Savings Bank Loans Decrease by 12 Trillion
Saemaeul Geumgo Shows Deposit Recovery
But Down 3 Trillion Won YoY... Turned to Deficit Last Year
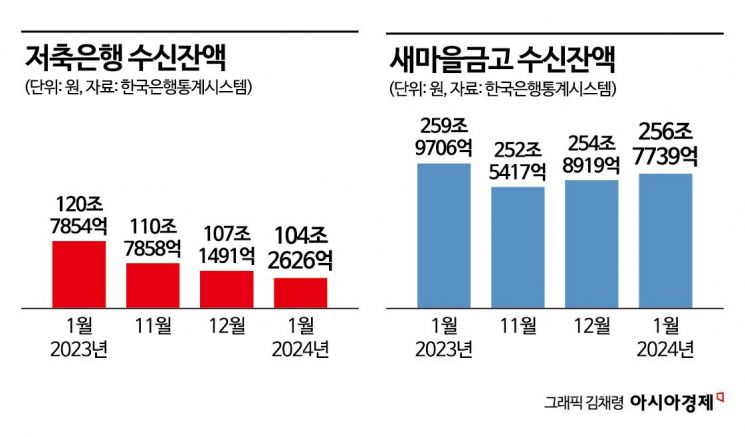
The deposit scale of savings banks, which have been struggling with poor performance, has decreased by more than 16 trillion won compared to the previous year. The loan scale also dropped by over 10 trillion won. Saemaeul Geumgo, which experienced a bank run crisis last year, is showing signs of deposit recovery but still fell by more than 3 trillion won compared to the previous year.
According to the Bank of Korea's Economic Statistics System on the 18th, the deposit balance of mutual savings banks at the end of January was recorded at 104.2626 trillion won. This amount decreased by 2.8865 trillion won compared to the previous month and by 16.5228 trillion won compared to the previous year. The loan balance also decreased to 103.2171 trillion won, down 876.5 billion won from the previous month and 12.3832 trillion won from the previous year.
This situation is due to savings banks reducing their size as profitability worsened amid rising interest expenses. With the continuation of high interest rates, savings banks, fearing negative interest margins, have reduced their loan assets, and as the demand for funds decreased, they lost the incentive to attract deposits by offering high interest rates.
According to the Korea Federation of Savings Banks, as of this day, the average interest rate for nationwide savings banks' fixed deposits (12 months) was 3.72%. This level is almost the same as the representative fixed deposit product rates (3.5~3.6%) of the five major banks: KB Kookmin, Shinhan, Hana, Woori, and NH Nonghyup.
Moreover, regulatory authorities recently ordered the secondary financial sector to strengthen reserve fund accumulation due to real estate project financing (PF) defaults and delinquency rates, increasing the burden of loan loss provisions. The financial authorities required that land-secured loans, previously classified as general corporate loans, be provisioned similarly to real estate PF loans, and that asset soundness classification for PF loans be conservative. As the burden of reserve fund accumulation grows, savings banks have no choice but to reduce their size.
With the added burden of provisions, the poor performance of savings banks continues. KB Savings Bank posted a net loss of 90.6 billion won last year, while Woori Financial Savings Bank (-49.1 billion won), IBK Savings Bank (-24.9 billion won), and Hana Savings Bank (-13.2 billion won) also recorded losses.
The situation is similar for mutual finance institutions such as Saemaeul Geumgo. At the end of January, Saemaeul Geumgo's deposit balance was 256.7739 trillion won, an increase of 1.882 trillion won compared to the previous month. Although deposits have been recovering since the bank run incident in July last year, the amount decreased by 3.1967 trillion won compared to the previous year. In contrast, the deposit balance of Shinhan Credit Cooperative, another mutual finance institution, increased by 2.084 trillion won compared to the previous year, reaching 135.1015 trillion won at the end of January.
Although official statistics are not yet available, the Saemaeul Geumgo Central Association is known to have turned to a deficit last year. This was caused by an increase in loan loss provisions due to the expanded risk of PF loan defaults. Regarding this, a representative of the Saemaeul Geumgo Central Association explained, "We classified asset soundness conservatively in anticipation of a worsening business environment."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.