[Asia Economy Reporter Junho Hwang] Domestic researchers have developed an inhalable nanostructure that targets the protein causing Alzheimer's disease (dementia). This structure can selectively absorb specific harmful substances within the body and is expected to aid in the prevention of various diseases in the future. On the 2nd, the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) introduced the research results of Dr. Joonseok Lee's team at the Molecular Recognition Research Center.
Development of Nanostructure That Inhales Dementia-Related Proteins
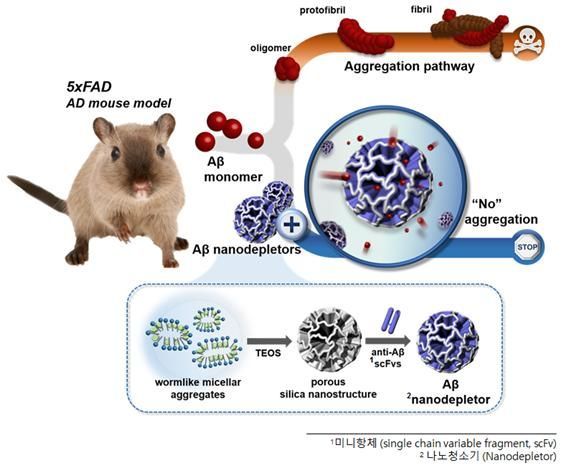
The research team began their study based on the hypothesis that inhaling and removing the causative substances of dementia could alleviate its symptoms, and they have achieved fruitful results. They developed a nanostructure capable of carrying antibodies that can inhale the main causative proteins of dementia and successfully removed these proteins.
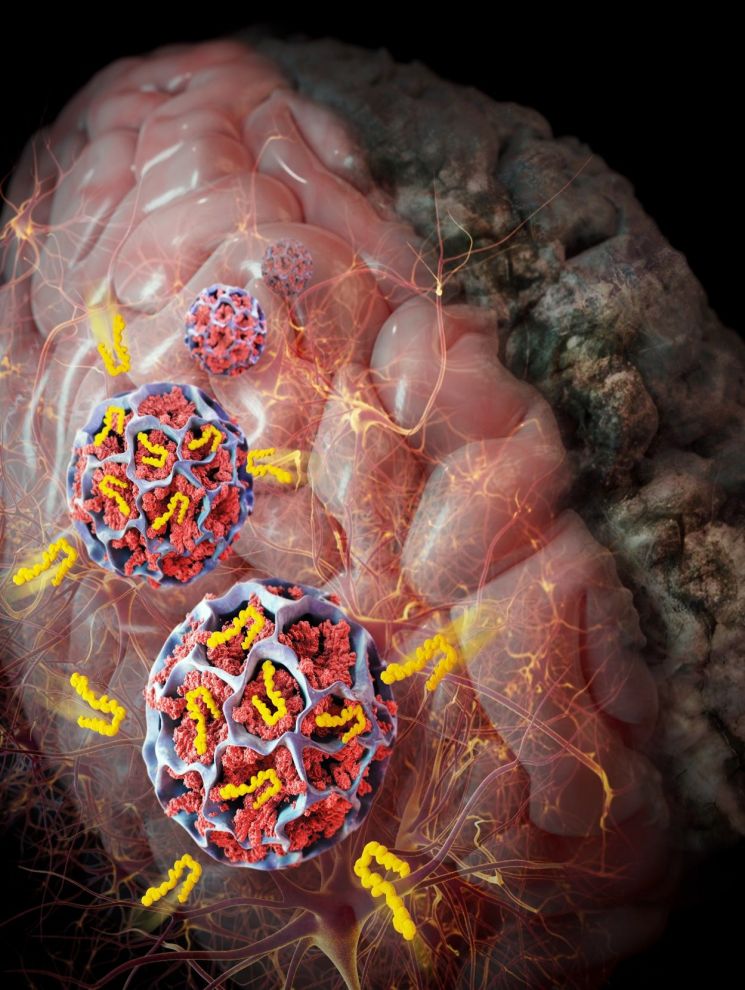
In the brains of dementia patients, beta-amyloid proteins abnormally accumulate. These proteins aggregate, causing the death of nerve cells, which accelerates dementia by impairing cognitive functions. The nanostructure developed by the research team inhaled these proteins and blocked abnormal aggregation by more than 80%.
The team demonstrated this effect through animal experiments and anticipates that this nanostructure could be used as an anti-amyloid inhibitor in the future.
Helps Prevent and Treat Various Diseases Beyond Dementia
Dr. Joonseok Lee of KIST, who led the study, stated, "Using the nanostructure to inhale beta-amyloid or tau proteins not only inhibits the aggregation of neurotoxic substances but also, by expanding its applications, it can serve as a nano-cleaner that selectively removes various harmful substances within the body, contributing to disease prevention and health promotion."
In addition to Dr. Lee's team, the research involved Professor Chanbeom Park's team from KIST's Department of New Materials Engineering and the Argonne National Laboratory in the United States. The research results are scheduled to be published as a cover paper in Advanced Functional Materials.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.