Usage Decreased by 34.2% Compared to 10 Years Ago but Still High
"Antibiotic Resistance May Make Proper Treatment Difficult
Prescription Must Be Based on Objective Evidence"
Antibiotic prescriptions in South Korea remain higher than the average of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
Although reduced by 34.2% compared to 10 years ago... Antibiotic usage still higher than OECD average
According to the OECD's publication "Health at a Glance 2023" released on the 14th, South Korea's antibiotic consumption in 2021 was 16.0 DDD (Defined Daily Dose, the standard daily dose of medication, units omitted hereafter) per 1,000 people, which is higher than the average of 13.1 among 38 OECD countries.
South Korea's antibiotic prescription volume was 24.3 in 2011, 23.7 in 2019, and 16.0 in 2021, showing a 34.2% decrease over 10 years. However, it still remains higher than most OECD countries.
The difference in antibiotic prescription volumes between countries was up to threefold.
In 2021, countries with relatively low antibiotic use included Austria (7.2), the Netherlands (7.6), and Germany (8.1), while countries with high usage were Greece (21.7), France (19.3), and Poland (18.8).
Antibiotic misuse leads to resistance... WHO states "Over 5 million deaths due to antibiotic resistance in 2019"
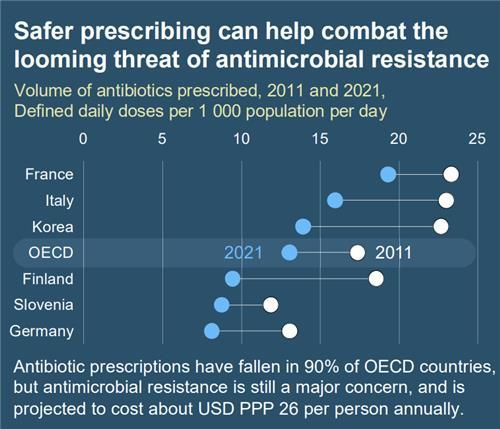 Changes in Antibiotic Prescription Volumes by Country (2011-2021). [Photo source=OECD Health at a Glance 2023 capture]
Changes in Antibiotic Prescription Volumes by Country (2011-2021). [Photo source=OECD Health at a Glance 2023 capture]
Antibiotics are substances that inhibit the growth or life of other microorganisms and are used to treat infectious diseases.
However, misuse or overuse of antibiotics can lead to resistance, making appropriate treatment impossible when needed. Therefore, prescriptions must be based on objective evidence.
Meanwhile, the World Health Organization (WHO) designates the third week of November each year as "World Antibiotic Awareness Week" to raise awareness about antibiotic resistance and promote responsible antibiotic use.
According to WHO, more than 5 million people worldwide died from bacterial infections caused by antibiotic resistance in 2019.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

















