Announcement of Monetary Policy Implementation Report on the 15th
CPI Expected to Remain Low Until July
The People's Bank of China, the country's central bank, has projected a strong economic rebound in the second quarter, dismissing the possibility of deflation (a continuous decline in prices amid economic recession). It stated that the recent slowdown in inflation is due to the lag in supply and demand recovery and base effects, and expects inflation to return to normal levels by the end of the year.
On the 15th, the People's Bank of China released its first-quarter monetary policy implementation report, stating, "Facing a severe and complex international environment and a difficult and challenging domestic reform and development process, macro policies have had a stable and positive start." It added, "In the second quarter, growth may rise significantly due to base effects, which will lay the foundation for smoothly achieving this year's overall growth target." The Chinese government previously set this year's gross domestic product (GDP) growth target at around 5%, while the first quarter recorded 4.5%, falling short of this target.
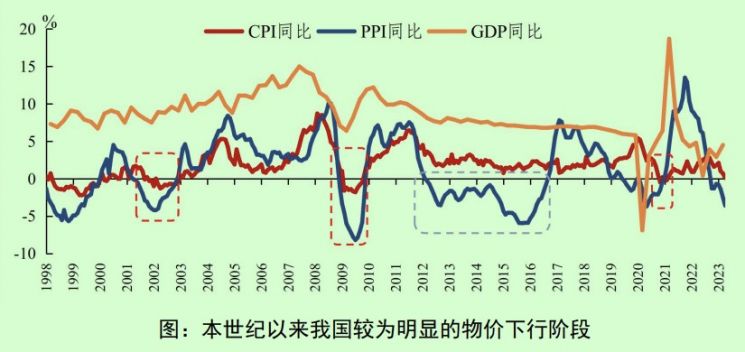 Trends in China's Consumer Price Index (CPI), Producer Price Index (PPI), and Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Growth Rate (Source: People's Bank of China)
Trends in China's Consumer Price Index (CPI), Producer Price Index (PPI), and Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Growth Rate (Source: People's Bank of China)
Regarding second-quarter growth, the report observed, "Due to the base effect from the 0.4% year-on-year GDP decline in the second quarter of last year caused by the COVID-19 shock, growth in the second quarter is expected to rise significantly."
In response to concerns about deflation arising from the recent slowdown in China's inflation rate, the People's Bank of China strongly denied these fears and forecasted a gradual rise in prices going forward. Notably, the report included a separate column emphasizing that China's prices are in a stable range. The column explained, "Deflation refers to a continuous negative growth in prices, accompanied by a reduction in money supply and economic recession," and added, "China's prices are rising moderately, and broad money supply (M2) and social financing are growing relatively rapidly."
Regarding the slowdown in the consumer price index (CPI) inflation rate, it emphasized that this is due to "a gradual decrease in price increases, the lag in supply and demand recovery, and base effects." China's April CPI, released last week, rose by 0.1% year-on-year, fueling deflation concerns. The column predicted, "Due to high base effects, the CPI will remain at a low level from May to July," and "It will recover moderately in the second half of the year, approaching average levels by year-end." Concerning the producer price index (PPI), which has recorded negative growth for seven consecutive months (April -3.6%), the report explained, "Historically, China's PPI has shown large fluctuations," and "A decline in PPI does not necessarily indicate a continuous decline in overall price levels."
Regarding monetary policy, the report stated, "It is necessary to maintain sufficient liquidity through adjustments of appropriate scale and speed," and "Focus will be placed on supporting domestic demand expansion and providing strong and stable support to the real economy to enhance the sustainability of real economic support."
The report also drew attention by mentioning the collapse of the U.S. Silicon Valley Bank (SVB). It noted, "The exposure of Chinese financial institutions is small, so the impact on China's financial market is controllable," but emphasized, "Lessons must be learned from the incident."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![User Who Sold Erroneously Deposited Bitcoins to Repay Debt and Fund Entertainment... What Did the Supreme Court Decide in 2021? [Legal Issue Check]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026020910431234020_1770601391.png)















