[Asia Economy Reporter Junho Hwang] Domestic researchers have identified an essential organ that regulates immune responses in the lymph nodes, which are responsible for our body's immunity. This discovery provides a clearer understanding of immune responses in lymph nodes and is expected to aid in the treatment of immune diseases.
The research team led by Kyu-Young Ko, head of the Vascular Research Division at the Institute for Basic Science (Distinguished Professor at KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering), announced on the 6th that they found the 'Hippo signaling pathway' within lymph nodes plays a crucial role in immune responses.
Essential for Lymph Node Pathogen Infection Response
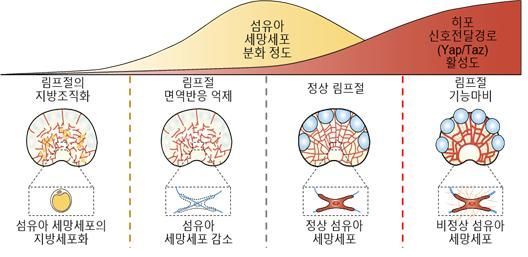
The research team revealed that the 'Hippo signaling pathway' in fibroblastic reticular cells, which form the internal structure of lymph nodes, is activated during the early differentiation of these cells and must be deactivated in the later stages for normal immune responses to occur.
The Hippo signaling pathway is known as a cellular signaling pathway that suppresses cell division and differentiation while promoting apoptosis, thereby inhibiting the growth of animal organs. Lymph nodes are bean-shaped immune organs with diameters ranging from 1 to 20 mm, distributed throughout the body. When pathogens enter the lymph nodes, immune cells trigger an immune response.
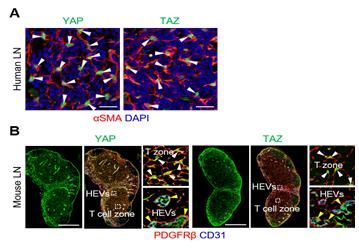
The team observed how immune responses are regulated according to the degree of fibroblastic reticular cell differentiation and the activation level of the Hippo signaling pathway by using 20 genetically modified mice with altered Yap/Taz proteins involved in the Hippo signaling pathway.
Experimental results showed that if the Hippo signaling pathway is deactivated during the early differentiation of fibroblastic reticular cells, abnormal immune responses and weight loss symptoms were observed. This indicates improper cell differentiation. Fibroblastic reticular cells secrete cytokines upon pathogen infection to activate immune cells and induce immune responses. If cell differentiation is abnormal and fibroblastic reticular cells become adipocytes, cytokines are not secreted, and immune responses do not occur properly.
Additionally, the team found that if the Hippo signaling pathway is activated during the late differentiation stage of fibroblastic reticular cells, lymph nodes become fibrotic, leading to immune function paralysis. When substances promoting fibrosis are secreted from fibroblastic reticular cells, lymph nodes harden and struggle to perform immune functions.
Helps in Treatment of Emerging Viruses like COVID-19
 Bae Hoseong, Research Fellow at IBS Vascular Research Division, First Author
Bae Hoseong, Research Fellow at IBS Vascular Research Division, First Author
Researcher Hoseong Bae stated, "This study revealed that the 'Hippo signaling pathway' in fibroblastic reticular cells within lymph nodes is a key mechanism regulating immune responses," adding, "It could provide a milestone for treating immune diseases such as infections by emerging viruses like COVID-19 and MERS, chronic inflammation, lymph node fibrosis, and lymph node cancer metastasis."
The research team also expects that Yap/Taz inhibitors will be utilized in the future for treating fibrosis in organs and tissues, given that activation of Yap/Taz proteins in the Hippo signaling pathway causes lymph node fibrosis.
The results of this study were published on the 24th of last month in the international journal Nature Communications.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![From Hostess to Organ Seller to High Society... The Grotesque Scam of a "Human Counterfeit" Shaking the Korean Psyche [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















