Inducing Targeted Cancer Cell Death
Treatment Effect Without Side Effects
A nanoparticle capable of effectively treating acute myeloid leukemia has been developed.
This nanoparticle selectively eliminates only leukemia cancer cells, reducing side effects and enhancing treatment efficacy.
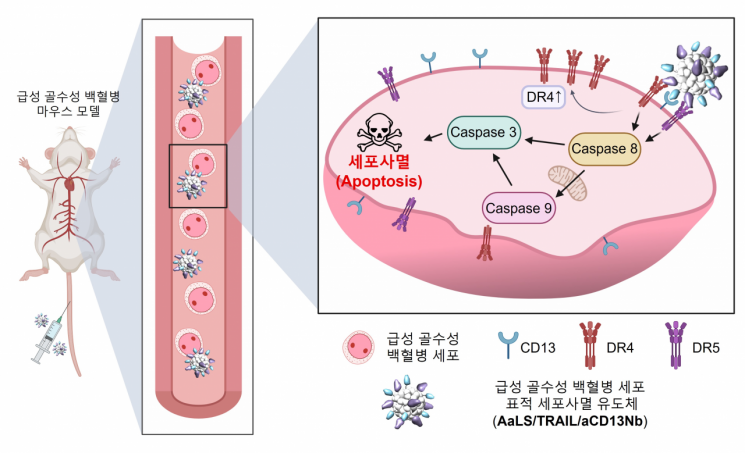
A research team from the Department of Life Sciences at UNIST (President Park Jongrae), including professors Kang Saebyung, Kim Eunhee, and Park Sungho, has created a protein nanoparticle (AaLS/TRAIL/aCD13Nb) that induces the death of only leukemia cancer cells. In animal experiments, this nanoparticle was shown to suppress the growth of leukemia cells and double the survival rate of mice.
 [Researchers] Professors Sungho Park, Sebyung Kang, Eunhee Kim, and researchers Mirae Yeo, Heejin Jeon, Junpyo Jeon (from the upper row, clockwise from the left).
[Researchers] Professors Sungho Park, Sebyung Kang, Eunhee Kim, and researchers Mirae Yeo, Heejin Jeon, Junpyo Jeon (from the upper row, clockwise from the left).
Acute myeloid leukemia is a fatal blood cancer with a 90% mortality rate without immediate treatment. Existing chemotherapy causes significant side effects, and elderly patients often cannot endure it, highlighting the need for new therapies.
The research team targeted the protein CD13 present on the surface of leukemia cells. They attached both a nanobody (aCD13Nb) that binds strongly to CD13 and a protein (TRAIL) that induces cancer cell death to the surface of the protein nanoparticle (AaLS). This enabled the rapid and selective destruction of leukemia cells.
The developed nanoparticle attached only to leukemia cells and eliminated them. In animal experiments, mice treated with the nanoparticle showed suppressed leukemia growth and a survival rate about twice as high as the control group.
Professor Kang Saebyung explained, "This technology can reduce side effects by selectively eliminating only cancer cells and will bring significant progress in leukemia treatment." First author Jeon Heejin stated, "This study has laid the foundation for developing a safe targeted therapy for acute myeloid leukemia."
The research results were published online in the international journal Nano Today on September 4. The study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea and Ulsan City.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![User Who Sold Erroneously Deposited Bitcoins to Repay Debt and Fund Entertainment... What Did the Supreme Court Decide in 2021? [Legal Issue Check]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026020910431234020_1770601391.png)














