[Asia Economy Reporter Junho Hwang] The cause of the excessive inflammatory response that pushes the progression stage of the novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19) into a severe phase has been identified by domestic researchers. It was found that one of the antiviral immune substances called 'cytokine,' specifically 'interferon,' is excessively secreted, which instead attacks normal cells and triggers an excessive inflammatory response. The research team expects that this finding could lead to the proposal of new anti-inflammatory drugs to regulate the excessive inflammatory response in severe COVID-19 patients. This could reduce the inflammatory response in severe COVID-19 patients and increase their survival rate.
Professor Shin Eui-cheol of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Professor Jeong In-kyung of the Department of Life Sciences at the same university, Professor Kim Seong-han of Seoul Asan Medical Center, Professors Choi Jun-yong and Ahn Jin-young of Yonsei University Severance Hospital, and Jeong Hye-won of Chungbuk National University Hospital jointly announced these research results on the 13th. This paper was also published on the 10th (local time) in the international academic journal Science Immunology.
Cytokine Storm Causes Excessive Inflammation in Severe COVID-19 Patients
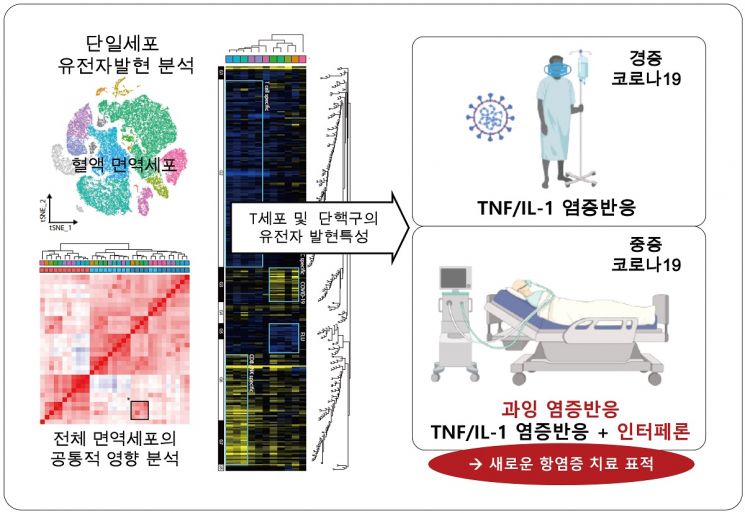
The research team confirmed that the cause of the excessive inflammatory response observed in severe COVID-19 patients is due to the over-secretion of a cytokine called interferon. Cytokines are protein immune regulators secreted by immune cells, but when excessively secreted, they attack even normal cells and cause inflammation.
The team obtained blood samples from COVID-19 patients, isolated immune cells, and applied a cutting-edge research technique called single-cell gene expression analysis to analyze their characteristics. As a result, they discovered a phenomenon where inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) commonly appeared in the immune cells of COVID-19 patients.
In particular, when comparing severe and mild patients, they confirmed that the cytokine response of interferon appeared only in severe patients. Interferon is a glycoprotein synthesized and secreted when host cells are infected by various pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, parasites, or in the presence of cancer cells.
Interferon has long been known as a beneficial protein with antiviral effects, but in the case of COVID-19 patients, it was confirmed that it can actually cause an excessive inflammatory response.
Mitigating Cytokine Storm to Increase Survival Rate of Severe Patients
The research team evaluated this as a study that could increase the survival rate of severe COVID-19 patients. First, it can alleviate the patient's excessive inflammatory response. Currently, non-specific anti-inflammatory drugs such as steroids are used to eliminate excessive inflammatory responses, but a new treatment method targeting interferon can be proposed. This could prevent COVID-19 from progressing to a severe stage.
The research team is currently developing a method to efficiently screen and discover drugs in vitro that can alleviate the excessive inflammatory response in severe patients and increase patient survival rates.
Professor Shin Eui-cheol stated, "This study is very important and meaningful in that it laid the foundation for designing future treatment strategies by studying in detail what happens in the immune cells of COVID-19 patients." Professor Jeong In-kyung emphasized, "We will continue research on new immune mechanisms and the use of patient-tailored anti-inflammatory drugs to increase the survival rate of severe COVID-19 patients."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.