Financial Burden on Insurance Companies Increases Amid Base Interest Rate Decline Trend
The financial authorities have decided to apply the planned expansion of the 'final observation maturity to 30 years,' which was scheduled to be introduced next year as a measure to reflect the discount rate on insurance liabilities, gradually over three years. This move is expected to address the increased financial burden on insurance companies due to the downward trend in the base interest rate.
On the 7th, the Financial Services Commission announced that the final observation maturity would be expanded to 30 years but applied gradually over three years starting next year. The specific method of phasing in the increase has not yet been detailed. A Financial Services Commission official stated, "Due to the recent decline in market interest rates, the financial impact has exceeded the initially expected level, creating a need to adjust the pace," adding, "We will closely monitor the implementation conditions according to the interest rate situation."
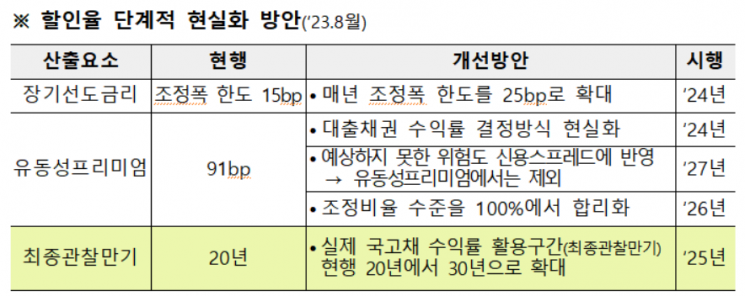 'Gradual Realization Plan for Discount Rates' announced by the Financial Services Commission in August last year. Provided by the Financial Services Commission
'Gradual Realization Plan for Discount Rates' announced by the Financial Services Commission in August last year. Provided by the Financial Services Commission
Unlike stocks and bonds, insurance contracts are not directly traded in the market, making it impossible to directly evaluate market prices. Therefore, the cash flows expected to occur in the future through insurance contracts are estimated and discounted to the present time to assess the market value. The discount rate on insurance liabilities (insurance payments) is the interest rate applied when converting the insurance payments that the insurer must pay into present value. When the discount rate decreases, the evaluated size of insurance liabilities increases, and when the discount rate rises, the evaluated size decreases.
Currently, when calculating the discount rate on insurance liabilities, a final observation maturity of 20 years linked to the 20-year government bond yield is applied up to a maturity of 20 years. The authorities announced a plan to reflect the discount rate on insurance liabilities in August last year, stating that the final observation maturity would be expanded from 20 years to 30 years starting next year. The intention was to suppress the effect of rising discount rates due to the sharp increase in interest rates. However, as market interest rates have recently declined and the possibility of further cuts in the U.S. base interest rate has increased, the authorities have decided to adjust the pace.
When the base interest rate falls and government bond yields decline accordingly, the discount rate decreases, causing an increase in insurance liabilities. The solvency ratio (K-ICS) of insurance companies, a financial soundness indicator, is calculated as the ratio of available capital to required capital; when insurance liabilities increase, available capital decreases, lowering the K-ICS. The Korea Insurance Research Institute recently analyzed that if the base interest rate falls by 1 percentage point, the K-ICS of life insurers would decrease by 25 percentage points, and that of non-life insurers by 30 percentage points.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
















