Ministry of Health and Welfare Releases Analysis of 594 Non-Reimbursable Items from Last September
Orthopedics Accounts for 28% of Total
The medical department with the largest scale of non-reimbursable medical expenses was found to be Orthopedics, and the medical service item was manual therapy.
The Ministry of Health and Welfare and the National Health Insurance Service disclosed on the 20th the results of analyzing the '2023 Second Half Non-Reimbursable Reporting System' data from medical institutions at the hospital level or higher.
The non-reimbursable reporting system is a system that requires medical institutions to report details of non-reimbursable medical services, which are not covered by health insurance, to understand the status of non-reimbursable services and to guarantee the public's right to know and medical choice. In the second half of last year, 4,078 medical institutions at the hospital level or higher reported the medical details for 594 non-reimbursable items for September.
Analysis of these data showed that the total amount of medical expenses for 594 non-reimbursable items at hospital-level medical institutions in September last year was 422.1 billion KRW.
By type, hospitals accounted for the largest share with 193.8 billion KRW (45.9%), followed by general hospitals with 89.8 billion KRW (21.3%), tertiary general hospitals with 66.7 billion KRW (15.8%), and dental hospitals with 34.3 billion KRW (8.1%).
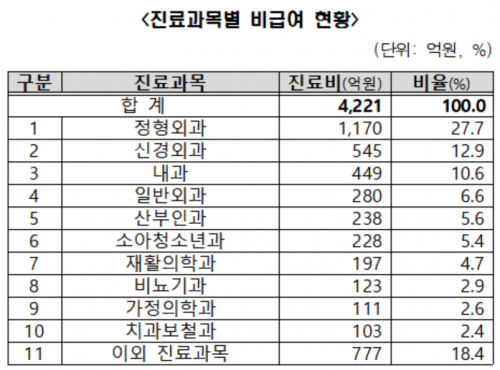
By medical department, Orthopedics had the largest amount at 117 billion KRW (27.7%), followed by Neurosurgery with 54.5 billion KRW (12.9%), Internal Medicine with 44.9 billion KRW (10.6%), General Surgery with 28 billion KRW (6.6%), Obstetrics and Gynecology with 23.8 billion KRW (5.6%), and Pediatrics with 22.8 billion KRW (5.4%).
By item, manual therapy was the highest at 49.4 billion KRW (11.7%), followed by single-room premium hospital room fees at 45.1 billion KRW (10.7%), and spinal-lumbar magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at 18.7 billion KRW (4.4%). The top 10 items accounted for 45.3% of the total non-reimbursable medical expenses.
The government judged, based on the analysis of this non-reimbursable reporting data, that some non-reimbursable services such as manual therapy are linked to indemnity insurance, showing a tendency toward excessive treatment, and decided to strengthen the management of non-reimbursable services that burden the public’s medical expenses and health insurance finances.
According to the first implementation plan of medical reform announced at the end of last month, the government plans to support consumers' rational medical choices by strengthening non-reimbursable monitoring and expanding related information, and to prepare standard medical guidelines for non-reimbursable services by collecting opinions from the medical field.
Additionally, for mild non-reimbursable treatments such as manual therapy that tend to be overused, the government plans to consider restricting 'concurrent treatment' coverage when medical necessity is low, and also to consider removing technologies that lack effectiveness or have safety issues from the non-reimbursable item list.
Kwon Byung-gi, Director of Essential Medical Support at the Ministry of Health and Welfare, said, "We will analyze the data collected through the reporting system to provide information that helps the public’s actual medical use and continue to strengthen non-reimbursable monitoring," and added, "We will prepare specific implementation plans for managing mild excessive non-reimbursable services presented in the first medical reform implementation plan through expert discussions including the medical community."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![User Who Sold Erroneously Deposited Bitcoins to Repay Debt and Fund Entertainment... What Did the Supreme Court Decide in 2021? [Legal Issue Check]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026020910431234020_1770601391.png)















