The Butterfly Effect of Samsung Electronics Pyeongtaek Campus
Population, Students, Businesses, and Income All Increase
June 2017. This marks the time when Samsung Electronics' Pyeongtaek Campus Line 1 (P1) began its first mass production. Samsung subsequently completed Line 2 in 2020 and Line 3 in 2023, establishing a large-scale semiconductor production base here, including DRAM, NAND flash, and foundry operations.
Six years after the start of the first mass production, the landscape of Pyeongtaek has changed significantly. The Pyeongtaek Campus has influenced not only the industrial structure of this city, which previously relied on port industries centered around Pyeongtaek Port and agriculture, but also the regional social structure, including population. We examined the changes in key social and economic indicators of Pyeongtaek City over the past six years since Line 1 began operation.
Investment Amounting to 110 Trillion Won... Pyeongtaek Campus Becomes the Heart of the Local Economy
Samsung Electronics' Pyeongtaek Campus has been described as the "world's largest" each time its mass production system expanded. The construction of Line 1 alone involved an investment of 32 trillion won, and Line 2 required 34 trillion won. Line 3, which began operation last year, saw an even larger investment of 50 trillion won. So far, the production lines built represent only about half of the total planned. Samsung intends to invest at least 180 trillion won to establish a total of six production lines here.
The Pyeongtaek Campus has completely transformed the local map. A representative example is the Godeok International New City (Godeok District), which comprises approximately 59,000 households. Located at the southernmost part of the Seoul metropolitan area’s new towns, Godeok District is essentially a new city being developed based on the demand from Samsung Electronics and its partner company employees.
There is also a station created because of Samsung Electronics: Pyeongtaek Jije Station. This station, served by Subway Line 1 as well as SRT trains, was built using the contributions Samsung Electronics made during the construction of the Pyeongtaek Campus.
Growing and Younger Pyeongtaek
Population decline due to low birth rates and regional extinction are issues far removed from Pyeongtaek City.
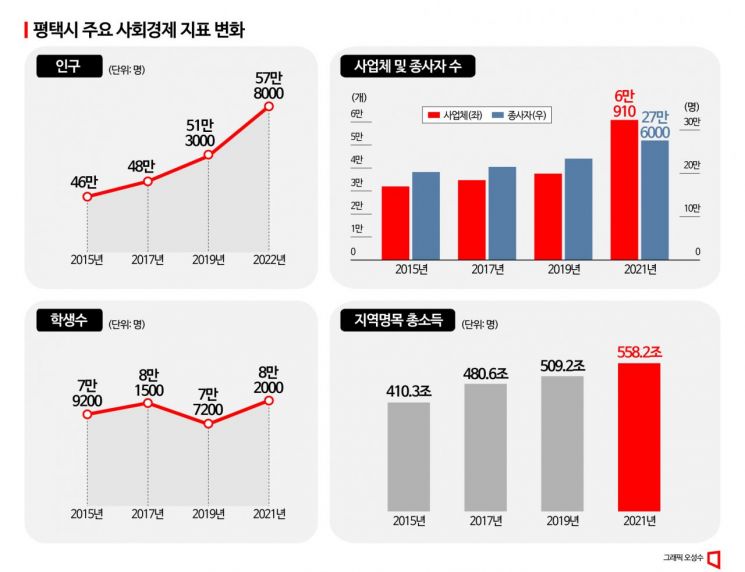
The population of Pyeongtaek City, which was around 460,000 in 2015 when the Pyeongtaek Campus was initiated, increased by 25.6% to approximately 578,000 last year when Line 3 began operation. This population growth is attributed to active in-migration. In 2017, the number of people moving into Pyeongtaek was 76,854, exceeding those moving out by 8,947 (67,907). The gap between in-migration and out-migration has continued to widen, with in-migration (115,557) surpassing out-migration (87,163) by 28,394 in 2021.
Notably, the economically active population (aged 15 and over) has increased. Before the start of mass production on Line 1, the economically active population was below 400,000, but it exceeded 400,000 for the first time in 2017 and steadily grew to 487,000 by 2021.
The younger demographic of Pyeongtaek is also evident in student numbers. The number of students in Pyeongtaek City rose from 79,231 in 2015 to 81,978 in 2021. Although the increase is not large, it stands in clear contrast to the trends in Seoul and most other local governments.
Expanding Economic Scale... Changing Industrial Structure
Semiconductors have also transformed Pyeongtaek City's industrial structure.
The number of businesses in Pyeongtaek City, which was 30,410 in 2015, remained below 40,000 until 2019 but surged to 60,910 in 2021. The number of businesses doubled in eight years.
The employment ratio by industry shows a similar trend. The proportion of workers in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries decreased from 4.9% in 2015 to 2.6% in 2021, while the share of workers in social overhead capital (SOC), other businesses, and service industries increased from 63.9% to 69.3% during the same period.
The overall income of the city also stands out. Pyeongtaek City's nominal regional gross income, which was 410 trillion won in 2015, rose sharply by 36% over six years to 558 trillion won in 2021.
Park Sang-bok, head of the Investment Attraction Team at Pyeongtaek City's Future Advanced Industry Division, said, "As reflected in objective indicators, the regional economic effect brought by Samsung Electronics' Pyeongtaek Campus is absolute," adding, "We will spare no administrative support to ensure continuous corporate investment expansion and job creation."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.