An integrated indoor-outdoor GPS system that can operate even in buildings without wireless signal infrastructure such as wireless LAN or Bluetooth has been developed. The strength of this system lies in its ability to provide location services not limited to specific buildings but available in all buildings worldwide.
KAIST announced on the 12th that Professor Dongsoo Han's research team at the Department of Computer Science's Intelligent Service Integration Laboratory developed a universal indoor-outdoor integrated GPS system called "KAILOS (KAIST LOcating System)."
 Professor Han Dong-su. Provided by KAIST
Professor Han Dong-su. Provided by KAIST
KAILOS's advantage is expanding the service range beyond a few specific buildings to all buildings worldwide. Through this, it is expected that in the future, a so-called "universal indoor-outdoor integrated GPS location recognition service" that operates even in buildings where wireless signals are not available will be possible.
First, the research team developed a sensor fusion location recognition technique that integrates AI methods for detecting indoor-outdoor transitions and AI methods for detecting building entrances.
This technique works in conjunction with pedestrian dead reckoning (PDR) by detecting building entrances, floors, and landmarks such as stairs and elevators.
The research team made it possible to determine the building a user enters and to detect the time and location of entry in real-time by comprehensively utilizing GPS signals and signals obtained from inertial sensors.
Inside buildings, vertical movement using stairs and elevators is detected using barometric and inertial sensors, and a floor detection technique using barometric information was also developed.
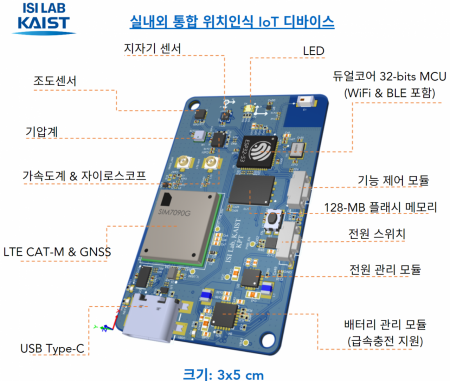
Additionally, they produced a location-dedicated Internet of Things (IoT) tag integrating GPS, WiFi, Bluetooth signal chips, inertial sensors, barometric sensors, geomagnetic sensors, and illuminance sensors. The GPS sensor mounted on the tag processes not only the L1 signals directly received from satellites but also the L5 signals reflected inside buildings, achieving high accuracy even in urban canyons.
Based on this, the research team explained that with just the location tag, it is possible to estimate locations indoors and outdoors in any building worldwide where LTE signals are available, enabling the development of various indoor-outdoor integrated location-based application services.
Regarding battery consumption of the IoT tag, it may vary depending on the location service cycle, but it was confirmed that in environments with relaxed real-time service conditions, the service can be provided for several days without battery charging.
The indoor-outdoor integrated GPS system developed by the research team is also expected to be utilized to expand the service area of the "Korean Positioning System (KPS)," which began development in 2022, into indoor spaces.
Professor Han said, "The KAILOS system proved its commercialization potential through six proof-of-concept processes evaluating the functions and performance of the system developed for construction sites and factory buildings without location infrastructure installed," adding, "It can be used in the future to protect children and dementia patients and ensure the safety of factory workers."
Meanwhile, this research was conducted with support from the Defense Acquisition Program Administration and the Agency for Defense Development (Future Challenge Defense Technology R&D Project).
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.