Hyundai Motor to Phase Out Domestic Production of Gasoline Engines for Compact Cars
Reflecting Decline in Domestic Demand for Internal Combustion Engine Compact Cars
Reorganizing Production Map to Match Regional Demand
Strengthening EV and HEV Production Capacity in Korea and the US
India Focuses on Small Internal Combustion Engines... Indonesia Leads Southeast Asia EV Production
Hyundai Motor Company decided not to produce small gasoline engines domestically due to the sharp decline in demand for some internal combustion engine vehicles such as compact cars and small sedans. Recently, Hyundai has been strengthening its regional strategy by increasing localized production according to regional demand.
Hyundai began producing small engines mainly used in compact cars in 1997 when it independently developed the 'Epsilon engine.' In 2008, it developed the successor Kappa engine and started domestic production from 2012.
Until 2012, when the Kappa engine began domestic production, the domestic compact car market size was over 200,000 units annually. However, nine years later in 2021, it sharply declined to about 95,000 units, and last year it barely recovered to around 100,000 units. During this process, small sedan models such as the Hyundai Accent and Kia Rio were discontinued early in the domestic market and have continued their presence in emerging markets such as India, South America, and Vietnam.
◆ Domestic ‘Popularity of Mid- to Large-Sized HEVs’= Hyundai has started to redraw its global production map considering these regional characteristics. In the domestic market, a preference for mid- to large-sized vehicles is clearly evident. Among the top 10 domestically sold models in the first quarter of this year, eight were mid-sized or large vehicles. Kia’s mid-sized SUV Sorento ranked first, followed by Hyundai’s mid-sized SUV Santa Fe, and Kia’s large recreational vehicle (RV) Carnival in third place. In the compact and small car segments, the Ray and SUV Seltos made it into the top 10.
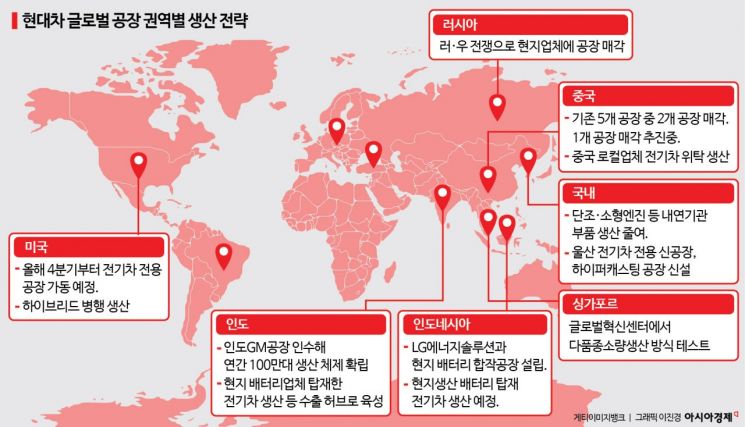
Hyundai’s change in regional production strategy reflects domestic consumers’ preference for eco-friendly vehicles. The plan is to reorganize domestic production focusing on hybrids (HEVs) and electric vehicles according to consumer demand. In a conference call last quarter, Hyundai mentioned that it is developing HEV systems specialized not only for mid- to large-sized vehicles but also for small vehicles, indicating the possibility of applying HEVs across the entire lineup. According to Kaizyu Data Research Institute, gasoline vehicle registrations in the domestic new car market in the first quarter of this year were 196,472 units, down 18% from the previous year, while hybrid vehicle registrations surged 46% to 99,832 units.
In line with the eco-friendly vehicle trend, Hyundai is also increasing production of the electric version of the compact car Casper domestically. Gwangju Global Motors (GGM), which produces the Casper, aims to start mass production of electric vehicles in July this year, planning to allocate 70% of the second half’s production volume to electric vehicles. Hyundai plans to supply domestically produced Casper electric vehicles to regions where compact cars are popular, such as Japan and Europe.
 Aerial view of Hyundai Motor Group's dedicated electric vehicle plant in the United States (HMGMA·Hyundai Motor Group Metaplant America)
Aerial view of Hyundai Motor Group's dedicated electric vehicle plant in the United States (HMGMA·Hyundai Motor Group Metaplant America) [Photo by Hyundai Motor Group]
◆ U.S. Focuses on Electric Vehicles; India Strengthens Small Internal Combustion Engines= Hyundai is also reorganizing its global production portfolio. In the United States, it is investing 6 trillion won to build a large-scale electric vehicle-only factory and increase local electric vehicle production. This is to benefit from subsidies under the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA).
In India, Hyundai plans to increase the production capacity of local factories to 1 million units annually and focus production on small internal combustion engine vehicles, which have high local demand. At the same time, recognizing India’s market growth potential as the world’s most populous country, Hyundai is also preparing for the electric vehicle market. Last month, Hyundai announced plans to produce electric vehicles equipped with LFP batteries from Exide, an Indian battery company. This is to ensure price competitiveness as well as a stable supply chain.
In the Southeast Asian market region, Hyundai continues electric vehicle production and testing mainly in Indonesia and Singapore. Hyundai plans to build a battery cell joint venture factory with LG Energy Solution in Indonesia and aims to produce electric vehicles equipped with locally produced batteries as early as the second half of this year.
On the other hand, production scale is being reduced in China and Russia. Hyundai once operated five factories in China but has sold two and is in the process of selling another. The Russian factory was sold at a low price to a local company in January due to the prolonged Russia-Ukraine war.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.