Tsinghua University in China Conducts Poll of 2,600 People
Over 50% Hold 'Unfavorable' Views of US, Japan, and India
38% of Chinese people were found to have unfavorable opinions about South Korea.
According to a report by Yonhap News on the 26th, the Tsinghua University Center for Strategic and Security Studies announced the results of the "2023 Public Opinion Survey on China's International Security Outlook" on the same day.
According to the results, when asked about their "impressions" of seven regions including South Korea, the United States, Japan, India, the European Union (EU), Russia, and Southeast Asia, 38.4% of respondents answered that they had an "unfavorable" impression of South Korea. Among them, 21.0% responded "somewhat unfavorable," and 17.4% answered "very unfavorable."
Nearly half of the respondents, 47.6%, said their impression of South Korea was "neutral," while only 13.9% answered "favorable" (2.1% very favorable, 11.8% somewhat favorable).
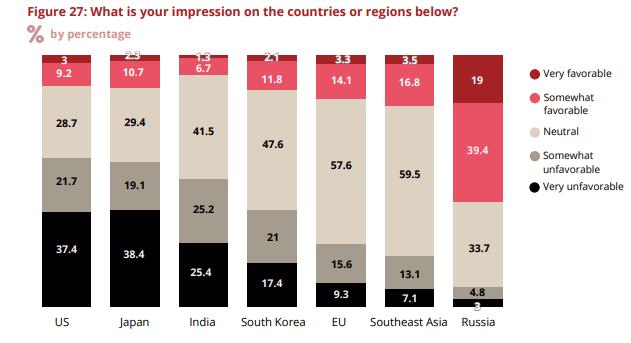 Graph of Chinese people's impressions of seven countries (regions) worldwide conducted by Tsinghua University, China [Image source=Yonhap News]
Graph of Chinese people's impressions of seven countries (regions) worldwide conducted by Tsinghua University, China [Image source=Yonhap News]
In this survey, the country that Chinese people regarded most "unfavorably" was the United States, with more than half of the respondents, 59.1%, answering "unfavorable." Additionally, more than half of the participants also had an "unfavorable" impression of Japan and India.
The percentage of Chinese respondents who answered "unfavorable" toward Japan and India was 57.5% and 50.6%, respectively. The proportions of those who had a "favorable" impression of the U.S., Japan, and India were 12.2%, 13%, and 8%, respectively, all hovering around 10%. The rates of "unfavorable" impressions toward the EU and Southeast Asia were 24.9% and 20.2%, respectively.
On the other hand, the country that Chinese people had the most favorable impression of was Russia, with 58.4% responding "favorable," exceeding half, while only 7.8% answered "unfavorable."
When asked about the influence of eight regions?including the seven mentioned above plus the United Kingdom?on China's security, most respondents named the United States as the country with the greatest influence. Regarding the U.S.'s influence on China's security, 82.9% of respondents said it had a "great influence," followed by Japan (48%), Russia (45.1%), the EU (39.2%), India (32%), the U.K. (26.9%), South Korea (23.3%), and Southeast Asia (22.7%). The proportion of respondents who said South Korea's influence on China's security was "small" was 29.2%, and 47.4% answered "moderate."
The survey was conducted online in November last year with 2,661 Chinese mainland citizens aged 18 and older participating, including 1,543 aged 18?44, 932 aged 45?60, and 186 aged over 60.
At the time of the survey, China was still maintaining its "zero-COVID" policy, and respondents cited the greatest threats facing their country as COVID-19, confrontation with the United States, and international military intervention in Taiwan. The proportion of respondents who said the security threat from "U.S.-China confrontation and conflict" was high was 74.1%, while the proportions who said the security threats from "international military intervention in Taiwan" and the "global pandemic" were high were both 72.4%.
80.1% of Respondents Say "The Ukraine War Is the Responsibility of the U.S. and Western Countries"
Meanwhile, in response to a question about responsibility for the Russia-Ukraine war, 80.1% of survey respondents said that the U.S. and Western countries bear the greatest responsibility for the Ukraine crisis. In contrast, only 8.2% said Russia was responsible, with the remainder blaming Ukraine.
This result is interpreted as related to about 40% of respondents naming state-run media as their main channel for obtaining information on international security news. When asked about their sources for international security issues, respondents answered state-run media (38.6%), social networking services (SNS) (18.5%), government websites and official SNS accounts (18.1%), and commercial media (10.8%) in that order.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















