Fund Management Development Committee Proposes Governance Reform to Increase Returns
To minimize social resistance while promoting pension reform centered on premium increases, it is also necessary to raise the fund management return rate. To achieve this, a fundamental governance reform is needed to change the decision-making structure of asset allocation, which accounts for more than 90% of returns, to be expert-centered.
On the 1st, the Fund Management Development Committee (Gibalwi) presented the "Improvement Plan for the National Pension Fund Management," which includes these key points. This is the result of 14 meetings held from November last year to August this year to discuss reform measures for improving returns.
 At the 5th National Pension Financial Review Public Hearing held at COEX on the 1st, members of organizations such as the Korean Confederation of Trade Unions and People's Solidarity stood holding placards opposing the deterioration of the National Pension next to the Financial Review Committee members seated. Photo by Younghan Heo younghan@
At the 5th National Pension Financial Review Public Hearing held at COEX on the 1st, members of organizations such as the Korean Confederation of Trade Unions and People's Solidarity stood holding placards opposing the deterioration of the National Pension next to the Financial Review Committee members seated. Photo by Younghan Heo younghan@
Gibalwi emphasized the need to establish a fundamental operating system that can continuously increase asset returns by raising the proportion of investments in risky assets. To this end, they proposed a fundamental governance reform to compose the National Pension Fund Management Committee, the highest decision-making body for fund management, with private sector experts.
"Strategic asset allocation determines management performance... Returns must be increased by shifting to expert-centered governance"
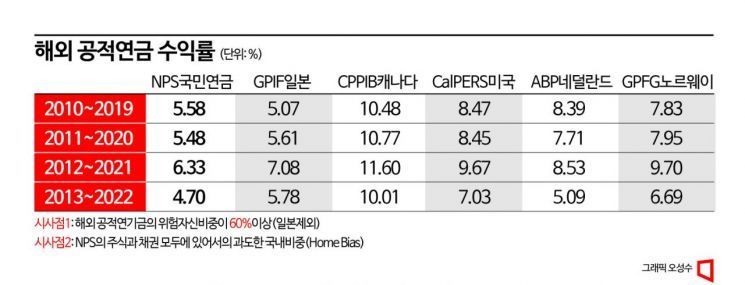
According to Gibalwi's analysis, over 95% of the overall performance of the National Pension Fund is determined by strategic asset allocation. However, the current asset allocation system of the National Pension Fund is diagnosed as a structure where reviewing the appropriateness of such an important strategic asset allocation is impossible, and consequently, no one takes responsibility for it.
According to the National Pension Act, the chairperson of the Fund Management Committee is the Minister of Health and Welfare. In addition, four vice ministers from the Ministry of Economy and Finance, Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, Ministry of Employment and Labor, and Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs, along with the President of the National Pension Service, attend as ex officio members, making a total of six government members. Besides them, there are three employer representatives, three worker representatives, six regional subscriber representatives, and two related experts serving as committee members. Thus, the highest decision-making body for fund management is filled with civil servants lacking expertise and labor representatives.
Gibalwi argued that through the reorganization of the Fund Management Committee, it should be composed of a private sector chairperson and expert members so that they can practically take charge of decision-making, including strategic asset allocation.
However, to supplement issues such as representativeness in the reformed system, they proposed the need to additionally establish an independent organization under the Ministry of Health and Welfare that determines the general investment direction. This would be a policy operation committee (tentatively named the National Pension Policy Committee), chaired by the Minister of Health and Welfare, with government and subscriber representatives as members. This committee would conduct long-term fiscal calculations (long-term financial projections), introduce the concept of a benchmark portfolio, review it, and take on related roles.
The policy operation committee was recommended to operate around the concept of a "benchmark portfolio." Park Young-seo, chairperson of the Fund Management Development Committee, explained, "The benchmark portfolio is a concept one level higher than deciding the investment proportions in domestic stocks, domestic bonds, foreign stocks, and foreign bonds. Simply put, it means deciding the ratio between risky assets and safe assets." He diagnosed that if the policy operation committee, centered on representativeness, decides and takes responsibility for the approximate proportion of risky asset investments, the expert-centered Fund Management Committee can move with concrete strategies to achieve this, thereby establishing a proper structure.
They also proposed significantly increasing the proportion of risky asset investments. Chairperson Park said, "The reason why the returns of advanced countries' public pensions such as Canada, the United States, and the Netherlands are higher than our pension fund is because their proportion of risky asset investments is higher (than the National Pension Fund). Since the basic principle of financial markets is high risk, high return, we also need to increase returns from risky asset investments."
However, since governance reform requires amendments to the National Pension Act, Gibalwi also presented improvement measures within the current system in addition to the fundamental reforms previously suggested. To establish an "expert-led investment decision-making system through a benchmark portfolio" without legal amendments, they proposed, as a secondary option, delegating strategic asset allocation decisions to the Fund Management Headquarters within the National Pension Service.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
!["The Woman Who Threw Herself into the Water Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag"...A Grotesque Success Story That Shakes the Korean Psyche [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















