Securities Firms' ABCP Debt Guarantee Risk Only 18%
Low Risk for Non-Residential and Overseas Real Estate
PF Debt Guarantee Incentives Inevitable
8 Years Since IMA Introduction... No News from Operators
Industry's Long-Standing Corporate Payment System Still Distant
The reason financial authorities are working to improve the comprehensive financial investment business operator (CIO) system is to attract capital market funds currently concentrated in real estate project financing (PF) toward corporate finance such as mergers and acquisitions (M&A) and corporate credit provision. Since the introduction of the new Net Capital Ratio (new NCR) in 2016, the NCR ratio has improved thanks to an increase in equity capital; however, paradoxically, as real estate PF investments increased, the total risk assets relative to equity capital (total risk amount) also rose significantly. The core of the CIO system improvement is expected to be an increase in the risk value of real estate PF when evaluating the NCR. Along with this, attention is also focused on whether new business approvals, such as corporate payment settlements requested by the financial investment industry, will be granted.
Relaxing soundness regulations led to increased securities firms' PF debt guarantees
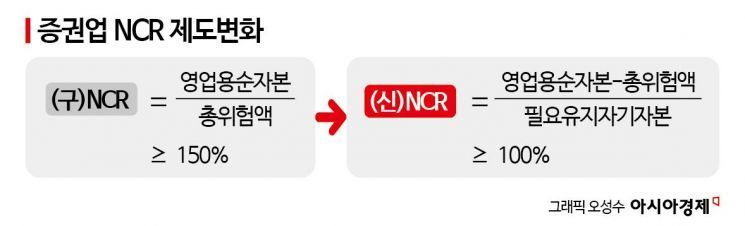
The NCR is an indicator that gauges the financial soundness of securities firms. The old NCR, first introduced in 1997, was calculated by dividing net capital for business use by the total risk amount. The larger the risk amount, the more net capital for business use must be held proportionally.
In the 2000s, there were criticisms that the NCR indicator excessively regulated the securities industry, which plays the role of venture capital. In response, financial authorities introduced the new NCR system in 2016 and changed the evaluation formula. The new NCR divides the amount obtained by subtracting the total risk assets (total risk amount) from net capital for business use by the required maintained capital per business unit.
The difference from the old NCR lies in the 'required maintained capital per business unit.' This is defined as 70% of the statutory required capital. Applying this to the formula limits the denominator, the required maintained capital per business unit, to a certain level. Therefore, securities firms have significantly reduced the burden of managing the NCR ratio.
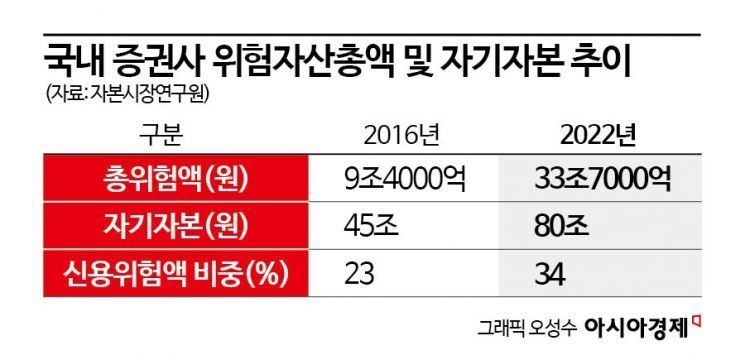
Did securities firms increase venture capital investments after the introduction of the new NCR? The answer is half yes and half no. According to the Korea Capital Market Institute, the total risk assets (total risk amount) of securities firms increased about fourfold from 9.4 trillion KRW in 2016 to 33.7 trillion KRW in 2022. During the same period, equity capital rose from 45 trillion KRW to 80 trillion KRW, an increase of 1.8 times.
The risk amount grew faster than the equity capital. In other words, not only brokerage fees earned from mediating stock or bond trades but also derivative-linked securities (DLS) and PF exposures increased significantly, leading to a rise in risk amounts.
The total risk amount is divided into market risk amount, credit risk amount, and operational risk amount. By risk type, the increase in credit risk amount is notable. From 2016 to 2022, the proportion of credit risk amount rose from 23% to 34%, an 11 percentage point increase. During the same period, market risk amount decreased from 64% to 56%, and operational risk amount fell from 14% to 9%.
Real estate PF risk value fixed at 18%... raising risk values
The Financial Services Commission is considering raising the risk weight for real estate PF above the current level. A likely approach is to refine the risk weight formula for real estate PF and apply different risk weights depending on the scale of debt guarantees and the degree of risk.
Currently, CIOs (securities firms with equity capital of 3 trillion KRW or more designated by the Financial Services Commission) apply a higher NCR risk value (100% application) for domestic residential loans. Conversely, NCR risk values for non-residential and overseas real estate investments are lower. This regulation was designed to encourage overseas alternative investments.
An official from the Korea Capital Market Institute pointed out, "Especially, the risk weight for real estate PF debt guarantees in the NCR risk value is uniformly applied at 18%. Regardless of PF risk, if there is a 10 billion KRW debt guarantee, only up to 1.8 billion KRW is calculated as the maximum possible loss amount, so there is inevitably a strong incentive to invest in PF debt guarantees."
From the securities firms' perspective, PF debt guarantees were considered to have relatively low risk weights while still having the nature of venture capital. However, since the Legoland incident in October 2022, calls for improving the NCR system have grown louder. At that time, due to the deterioration of the real estate PF market, securities firms faced liquidity crises as asset-backed commercial papers (ABCP) guaranteed by them had difficulty refinancing. The Financial Services Commission decided to temporarily lower the NCR risk value if ABCP debt guarantees were converted directly into loans by the end of the year.
A Financial Services Commission official said, "Nothing has been decided yet regarding the CIO system improvement," adding, "We have announced the direction to adjust real estate-related risk weights and plan to commission related research."
Financial investment industry: "First IMA operator should emerge, and corporate payment settlements should be allowed"
The financial investment industry demands that new businesses be allowed to enhance the competitiveness of CIOs. Approval of comprehensive investment account (IMA) operators is a representative example. An IMA is an account where securities firms guarantee principal and invest customers' deposits in various corporate finance such as corporate loans and corporate bonds to seek profits. The Financial Services Commission introduced it in 2016, but no securities firm has been approved for eight years. Only large securities firms with substantial capital can qualify because they must reserve more than 5% of entrusted assets as loss provisions.
A securities firm official said, "Recently, NH Investment & Securities succeeded in a package deal with Ostem Implant, significantly improving securities firms' corporate finance capabilities," adding, "The first IMA operator should emerge to facilitate fundraising for investment banking (IB) operations."
Corporate payment settlement is also one of the long-standing wishes of securities firms. Currently, securities firms can only make payment settlements with 'individuals.' Therefore, corporations and other legal entities pay salaries and supplier fees through bank accounts. Expanding this to corporations would enable salary transfers and utility bill payments through securities firm accounts.
Corporate payment settlement has been a recurring complaint for 15 years since 2006. It requires amendments to the Capital Markets Act but has repeatedly failed due to opposition from the banking sector. A senior official from the Korea Financial Investment Association said, "Corporate payment settlement is infrastructure for corporate finance," adding, "Securities firms effectively have to use bank accounts to conduct corporate finance business, making it difficult to provide consistent integrated services independently."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.