Financial Supervisory Service 2023 Actual Performance of Indemnity Medical Insurance Business
Deficit Increases by 30% Compared to Previous Year
Last year, insurance companies reported a loss of approximately 2 trillion KRW in indemnity health insurance. This figure increased by 448.2 billion KRW compared to the previous year. Although the number of policies held and premium income increased, excessive non-reimbursable medical treatments led to continued insurance payout leakage.
According to the "2023 Indemnity Health Insurance Business Performance (Preliminary)" released by the Financial Supervisory Service on the 10th, the loss from indemnity health insurance last year was 1.9738 trillion KRW. This represents a 29.3% increase compared to the previous year's loss of 1.5301 trillion KRW.
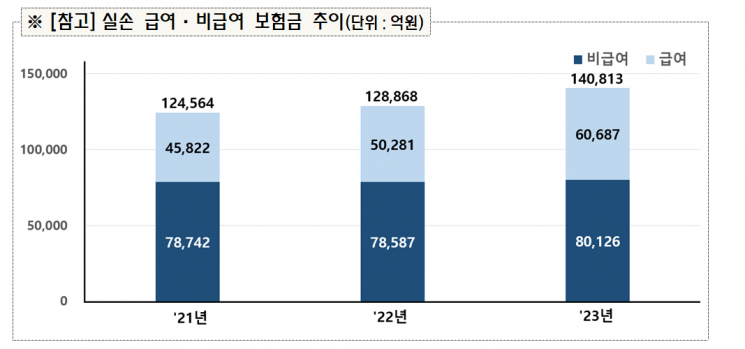
The financial authorities analyzed that non-reimbursable insurance payouts, which had somewhat decreased due to the 'Supreme Court ruling on cataracts,' have turned to an increasing trend again. Non-reimbursable insurance payouts last year amounted to 8.0126 trillion KRW, a 2% increase from the previous year. In June 2022, the Supreme Court ruled that cataract insurance payouts should be paid within the outpatient coverage limit when inpatient treatment is unnecessary. Influenced by this, insurance payouts in 2022 (7.8587 trillion KRW) decreased by 15.5 billion KRW compared to 2021 (7.8742 trillion KRW).
Among the non-reimbursable insurance payouts, non-reimbursable injection fees accounted for the largest share at 28.9%, an increase of 5.4 percentage points from the previous year. This is believed to be due to an increase in respiratory diseases following the relaxation of COVID-19 preventive measures and reduced mask-wearing. Physical therapy, which ranked first in 2021 and 2022, dropped to second place, although its share (28.6%) increased. Cataract multifocal lens implantation (hospital/clinic level) dropped out of the top five items, while varicose vein surgery (1.6%) newly entered the list.
The loss ratio, which is the ratio of insurance payouts to premiums received, also rose again. The loss ratio, which had fallen by 11.8 percentage points from 113.1% in the previous year to 101.3% in 2022, increased by 2.1 percentage points to 103.4% last year. For life insurance companies, the loss ratio rose by 1.7 percentage points to 86.4%, while for non-life insurance companies, it increased by 2.3 percentage points to 107.1%.
By product, the third generation had the highest loss ratio at 137.2%, followed by the fourth generation (113.8%), first generation (110.5%), and second generation (92.7%). The third generation, launched in 2017, raised premiums for the first time in 2023, while the fourth generation, launched in 2021, has not adjusted premiums until 2026, five years after its launch. Indemnity insurance is categorized by sales period and coverage structure into first generation (old indemnity), second generation (standardized indemnity), third generation (new indemnity), fourth generation, and others (elderly and those with pre-existing conditions). The expense ratio, which represents actual business expenses relative to premium income, remained at a similar level to the previous year at 10.3%.
The number of policies held as of the end of last year was 35.79 million, an increase of 0.4% (140,000 policies) compared to the previous year. Life insurance companies saw a decrease of 80,000 policies, but non-life insurance companies increased by 220,000 policies. Premium income, which is equivalent to sales, was 14.4 trillion KRW, up 9.5% (1.2 trillion KRW) from the previous year. Insurance profit and loss, which is premium income minus incurred losses and actual business expenses, showed a loss of 1.97 trillion KRW, an increase of 440 billion KRW compared to the previous year's loss of 1.053 trillion KRW.
Accordingly, the Financial Supervisory Service plans to continue improving systems to prevent insurance payout leakage. Since new non-reimbursable items such as knee stem cell injections continue to emerge, non-reimbursable payouts still account for a high proportion of total indemnity insurance payouts, raising concerns that both insurance companies' loss ratios and the premium burden on customers who do not receive treatment are increasing.
A Financial Supervisory Service official emphasized, "We plan to support the stable establishment of the fourth-generation non-reimbursable premium differentiation system starting in July this year and the suspension system for indemnity health insurance for military personnel, and strengthen supervision to ensure prompt payment for legitimate insurance claims."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)










