 Source: SNE Research, 'Next-Generation Si Anode Materials Beyond Volume Expansion' Report. *Period 1: 2000-2004, Period 2: 2005-2009, Period 3: 2010-2014, Period 4: 2015-2019, Period 5: 2020-2024
Source: SNE Research, 'Next-Generation Si Anode Materials Beyond Volume Expansion' Report. *Period 1: 2000-2004, Period 2: 2005-2009, Period 3: 2010-2014, Period 4: 2015-2019, Period 5: 2020-2024
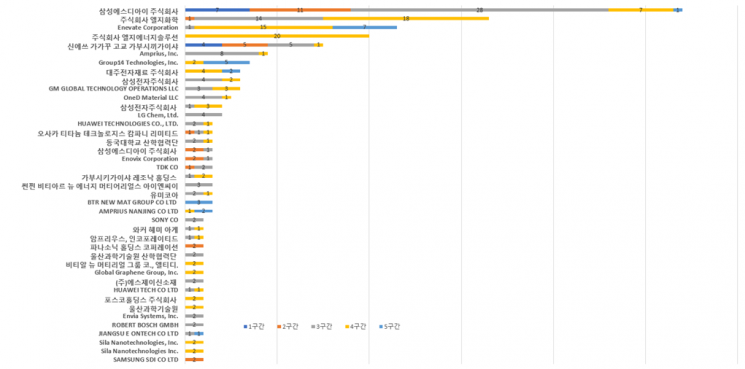
It has been found that Korean companies hold a significant number of key patents related to silicon anode materials, which are next-generation materials capable of greatly improving the capacity and charging speed of secondary batteries. However, in terms of the total number of patents, China overwhelmingly dominates the field.
According to the 'Silicon Oxide (SiO)-Silicon Carbide (SiC) Patent Report' published by SNE Research, a secondary battery market research firm, on July 14, China filed 2,726 patents as of 2024, accounting for 68% of the total.
Korea followed with 801 patents, representing 20% of the total. The United States (9%) and Japan (3%) came next.
When considering the number of patent citations and patent families (groups of patents based on the same invention), Korean companies such as LG Chem, LG Energy Solution, Samsung SDI, and Daejoo Electronic Materials are leading in the number of key patents. American company Enevate and Japan's Shin-Etsu also hold a considerable number of key patents.
Silicon anode materials are attracting attention as materials that can overcome the capacity limitations of lithium-ion batteries, as their theoretical capacity is more than ten times higher than that of conventional graphite anode materials. In addition, the rapid lithium diffusion rate enables fast charging and discharging. However, they have a chronic issue of volume expansion (swelling) during charging and discharging, which deteriorates battery lifespan and stability. The manufacturing process for silicon anode materials is also complex, leading to higher costs. In the battery industry, silicon anode materials are typically mixed with graphite anode materials.
Initially, silicon oxide-based composites attracted attention, but due to the issue of electrode breakage caused by repeated expansion and contraction, the focus has recently shifted to silicon carbide, which offers superior electrical conductivity and stability.
SNE Research explained, "The yolk-shell structure, which secures internal space to absorb expansion, is emerging as a new standard." The yolk-shell structure refers to a design in which the internal silicon, like the yolk of an egg, is surrounded by an external protective shell to address the expansion problem.
In China, companies such as BTR and BYD hold a large number of patents related to silicon carbide structures and mass production processes, giving China a global advantage in terms of patent quantity. Japan's Shin-Etsu has strengths in material synthesis and surface modification.
In Korea, companies such as LG Energy Solution and Samsung SDI are advancing composite structure design and interface stabilization technologies (SiC-SiO composites), increasing their market share based on the qualitative competitiveness of their patents.
SNE Research analyzed, "Silicon anode materials have become essential, especially for next-generation applications such as all-solid-state batteries and high-power electric vehicles. Despite China's quantitative advantage, Korea is securing technological leadership in the market based on the qualitative competitiveness of its patents. Intensive investment and research in structure design, interface stabilization, and high-energy composites will be the key to changing the market landscape."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![A Woman with 50 Million Won Debt Clutches a Stolen Dior Bag and Jumps... A Monster Is Born [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















