 There is a forecast that Alzheimer's disease will spread like an epidemic. (The above photo is not related to the article content). Photo by Asia Economy DB
There is a forecast that Alzheimer's disease will spread like an epidemic. (The above photo is not related to the article content). Photo by Asia Economy DB
[Asia Economy Reporter Junho Hwang] A natural substance produced by bacteria living in the root soil layer of ginseng fields has been found to have the ability to decompose proteins that cause Alzheimer's disease. The research team stated that it is meaningful in that it can simultaneously remove two substances known as the causes of Alzheimer's and that the causative substances can be removed by compounds rather than antibody therapy. It is expected that a new chapter in Alzheimer's treatment may open.
The research teams led by Professor Dongchan Oh of Seoul National University College of Pharmacy and Professor Youngsoo Kim of Yonsei University College of Pharmacy announced on the 31st that the results of this study were published in the international academic journal Angewandte Chemie.
Natural substance produced by bacteria, structure analyzed for the first time
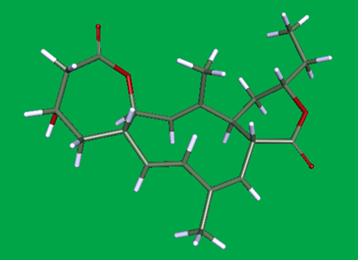 The research team studied a substance produced by bacteria inhabiting the root soil of ginseng fields and named it Rhizolutin. This substance is a natural compound composed of three cyclic structures with seven, ten, and six members, which have never been reported before.
The research team studied a substance produced by bacteria inhabiting the root soil of ginseng fields and named it Rhizolutin. This substance is a natural compound composed of three cyclic structures with seven, ten, and six members, which have never been reported before.
The research team elucidated the structure of a new substance (named Rhizolutin) composed of three cyclic structures with 7, 10, and 6 members, produced by bacteria inhabiting the root soil layer of ginseng fields. To study this substance, which is produced in extremely small amounts, the team increased its production tenfold by adding 6-year-old ginseng powder to the bacterial culture medium. Then, through large-scale cultivation of up to 700L, they confirmed the structure using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, chemical reactions, and molecular modeling techniques.
Professor Dongchan Oh said, "We discovered a substance (Rhizolutin) with a new structural skeleton by studying a substance produced by bacteria in the root soil layer of ginseng fields, which has hardly been researched before. By dramatically increasing the production of this substance, we were able to conduct research related to Alzheimer's disease."
Proven Alzheimer's efficacy through experiments
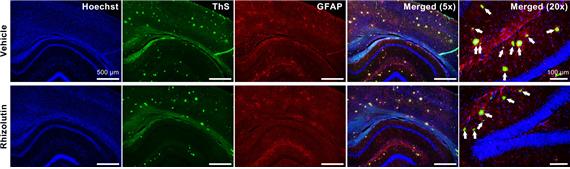 As a result of administering rhizolutin to Alzheimer’s transgenic mice, the amounts of amyloid-beta (ThS staining) and activated astrocytes (GFAP staining) in the mouse brain decreased.
As a result of administering rhizolutin to Alzheimer’s transgenic mice, the amounts of amyloid-beta (ThS staining) and activated astrocytes (GFAP staining) in the mouse brain decreased.
Furthermore, the research team demonstrated that this newly secured substance has therapeutic efficacy for Alzheimer's disease. They administered this substance to experimental mice induced with Alzheimer's through transgenesis and confirmed a decrease in the amounts of amyloid-beta and tau proteins.
The research team stated, "The newly discovered substance is the first novel compound that simultaneously decomposes amyloid-beta and tau protein aggregates, and it is highly valued as a lead compound for future new drug development to overcome Alzheimer's disease."
Professor Youngsoo Kim said, "The key to new drug development for Alzheimer's disease by global pharmaceutical companies is the removal of amyloid-beta or tau proteins using antibodies. This study is meaningful in that it suggested the possibility that protein removal, previously thought possible only with antibodies, can also be done with compounds, and it demonstrated a therapeutic strategy that can simultaneously remove amyloid-beta and tau proteins."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















