Discovery of Predictive Biomarkers for Immuno-Oncology Treatment
Fast and Accurate Prediction of Cancer Recurrence Risk
 (Photo from left) Youngjoo Kim, PhD candidate (first author), Jaeho Cho, Professor (corresponding author), Injae Oh, Professor (corresponding author), Seongwoo Lee, PhD (first author). Provided by Chonnam National University
(Photo from left) Youngjoo Kim, PhD candidate (first author), Jaeho Cho, Professor (corresponding author), Injae Oh, Professor (corresponding author), Seongwoo Lee, PhD (first author). Provided by Chonnam National University
Professor Jaeho Cho's research team at Chonnam National University Medical School, in collaboration with Professor Injae Oh's respiratory medicine team at Hwasun Chonnam National University Hospital, developed a new method to measure the ex vivo phosphorylation level of STAT3 (pSTAT3ex vivo) in immune cells from the blood of lung cancer patients through basic-clinical cooperation. Using this method, they discovered a biomarker capable of early lung cancer diagnosis and predicting the responsiveness to immuno-oncology treatment.
The research team measured pSTAT3ex vivo expression in immune cells from the blood of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients and healthy individuals using the newly developed method. They confirmed that, unlike healthy individuals, NSCLC patients exhibited significantly elevated pSTAT3ex vivo expression from the early stages of cancer.
According to the study results, this pSTAT3ex vivo expression was found to be regulated by the inflammatory factor IL-6 in the blood.
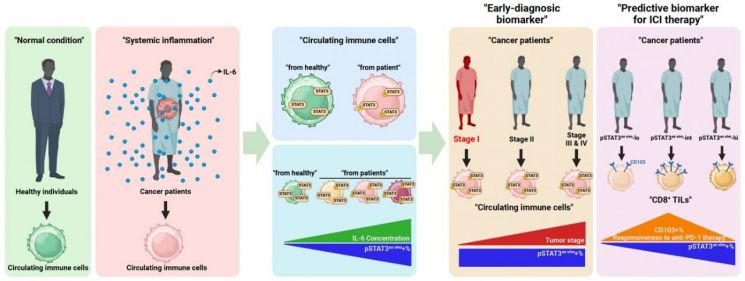 Schematic diagram of the development of early lung cancer diagnosis and immuno-oncology treatment prediction biomarkers by the research team at Chonnam National University Medical School. Provided by Chonnam National University
Schematic diagram of the development of early lung cancer diagnosis and immuno-oncology treatment prediction biomarkers by the research team at Chonnam National University Medical School. Provided by Chonnam National University
The research team analyzed the relationship between IL-6 and pSTAT3ex vivo and revealed that immune cells respond to IL-6 with 1,000 times greater sensitivity than previously reported. Based on this, they newly established the relationship between immuno-oncology treatment response?which was previously limited and inaccurately predicted by IL-6 concentration alone?and pSTAT3ex vivo.
Professor Jaeho Cho stated, “Through this study, we were able to more accurately understand the effect of inflammatory factors in the blood on immune cells. Based on this, it will greatly contribute to the development of biomarkers with various applications, including rapid and accurate early cancer diagnosis, post-surgical recurrence diagnosis, and prediction of immuno-oncology treatment response.”
This research was conducted with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Ministry of Education, led by the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Basic Research Program (Complex Cancer Immunotherapy Center) and the Original Technology Development Program (Immunotherapy Innovation Center). The research findings were published online on the 20th in the international journal Cancer Communications.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
















