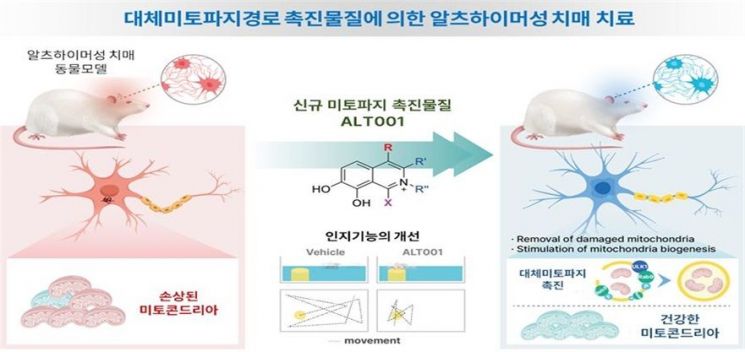
Domestic researchers have developed a new substance called 'ALT001' that promotes mitophagy function, known as the mitochondrial recycling process, for the first time. Mitophagy refers to a series of cellular processes that selectively remove damaged or aged mitochondria and promote the biosynthesis of new mitochondria. It is explained that by promoting this process, the possibility of developing a treatment for Alzheimer's dementia has been confirmed.
The Korea Health Industry Development Institute announced on the 8th that a collaborative research team consisting of Professor Jin-Ho Yoon of Dong-A University College of Medicine, Professor Jong-Hyun Cho of Dong-A University Department of Biomedical Engineering, Professor Ji-Hoon Jo of Chonnam National University, and Alt Medical succeeded in developing ALT001. ALT001 is a new mitophagy-promoting substance synthesized through chemical optimization of a newly discovered mitophagy-promoting structure called 'isoquinoline scaffold' by the research team. It is explained that it has low toxicity and safety that does not interfere with cell growth, and animal experiments have proven that it effectively improves impaired cognitive function, demonstrating its potential as a clinically applicable dementia treatment substance.
Until now, Alzheimer's dementia treatment research has mainly focused on amyloid beta (Aβ) and tau (Tau) proteins, but recent studies have confirmed that mitochondrial dysfunction interacts with Aβ and plays an important role in the onset of dementia, drawing attention to the promotion of mitophagy processes that maintain mitochondrial function as a new therapeutic strategy. However, no mitophagy-promoting compounds with proven clinical applicability have been developed, so dementia treatment through mitophagy has not yet been realized.
To improve this situation, the research team conducted compound library screening using a self-developed mitophagy activity analysis system. Compound library screening is an experimental process to discover compounds with specific activities among many compounds. As a result, the researchers found that compounds with the same isoquinoline scaffold exhibited mitophagy-promoting activity, and to derive compounds with improved mitophagy-promoting activity, they chemically optimized the isoquinoline scaffold and developed the compound ALT001. The isoquinoline scaffold is an organic compound commonly found in medicinal plants and has traditionally been used for anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
Experiments evaluating learning and memory abilities using ALT001 on an Alzheimer's dementia mouse model showed recovery of learning and memory abilities in the dementia mouse model, and this therapeutic effect was also confirmed in other mouse models widely used in dementia research.
Professor Jin-Ho Yoon, who led the research, said, “Thanks to the support of national projects in the fiercely competitive field of mitophagy-based therapeutic development, domestic researchers were able to succeed in developing a dementia treatment substance applicable to clinical use. Through this research, the development of mitophagy-based dementia treatments, which was difficult to commercialize due to the lack of molecular mechanism verification drugs, will become possible. We will devote ourselves to follow-up research aiming at the commercialization of dementia treatments utilizing these research results.”
The results of this study, conducted with the support of the Dementia Overcoming Research and Development Project Group, were published online on the 27th of last month in 'Theranostics,' a world-renowned academic journal ranked in the top 5.8% in the field of medical research.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.