in the journal Critical Care Medicine, applied technology that identifies correlations among various variables in data prediction to improve the accuracy of sepsis occurrence prediction.
The deep learning algorithm learned from electronic health record (EHR) data of more than 60,000 critically ill patients, and when screening sepsis patients in actual intensive care units, it showed a 3% improvement in cardiac arrest prediction accuracy compared to existing prediction indices such as early warning scores and organ failure assessment scores, and an 18% improvement in precision/recall curve values, thereby enhancing prediction accuracy, according to VUNO.
A VUNO official said, “If this algorithm is introduced to medical sites, it will be possible to predict sepsis occurrence early with high accuracy. Based on this development, we will do our best to develop early prediction solutions for various diseases based on vital signs to help medical sites.”
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
















