SNE Research Releases Mid-to-Long-Term Outlook for Conductive Additives
Gradual Shift from Carbon Black to CNT
 2026 Lithium-Ion Secondary Battery Anode Material Development Status and Mid-to-Long-Term Outlook (~2035), SNE Research
2026 Lithium-Ion Secondary Battery Anode Material Development Status and Mid-to-Long-Term Outlook (~2035), SNE Research
The market for conductive additives, which are used in the cathodes and anodes of secondary batteries to enhance electrical conductivity, is projected to grow to 3 trillion won by 2035.
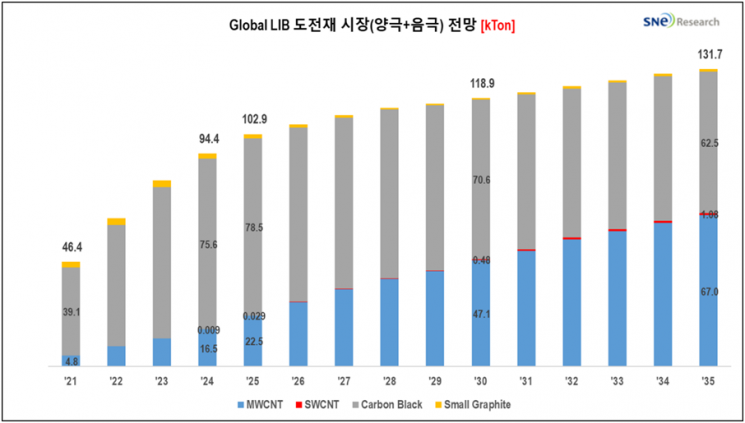
According to a recent report titled "2026 Lithium-Ion Secondary Battery Anode Material Development Status and Mid-to-Long-Term Outlook (~2035)" published by battery market research firm SNE Research, demand for lithium-ion battery conductive additives is expected to increase from 46 kilotons (kTon) in 2021 to 103 kilotons in 2025, and 132 kilotons in 2035, representing an average annual growth rate of 7.7%.
As a result, the total lithium-ion battery conductive additive market is forecast to grow at an average annual rate of 11.7% in terms of value, from 650 billion won in 2021 to 1.78 trillion won in 2025, 2.43 trillion won in 2030, and 3.07 trillion won in 2035.
Conductive additives are materials that connect the active materials in the cathode and anode of secondary batteries, facilitating the movement of electrons. In the past, carbon black was widely used, but recently, the use of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) has been increasing.
Carbon nanotubes are cylindrical carbon nanostructures, divided into multiwall CNTs (consisting of multiple layers) and single wall CNTs (consisting of a single layer). Single wall CNTs offer superior performance, but are more technologically challenging and expensive to produce.
Replacing carbon black with CNTs allows for a reduced amount of conductive additive, thereby increasing the proportion of active material and enhancing battery performance. Battery manufacturers are currently mixing carbon black and multiwall CNTs in both cathodes and anodes, and are gradually increasing the proportion of multiwall CNTs.
Major Korean battery manufacturers, including LG Energy Solution, SK On, and Samsung SDI, plan to partially adopt or increase the proportion of single wall CNTs in anodes. When silicon anode materials are used, adding single wall CNT conductive additives can help suppress swelling phenomena.
SNE Research stated, "As carbon black is replaced by multiwall CNTs and single wall CNTs, total demand for conductive additives is expected to gradually reach saturation starting in 2027." The firm also projected, "Between 2025 and 2035, demand for multiwall CNTs will increase about threefold (from 22.5 kilotons to 67 kilotons), while demand for single wall CNTs will grow approximately 36 times (from 0.03 kilotons to 1.08 kilotons)."
The market share of traditional carbon black and fine graphite is expected to decline sharply from 44% in 2025 to 18% in 2030 and 8% in 2035. In contrast, the market for multiwall CNTs is forecast to grow from 960 billion won in 2025 to 1.52 trillion won in 2030 and 1.87 trillion won in 2035, accounting for 60-65% of the total market.
Despite relatively low demand, the high unit price of single wall CNTs is expected to drive a significant increase in market size, from 50 billion won in 2025 to 500 billion won in 2030 and 930 billion won in 2035.
Major companies in the lithium-ion battery carbon black/acetylene black conductive additive sector include Imerys, Cabot, Denka, and Lion. Key players in multiwall CNTs are Korea's LG Chem, JEIO, Kumho Petrochemical, China's DHnano, Dynanonic, and Cnano.
In the single wall CNT market, Luxembourg-based OCSiAl supplies over 90% of the global demand and dominates the market. Other competitors include China's Timesnano, Faymo, and EASTCHEM; the United States' Nano-C and CHASM Advanced Materials; Japan's Meijo Nanocarbon; and Korea's Coborn and JEIO.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
















