Procurement Interest Rates Surge from 3-4% to 7% Range
Grade A Construction Firms Expecting Performance Decline Also Enter Private Bond Market
Companies struggling with poor performance and deteriorating financial conditions, making it difficult to access the public corporate bond market, have been flocking to the private placement bond market since the beginning of the year. Mainly construction companies whose credit ratings fall short of A-grade or have recently experienced a sharp decline in creditworthiness are frequenting the private placement bond market. Although they are securing funds by finding investors with difficulty, they are suffering from a double burden of poor performance and increased interest expenses due to soaring interest rates.
Heavy Industry and Construction Firms Rated BBB or Below Raise Funds Through Private Placement Bonds
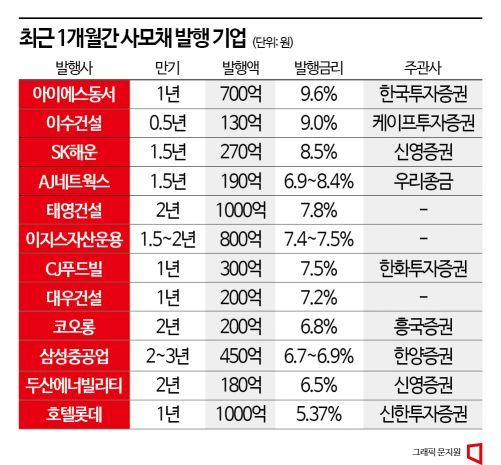
According to the investment banking (IB) industry on the 14th, LS Networks, an affiliate of LS Group, issued private placement bonds worth 30 billion KRW on the same day. It is known that NH Investment & Securities was selected as the lead manager and contacted institutional investors. LS Networks' credit rating is BBB+ (negative outlook). Since its credit rating dropped from A-grade to BBB-grade, it has not issued public bonds and has been raising funds through private placement bonds.
Samsung Heavy Industries issued private placement bonds worth 45 billion KRW on the 10th. This is the first private placement bond issuance by Samsung Heavy Industries this year, which issues several tens of billions of KRW in private placement bonds annually. Hanyang Securities reportedly purchased all the bonds and then sold them to other institutional investors. Samsung Heavy Industries has recorded large-scale deficits for several years, causing its credit rating to plummet to BBB. Although there is growing optimism about performance recovery due to recent order increases, it has failed to turn a profit each quarter, preventing credit improvement.
CJ Foodville and Kolon also raised funds by issuing private placement bonds worth 30 billion KRW and 20 billion KRW, respectively, on the same day. Their credit ratings were BBB (negative) and BBB+ (stable), respectively.
Unlike public bonds, private placement bonds do not go through a demand forecasting process based on an auction method to determine the bond issuance interest rate. Companies privately contact investment institutions to gauge investment intentions and set the interest rate. If both the company and investors find an acceptable interest rate level, the bonds are issued at that rate. For this reason, companies that find it difficult to issue public bonds due to credit deterioration or avoid submitting public offering documents such as securities registration statements mainly use private placement bonds as a funding method.
Recently, the frequency of private placement bond issuance by construction companies expected to experience performance deterioration due to the real estate market downturn has increased. SK Ecoplant issued private placement bonds worth 36 billion KRW on the 9th, IS Dongseo issued 70 billion KRW on the 3rd, and Daewoo Construction issued 20 billion KRW at the end of last month. An IB industry official explained, "Until the first half of last year, the private placement bond market was mainly used by companies rated below A-grade as a funding method. Since the beginning of this year, A-grade construction companies expected to experience performance deterioration have also joined the private placement bond market, increasing the frequency and volume of private placement bond issuance."
Polarization Deepens... Interest Burden Increases for Low-Credit Companies
As polarization intensifies in the corporate bond market, companies raising funds through the private placement bond market are facing high funding interest rates. The issuance interest rates for Samsung Heavy Industries' recently issued 2-year and 3-year private placement bonds were 6.7% and 6.9% per annum, respectively, approaching the 7% mark. Compared to last year when funds were raised at the high 3% to low 4% range, the funding cost has nearly doubled.
CJ Foodville raised 1-year funds at an annual interest rate of 7.5%, and Kolon raised 2-year funds at 6.8% per annum. These companies had been issuing private placement bonds at the low 4% range until last year. LS Networks' private placement bond issuance interest rate also surged from the 4% range to the mid-7% range.
Construction companies' private placement bond funding interest rates have exceeded 7%. Daewoo Construction and Taeyoung Construction issued bonds at the low 7% range, while mid-sized construction companies such as IS Dongseo and Isu Construction issued private placement bonds at interest rates above 9%. An IB industry official evaluated, "Most companies raising funds in the private placement bond market are those whose credit ratings have fallen due to poor performance or deteriorating financial conditions, and the rising funding interest rates are adding additional burdens to profitability."
The upward trend in private placement bond funding interest rates is expected to continue for some time. A bond market official predicted, "With the U.S. tightening stance expected to continue and the recent bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) in the U.S. raising corporate credit risks, the funding interest rates for some low-credit companies in heavy industry and construction are likely to keep rising."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















