KITA Report on Export Competitiveness among Korea, China, and Japan
China Accelerates Ahead of Korea and Japan across Manufacturing Sectors
Korea Maintains Competitiveness Centered on Semiconductors
As Korea, China, and Japan fiercely compete for dominance in the global export market, particularly in five major manufacturing sectors such as semiconductors and automobiles, a new analysis indicates that China's export competitiveness is rapidly strengthening both quantitatively and qualitatively.
According to the report "Comparative Export Competitiveness of the Five Major Key Items among Korea, China, and Japan," released by the Korea International Trade Association's Institute for International Trade and Commerce on December 23, Korea has maintained and strengthened its competitiveness, mainly in semiconductors, from 2019 to 2024. In contrast, China has significantly improved its competitiveness across traditional manufacturing industries, excluding semiconductors.
The report compared and analyzed the competitiveness of the three countries by combining "quantitative competitiveness," based on global export market share and volume, with "qualitative competitiveness," which reflects global comparative advantage and added value. As a result, China surpassed both Korea and Japan in terms of export volume and competitiveness for most items except semiconductors. Meanwhile, Korea and Japan were found to be focusing their capabilities on core items where they maintain high competitiveness.
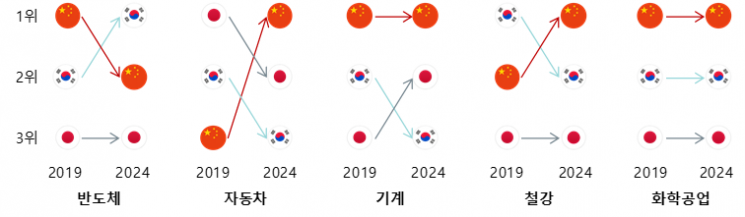 Changes in the overall export competitiveness rankings of the five major key items among Korea, China, and Japan (2019→2024). Korea International Trade Association.
Changes in the overall export competitiveness rankings of the five major key items among Korea, China, and Japan (2019→2024). Korea International Trade Association.
Examining the changes in the overall rankings of Korea, China, and Japan, which combine both quantitative and qualitative competitiveness, China's remarkable progress stands out. Over the past five years, China has maintained its traditional advantage in machinery and chemical industries, while also rising to the top in competitiveness in the automobile and steel sectors. In particular, China has rapidly expanded its export volume in traditional manufacturing sectors based on large-scale production, while also quickly increasing the added value of its export items, significantly widening the gap with Korea and Japan.
Korea has notably strengthened its competitiveness in semiconductors, rising from second to first place. The main factors cited are the increase in demand for high-value-added memory semiconductors driven by the spread of artificial intelligence (AI), and solid real demand for Korean semiconductors. However, in the automobile sector, despite Korea's expansion in export volume and market share, its competitiveness ranking fell to third place due to China's rapid rise, which was driven by price competitiveness and the expansion of eco-friendly vehicle production. Korea's competitiveness in machinery and steel/non-ferrous metal exports also weakened compared to Japan and China, respectively.
Japan saw some improvement in export competitiveness in the machinery sector, but experienced an overall decline in major items such as automobiles, semiconductors, steel, and chemicals. In particular, Japan showed the lowest competitiveness compared to Korea and China in semiconductors, steel, and chemicals over the past five years, revealing clear limitations.
Jin Okhee, a researcher at the Korea International Trade Association's Institute for International Trade and Commerce, stated, "China's strengthening export competitiveness should be seen as a structural change across the entire manufacturing industry, not just in specific sectors. Korea's exports need to shift focus from volume competition to technology and added value. In sectors where Korea has a competitive edge, such as semiconductors, the gap should be further widened, while for industries facing intensified competition, more sophisticated response strategies are needed, including segmenting strategies by market and item."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
!["The Woman Who Threw Herself into the Water Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag"...A Grotesque Success Story That Shakes the Korean Psyche [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















