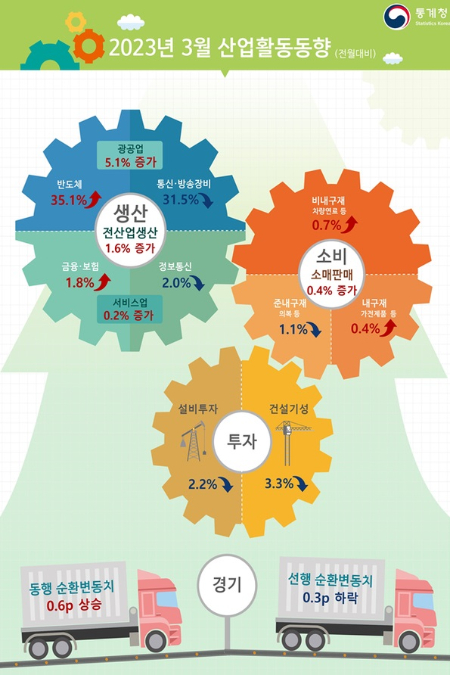
Semiconductor production increased by 35.1% last month, marking the largest growth in production in 12 months. However, this is seen as a base effect following a recent downward trend, and it is considered premature to conclude that the economy has entered a full-fledged recovery phase.
According to the 'March 2023 Industrial Activity Trends' released by Statistics Korea on the 28th, total industrial production last month rose by 1.6% compared to the previous month. This is the largest increase in a year since March last year (1.9%). Total industrial production showed a decline in October (-1.1%) and November (-0.5%) of last year, then recorded increases in December (0.1%), January (0.0%), February (0.7%), and March (1.6%). Mining and manufacturing production decreased in areas such as telecommunications and broadcasting equipment (-31.5%), but manufacturing production increased in semiconductors (35.1%) and automobiles (6.5%), resulting in a 5.1% increase compared to the previous month.
In particular, semiconductor production rose by 35.1% compared to the previous month, marking the largest increase in 14 years and 2 months since January 2009 (36.6%). However, this is analyzed as a temporary effect due to the base effect from the recent decline and contract effects. On a quarterly basis, it decreased by 9.1% compared to the fourth quarter of last year and by 33.8% compared to the same quarter last year. Kim Bo-kyung, Economic Trend Statistics Officer at Statistics Korea, said, "It appears to be a temporary factor due to the base effect from the recent decline and contract schedules," adding, "Samsung Electronics recently officially announced production cuts, so the overall semiconductor production trend should be seen as a downward trend."
Manufacturing inventories increased in telecommunications and broadcasting equipment and machinery, but decreased in semiconductors and petroleum refining, resulting in a 0.5% decrease compared to the previous month. The inventory-to-shipment ratio in manufacturing was 117.8%, down 4.6 percentage points from the previous month. The manufacturing production capacity index decreased by 0.1% compared to the previous month, continuing a six-month consecutive decline. Service industry production decreased in information and communications (-2.0%) and accommodation and food services (-3.4%), but increased in finance and insurance (1.8%) and real estate (3.1%), resulting in a 0.2% increase compared to the previous month. Accommodation and food services declined by 3.4% compared to the previous month, with decreases in restaurants and bars (-2.5%) and lodging (-9.1%).
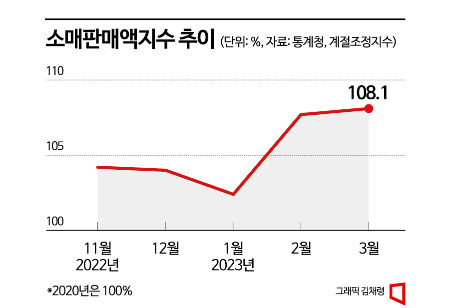
Retail sales increased by 0.4% compared to the previous month. After three consecutive months of decline from November last year (-2.3%) to January this year (-1.5%), retail sales showed two consecutive months of growth starting in February (5.2%). Sales of semi-durable goods such as entertainment, hobbies, sports goods, and clothing decreased by 1.1%, but sales of durable goods like home appliances (0.4%) and non-durable goods such as vehicle fuel (0.7%) increased. By business type, sales increased mainly in large discount stores (5.6%) and duty-free shops (7.5%) compared to the previous month. Statistics Korea evaluated that "the improvement in duty-free shop sales was notable due to the increase in Chinese tourists visiting Korea." Retail sales in March amounted to 54.5717 trillion won, a 4.5% increase compared to the same month last year (48.3131 trillion won).
Facility investment decreased by 2.2% compared to the previous month, with increased investment in machinery such as special industrial machinery (0.5%) but decreased investment in transportation equipment such as ships (-9.7%). Construction-related indicators also showed weakness due to the downturn in the real estate market. Construction performance (constant prices), which reflects completed construction work, increased in civil engineering (12.2%) but decreased in building construction (-7.6%), resulting in a 3.3% decrease compared to the previous month. Construction orders (current prices) decreased by 44.4% year-on-year, with declines in building construction such as housing (-39.2%) and civil engineering such as machinery installation (-59.4%).
The coincident composite index, which reflects the current economic situation, rose by 0.6 points compared to the previous month, while the leading composite index, which predicts future economic conditions, fell by 0.3 points due to inventory increases and decreased domestic shipments of machinery, marking a decline for five consecutive months. Officer Kim said, "Although the overall figures continue to fluctuate, the coincident index at 99.9, below 100, indicates sluggishness or slowdown in terms of the economic cycle," adding, "Although it has risen in the last two months, the level is still low to say that the downward trend has been overcome."
Bang Ki-seon, Deputy Minister of Economy and Finance, said at the emergency economic vice minister meeting and export investment responsibility meeting on the same day, "For our economy to recover fully, it is necessary to maintain the consumption recovery trend that drove growth in the first quarter as much as possible, while also revitalizing the still sluggish exports and investment."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)










