KIGAM-Gwangju Metropolitan City Agreement Signed on the 15th
Application of Technology for Securing Promising Water Sources and Selecting Optimal Sites
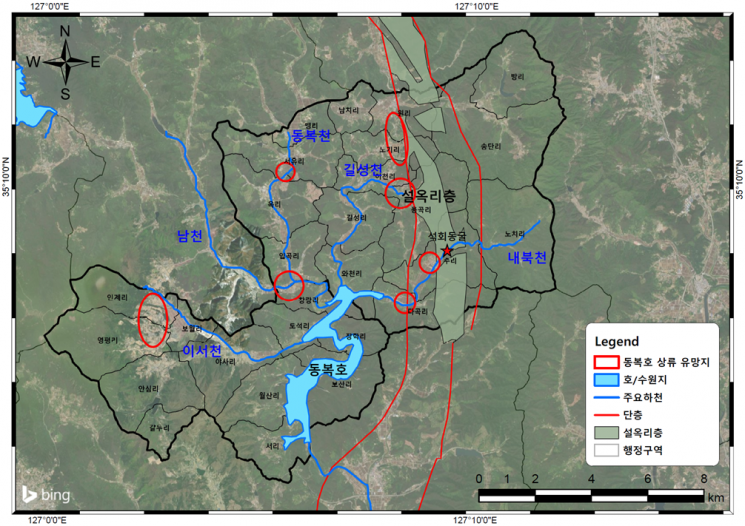
Completion of Suitable Site Selection for Groundwater Development in the Upper and Inner Areas of Dongbok Dam
In response to recent extreme climate changes causing severe droughts in spring and autumn in the Jeonnam and Gwangju regions, a plan is underway to secure water by drilling a super-large underground well.
The Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM) announced on the 16th that it has finalized the site for a large-scale underground well by applying promising water source securing and optimal site selection technologies to Dongbok Dam, a major water source in Gwangju. In this regard, KIGAM signed a business agreement with Gwangju City the day before to cooperate on the development of riverside filtered water and groundwater for drought response. The agreement focuses on geological and groundwater surveys and development, as well as securing and developing riverside filtered water sources.
Recently, abnormal droughts have frequently occurred on the Korean Peninsula, increasing the number of areas implementing emergency or restricted water supply. Although emergency groundwater wells are installed to address drought issues in the short term, the locations and quantities of wells are decided without information on promising water sources, making these measures temporary solutions.
KIGAM’s Groundwater Environment Research Center applied the research results of the 'Development of Large-Capacity Groundwater Securing and Optimal Utilization Technologies for Climate Change Response' to Dongbok Dam, a major water source in Gwangju Metropolitan City, to secure promising water sources and select optimal sites for use in drought and emergency situations. Due to drought occurrences in Jeonnam last year, the water storage of Dongbok Dam remained below 30%, necessitating the securing of alternative water sources.
Gwangju City is considering developing public wells in Baek-a-myeon and Iseo-myeon of Hwasun-gun, upstream of Dongbok Dam, and drilling large-capacity wells inside Dongbok Dam to supply groundwater in cooperation with KIGAM. To develop large-capacity wells and others, the groundwater environment research center applied promising water source selection methods and large-capacity groundwater securing technologies.
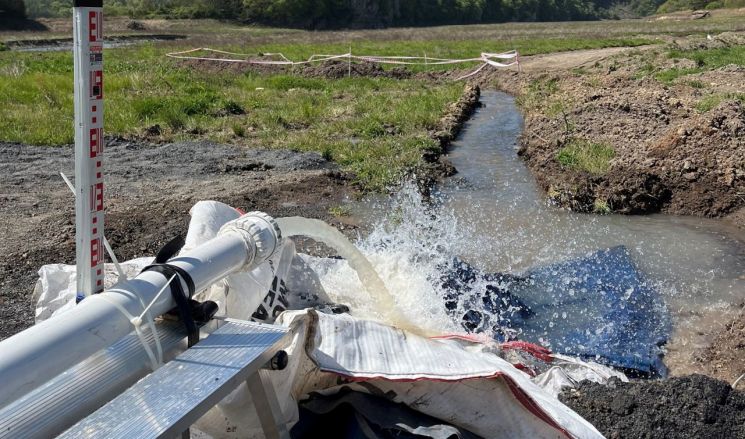
The research team selected promising groundwater sites necessary for the development of public wells upstream of Dongbok Dam. They identified promising rock formations and fault zones for groundwater yield and completed hotspot analysis using data such as pumping capacity and drilling depth of existing groundwater wells. As a result, they derived promising groundwater sites upstream of Dongbok Dam and provided them to Gwangju City. Additionally, they succeeded in demonstrating the 'large-capacity vertical alluvial and bedrock composite well' method for developing large-capacity groundwater wells inside Dongbok Dam.
This method differs from conventional groundwater wells by drilling boreholes over 500mm in diameter that penetrate both alluvial and bedrock layers, enabling the securing of large water volumes. Moreover, compared to other methods, the construction period is relatively short (3 days per well), making it easier to apply in urgent situations to resolve droughts.
In December, the research team actually applied this technology as a pilot in Hoein-myeon, Boeun-gun, Chungbuk, in the Geum River basin, developing two large-capacity groundwater wells (500㎥ (500,000 liters)/day and 330㎥ (330,000 liters)/day) and transferred them free of charge to Hoein-myeon.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![User Who Sold Erroneously Deposited Bitcoins to Repay Debt and Fund Entertainment... What Did the Supreme Court Decide in 2021? [Legal Issue Check]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026020910431234020_1770601391.png)















