[Asia Economy Reporter Moon Hyewon] Although new startups generally increased in the first quarter of this year, some sectors such as manufacturing showed a slowdown due to the impact of the novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19).
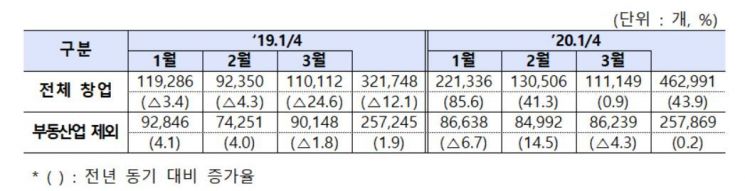
According to the 'Startup Business Trends' announced by the Ministry of SMEs and Startups on the 27th, new startups in the first quarter of this year reached 462,991, an increase of 43.9% (141,243) compared to 321,748 in the first quarter of last year.
At the beginning of this year, the surge in real estate startups caused a significant overall increase in startups, but the growth slowed down in March due to the spread of COVID-19 and other factors.
During the same period, both individual and corporate startups increased significantly, with corporate startups, which have a relatively large employment creation effect, rising sharply by 15.7%. However, excluding real estate, individual startups decreased by 1.3%.
Despite the impact of COVID-19, technology startups recorded 58,892, an increase of 0.3% (198), continuing a steady upward trend since statistics began in 2016.
In particular, startups by those under 30 years old (up 8.9%) and those over 60 years old (up 12.9%) increased, indicating active entry of the youth into the knowledge service industry and expansion of senior entrepreneurship based on field experience.
By industry, newly established startups in the first quarter of this year were dominated by real estate with 205,122 companies, accounting for 44.3% of all industries. This was followed by wholesale and retail trade with 91,166 (19.7%), accommodation and food services with 40,586 (8.8%), and construction with 17,777 (3.8%).
Go Geonho, a statistics analyst at the Ministry of SMEs and Startups, analyzed, "Real estate accounted for nearly half of all startups in the first quarter of this year. This is believed to be due to the mandatory business registration within 20 days from the start of rental to tax rental income under 20 million KRW per year, which caused a concentration of registrations at the beginning of the year."
Technology startups showed differences by industry due to the impact of COVID-19, increasing by 0.3% compared to the same period last year. The growth of information and communication industry (up 9.4%) accelerated compared to last year due to the digital transformation such as non-face-to-face ICT services. Startups in professional, scientific, and technical services such as research and development and specialized services also increased significantly by 20.2%.
However, manufacturing decreased by 11.0% due to continued sluggish business conditions since last year and concerns over COVID-19. Education services and creative, arts, and leisure services also decreased by 10.4% and 9.0%, respectively.
From January to February this year, manufacturing decreased by 11.5% compared to the same period last year, followed by a 10.1% decrease in March, maintaining a similar downward trend. However, education services and creative, arts, and leisure services decreased by 3.2% and 5.6% in January and February, respectively, but saw a larger decline in March, with decreases of 23.8% and 15.9%, respectively, as the impact of COVID-19 intensified.
Wholesale and retail trade increased by 5.9%, mainly in retail centered on non-face-to-face online transactions, but startups in face-to-face and gathering industries such as accommodation and food services and personal services (hair salons, laundries, repair shops, etc.) decreased by 5.8% and 6.7%, respectively, during the same period. Accommodation and food services increased by 1.7% in January and February compared to the same period last year but decreased by 18.4% in March. Personal services also increased by 0.6% in January and February but decreased by 18.3% in March, reflecting the impact of the spread of COVID-19.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.