Global Healthcare Services Market Projected to Reach USD 11.2 Trillion by 2029
As the number of foreign patients visiting Korea surges, the number of overseas expansions by domestic medical institutions is also showing strong growth, with an average annual increase of 17%. The government plans to accelerate the overseas expansion of the medical sector by broadening the current Asia-focused trend to a global scale in the future.
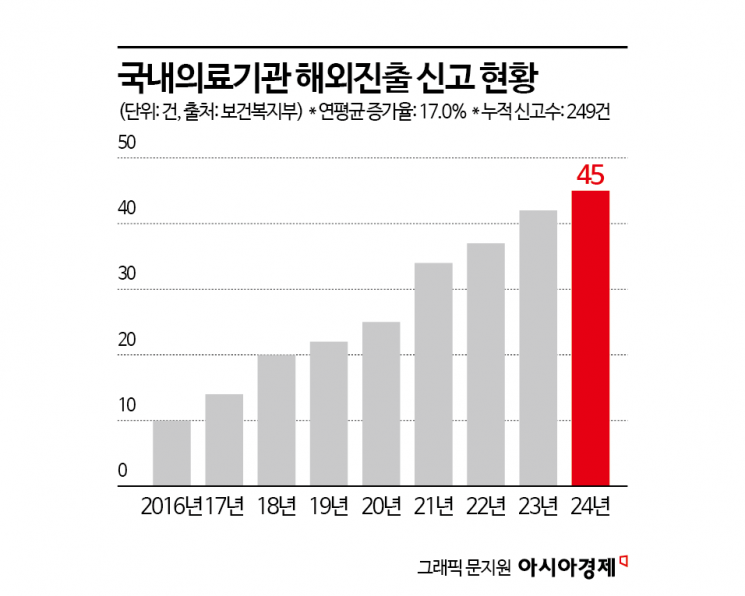
According to the "2024 Health and Welfare White Paper" released by the Ministry of Health and Welfare on October 29, the number of overseas expansion filings by domestic medical institutions last year reached 45. When the overseas expansion filing system for medical institutions was first introduced in 2016, there were only 10 cases. Since then, the Ministry has identified an average annual increase of 17%.
By type of overseas expansion, the establishment and operation of overseas medical institutions accounted for 107 cases (43%), followed by consulting for medical institution operations with 70 cases (28.1%), dispatch of personnel with 31 cases (12.4%), and medical professional training with 20 cases (8%).
Diversification of export items is cited as a key driver of this trend. In the past, exports were mainly B2C (business-to-consumer) services focused on beauty and plastic surgery treatments. Recently, however, there has been a growing trend of B2B (business-to-business) and B2G (business-to-government) medical system exports, involving the transfer of hospital management expertise and ICT-based systems as a whole. Notable examples include Seoul National University Hospital’s management of Sheikh Khalifa Specialty Hospital in the United Arab Emirates and Bundang Seoul National University Hospital’s contract to export its hospital information system to the Saudi Arabian Ministry of National Guard Health Affairs.
The overseas expansion of Korean medical institutions aligns with the growth of the global healthcare market, driven by factors such as global population aging, increased demand for health services, and advances in convergent medical technologies. The global healthcare services market, which was valued at 8.7787 trillion dollars (approximately 1,259.5 trillion won) last year, is projected to grow at an average annual rate of 4.9% to reach 11.222 trillion dollars (about 1,609.8 trillion won) by 2029.
Government support is being provided across the board, with the "Medical System Overseas Expansion Project Support Program" being a representative example. Medical institutions selected for this program receive support tailored to each stage of their expansion, including preliminary feasibility studies, business planning, obtaining permits for establishing and designing local corporations and hospitals, recruitment and training of personnel, promotional marketing, and expansion or relocation.
Since 2011, the government has supported a total of 233 projects through this program. For example, Hyundai Hospital in Namyangju, Gyeonggi Province, opened a six-story, 14-department, 40-bed medium-sized surgical specialty hospital in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, in July last year, based on government support.
The government aims to expand the current focus on China, Southeast Asia, and other Asian regions to include Western countries. Kim Donghyun, Director of the Overseas Expansion Division of the Health Industry at the Ministry of Health and Welfare, stated, "As the quality of Korean medical care is recognized as world-class, global interest is also increasing. We are preparing policy support to ensure that overseas expansion, currently concentrated in China and Southeast Asia, can be broadened worldwide."
Currently, by country, China accounts for the largest share of overseas expansion filings with 80 cases (32.1%), followed by Vietnam with 37, Mongolia with 20, the United States and Kazakhstan with 11 each, Thailand with 10, Japan and Uzbekistan with 9 each, and Indonesia with 8. In the Middle East, filings have also been reported based on intergovernmental cooperation, with 7 cases in the United Arab Emirates, 6 in Qatar, and 2 in Saudi Arabia.
Lim Youngyi, Director of the Medical Expansion Division at the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, commented, "It appears that initial expansion occurred in Asia due to frequent cooperation with these countries and the lower barriers to entry owing to geographic proximity. Considering the high standard of Korean medical care, if supported by the government, there is ample potential to expand exports to Western countries as well."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.