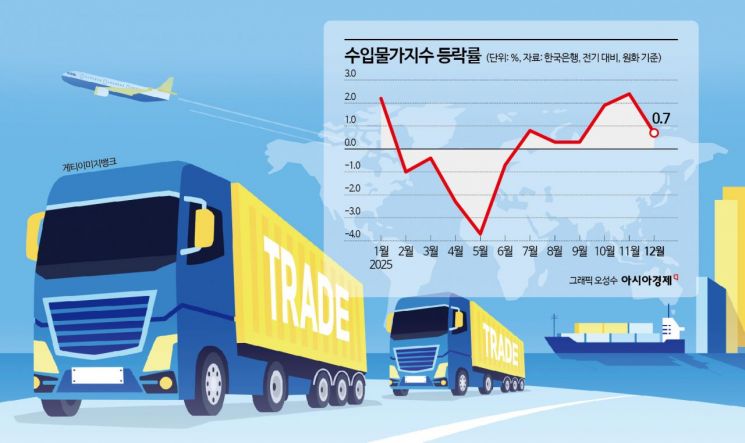
Import Prices Up 0.7% from Previous Month, Rising for Six Consecutive Months
Longest Upward Trend Since May-October 2021
Import Price Increases Typically Reflected in Consumer Prices After 1-3 Months
"Further Monitoring Needed for This Mont
As the high exchange rate situation persists, import prices have continued to rise for six consecutive months. This is the longest period of increase since May to October 2021. This sustained upward trend in import prices could exert upward pressure on consumer prices with a lag of one to three months. So far this month, both the won-dollar exchange rate and international oil prices, which significantly impact import prices, have declined compared to the previous month's average. However, given the high level of uncertainty in both domestic and international conditions, it is assessed that it is too early to determine whether this downward trend will be sustained.
According to the "Export and Import Price Index and Trade Index (Preliminary) for December 2025" released by the Bank of Korea on January 14, last month’s import price index (based on the Korean won) was 142.39 (2020=100), up 0.7% from the previous month. Compared to the same month last year, it rose by 0.3%. Despite the decline in international oil prices, the increase in the won-dollar exchange rate and the rise in prices of primary metal products led to this result. In December 2025, the average monthly price of Dubai crude oil was $62.05 per barrel, down 3.8% from $64.47 in November. On the other hand, the average won-dollar exchange rate rose by 0.7%, from 1,457.77 won in November to 1,467.40 won in December.
By usage, intermediate goods rose by 1.0% from the previous month, mainly due to higher prices of primary metal products. For raw materials, although crude oil prices fell, the prices of products such as liquefied natural gas (LNG) increased, leading to a 0.1% rise in mining products compared to the previous month. Capital goods and consumer goods also rose by 0.7% and 0.4%, respectively, from the previous month. Excluding exchange rate effects, import prices based on contract currency remained flat compared to the previous month. Year-on-year, they declined by 2.4%. For the entire year, import prices fell by 0.4% compared to the previous year, mainly due to declining international oil prices. On a contract currency basis, they dropped by 4.6%.
It remains uncertain whether the continued rise in import prices this year will put pressure on consumer prices. Lee Moonhee, head of the Price Statistics Team at Economic Statistics Department 1 of the Bank of Korea, said, "Both the won-dollar exchange rate and international oil prices, which have a significant impact on import prices, have declined compared to last month's average this month." However, he added, "Given the high level of uncertainty in domestic and international conditions, we need to monitor the situation further for the time being." The continued upward trend in import prices is one of the factors driving up consumer prices. Import prices are typically reflected in consumer prices with a lag of one to three months.
Last month, export prices rose by 1.1% from the previous month, as the won-dollar exchange rate increased and prices of semiconductors, as well as computers, electronics and optical devices, and primary metal products, went up. Compared to the same month last year, export prices increased by 5.5%. By item, prices of manufactured goods, especially computers, electronics and optical devices, and primary metal products, rose by 1.1% from the previous month. Prices of agricultural, forestry, and fishery products fell by 0.4% compared to the previous month. Last month, export prices based on contract currency rose by 0.4% from the previous month and by 2.7% year-on-year. For the entire year, export prices, led by semiconductors and computers, electronics and optical devices, increased by 2.3% compared to the previous year. On a contract currency basis, they fell by 2.1%.
The export volume index, which shows export and import fluctuations in December 2025, rose by 11.9% year-on-year. This is the highest increase in three months since the 14.5% rise in September 2025. The increase was driven by computers, electronics and optical devices, and chemical products. Lee explained, "Exports of computers, electronics and optical devices increased, especially computer memory and mobile phones, and semiconductor exports also continued to rise in volume." The export value index rose by 14.8%, marking the highest level in one year and five months since the 14.8% increase in July 2024. For the entire year, the export volume index and value index rose by 5.0% and 3.2%, respectively, compared to the previous year. Last month, the import volume index rose by 8.7%, driven by increases in primary metal products and mining products. The import value index rose by 5.9%. For the entire year, the import volume index increased by 4.6% year-on-year, while the value index fell by 0.3%.
Last month, the net barter terms of trade index rose by 5.4% year-on-year, as export prices (up 2.6%), led by semiconductors, increased, while import prices (down 2.6%), especially for mining products such as crude oil and natural gas, declined. The income terms of trade index jumped by 17.9%, as both the net barter terms of trade index (up 5.4%) and the export volume index (up 11.9%) increased. For the entire year, the net barter terms of trade index and the income terms of trade index rose by 3.0% and 8.2%, respectively, compared to the previous year.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.