Japan Lags Behind Korea and Taiwan, Aims for Rebound
Japanese Government Also Invests 33 Trillion Won
Eight major Japanese companies, including Sony and Mitsubishi, plan to invest 5 trillion yen (approximately 43 trillion won) in semiconductors by 2029, according to a report by Nihon Keizai Shimbun (Nikkei) on the 9th.
Nikkei reviewed the capital investment plans for 2021-2029 of eight major Japanese semiconductor manufacturers: Sony, Mitsubishi Electric, ROHM, Toshiba, Kioxia Holdings, Renesas Electronics, Rapidus, and Fuji Electric, revealing these findings.
These companies are significantly increasing production of power semiconductors for power control, image sensors, and other key economic and national security materials in line with the expansion of artificial intelligence (AI), decarbonization, and the electric vehicle market.
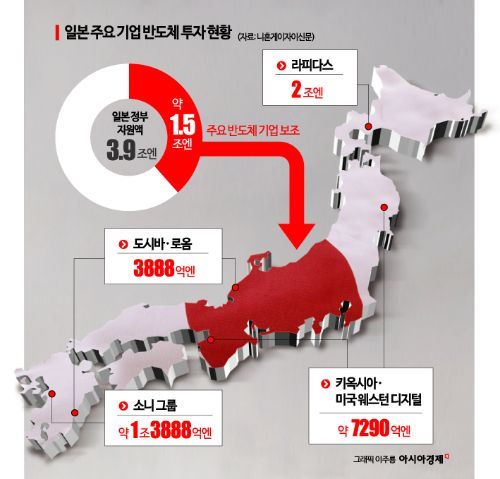
Sony will invest 1.6 trillion yen (approximately 13.77 trillion won) over five years from 2021 to 2026 to increase semiconductor image sensor production. Image sensors have strong demand for smartphone cameras and are expanding in use due to advancements in autonomous driving. In 2023, Sony expanded its factory in Nagasaki Prefecture and plans to establish a new factory in Kumamoto Prefecture.
Considering the market expansion of AI data centers and electric vehicles, investments to increase power semiconductor production for efficient power control are also continuing.
Toshiba and ROHM plan to invest a combined 380 billion yen (approximately 3.27 trillion won). Mitsubishi Electric aims to increase its production capacity of silicon carbide (SiC) power semiconductors, which have excellent energy-saving performance, to five times the 2022 level by 2026. It plans to invest 100 billion yen (approximately 860.5 billion won) to build a new factory in Kumamoto Prefecture.
In the AI semiconductor field, Rapidus is targeting 2-nanometer semiconductor production. The goal is to start operating a prototype line in April 2025 in Chitose City, Hokkaido. The company stated that an investment of 2 trillion yen (approximately 17.21 trillion won), including research and development costs, is necessary.
The Japanese government is also expanding semiconductor support. According to Nikkei, the scale of government subsidies for semiconductors in the past three years has reached 3.9 trillion yen (approximately 33.56 trillion won).
Japanese semiconductors held about 50% of the global market share in 1988. However, since the 1990s, Japanese companies lost to Korean and Taiwanese firms that invested huge amounts, leading Japanese companies to withdraw from advanced semiconductor development in the early 2000s. By 2017, their market share had fallen below 10%.
In the 2020s, the importance of semiconductors has emerged in terms of economy and security due to the US-China trade war. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted supply chains, increasing the necessity to secure semiconductor production capacity domestically, which determines the competitiveness of the digital industry. This is why the Japanese government and companies are investing astronomical amounts to promote the semiconductor industry's resurgence.
According to the Ministry of Finance's corporate statistics survey, investment in information and communication machinery equipment used in semiconductor manufacturing reached 2.1085 trillion yen (approximately 18.11 trillion won) in 2022, a 30% increase over five years. The share of semiconductors in manufacturing rose from 11% to 13%, matching the scale of transportation machinery such as automobiles (15%) and chemicals (14%). Nikkei stated, "Large-scale semiconductor investments are long-term and are driving capital investment in manufacturing."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.