Serious Complications from Hip Fractures in the Elderly
Pressure Sores, Pneumonia, and Cardiovascular Diseases
Increased Mortality Risk from Being Bedridden
Typically, in the elderly, aging of body organs leads to weakened joints, bones, and muscles, as well as reduced balance, which increases the risk of falls.
Falls or loss of balance frequently occur due to weakened vision and hearing, as well as slowed nervous system responses. In particular, during the cold winter months, extra caution is needed to prevent fractures caused by falls.
Additionally, osteoporosis, which weakens bone tissue in the elderly, makes bones more susceptible to fractures even from minor impacts. Fractures commonly occur in the wrist, hip joint, femur (thigh), and as compression fractures of the spine.
▲Serious Complications
Lee Woonseong, Director of Orthopedics at Centum General Hospital, said, "The reason fractures are so dangerous for the elderly is that being bedridden for a long period after a fracture itself poses a significant risk." He added, "In such cases, there is a high risk of systemic complications such as pressure sores that cause skin to peel off around the hips or tailbone, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, and muscle atrophy."
Other possible complications include circulatory diseases such as arrhythmia, orthostatic hypotension, myocardial infarction, as well as endocrine disorders and back pain.
In particular, hip fractures can cause severe complications and may even be life-threatening.
According to related statistics from 2021, the one-year mortality rate for elderly patients with hip fractures is 18.2%, which is significantly higher than the one-year mortality rate for spinal fractures (6.3%). In particular, the mortality rate for men is 24.2%, about 1.5 times higher than that for women (15.7%), indicating a greater risk for men.
Among those aged 70 and older, the one-year mortality rate after a hip fracture is known to be around 25%. Therefore, rapid treatment (surgery) and rehabilitation after a fracture are key factors in preventing complications.
The most important thing is to help the patient stand and walk. Early ambulation reduces the risk of complications.
In the case of Mr. A (85), he suffered a femur (part of the hip joint) fracture due to a fall and was afraid to undergo surgery due to his advanced age. However, without surgery, he would have remained bedridden. Taking this into account, the medical team completed the surgery within 30 minutes, and Mr. A was able to walk normally one month later.
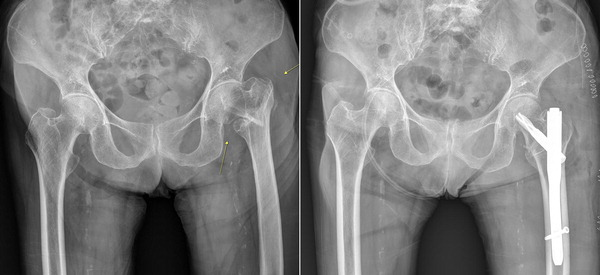
▲Surgical Treatments
After a fracture, tests such as MRI, CT, and bone density scans are necessary for an accurate diagnosis. For hip fractures in the elderly, non-surgical treatments are generally ineffective, so surgery is recommended.
Surgical options include metal fixation (using screws, pins, or metal plates to stabilize the fracture and allow natural bone healing), partial hip replacement (removing the damaged femoral head and replacing it with an artificial one), and total hip replacement (replacing both the femoral head and the pelvic joint surface with artificial joints).
For spinal fractures, depending on the severity of osteoporosis, about a week of bed rest may be required, after which mobility can be resumed with a brace. Generally, symptoms gradually improve within one to two months after a fracture as bone union progresses. However, if there is no improvement after three weeks, or if long-term bed rest is expected to cause complications, vertebroplasty-injecting medical bone cement into the vertebra-can be performed.
If the spinal fracture is severe enough that bone fragments compress the nerves or if bone union does not occur properly and instability persists, spinal fixation surgery may be necessary.
Director Lee Woonseong of Centum General Hospital advised, "If a fracture occurs, come to the hospital immediately. If the hospital is far away, it is best to temporarily immobilize the fractured area as an emergency measure." He added, "A simple method is to use a clothes hanger wrapped with a towel to stabilize the fracture, which can help prevent further injury."
▲Tips for Preventing Fractures
It is important to consistently engage in exercises and stretching that help strengthen muscles and improve balance. It is also advisable to have a bone density test to check for osteoporosis or osteopenia.
Director Lee Woonseong said, "If you have osteoporosis, appropriate medication can help increase bone density and prevent fractures. It is also important to get enough nutrition, such as foods rich in calcium and protein. Calcium and vitamin D play roles similar to bricks and cement in building bones. Since it is not easy to get enough vitamin D from food alone, supplements can be used."
It is also necessary to improve your living environment to prevent fractures caused by falls. For example, you can place non-slip mats on the bathroom floor. When going outside, it is advisable to wear shoes with low heels and wide soles.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![User Who Sold Erroneously Deposited Bitcoins to Repay Debt and Fund Entertainment... What Did the Supreme Court Decide in 2021? [Legal Issue Check]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026020910431234020_1770601391.png)















