Turkey, Location of the Most Active Seismic Zone
Major Earthquake Occurs After 83 Years Since 1939
[Asia Economy Reporter Yoon Seul-gi] Turkey has once again been struck by the agony of a major earthquake. Earthquakes have occurred in the southern part of Turkey and the northern border region of neighboring Syria, causing numerous casualties.
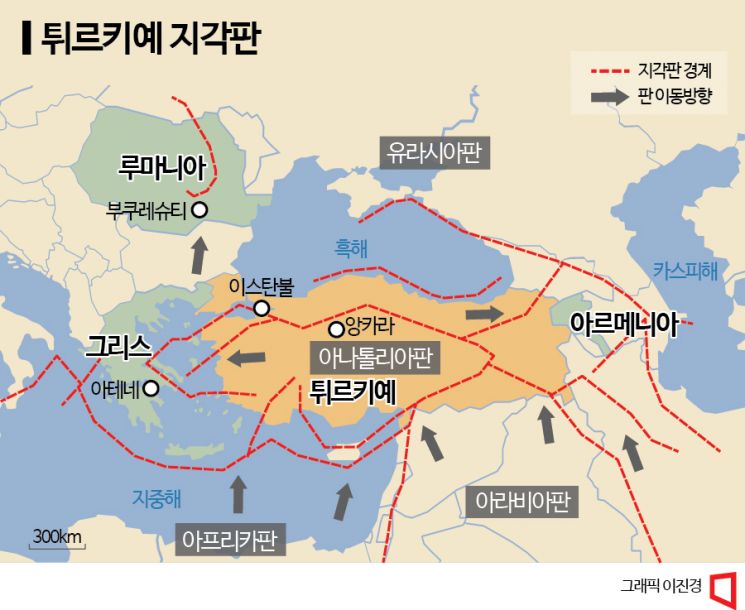
Turkey is located at the convergence of four tectonic plates: the Anatolian Plate, the Eurasian Plate, the African Plate, and the Arabian Plate. It is also situated on the most active fault zone, resulting in frequent strong earthquakes.
According to AFP and other sources, at 4:17 a.m. local time on the 6th, a magnitude 7.8 earthquake struck southeastern Turkey’s Gaziantep, followed by a magnitude 7.5 aftershock at 1:24 p.m. in the northeastern area of Kahramanmara?.
This earthquake is the largest in Turkey in 83 years since 1939 in terms of magnitude. The first earthquake occurred inland about 33 km from the southern Turkish city of Gaziantep, at a depth of 17.9 km underground, and the aftershock occurred 59 km northeast of Kahramanmara?. Gaziantep and Kahramanmara?, near the epicenter, border Syria.
The two strong earthquakes and over 80 aftershocks have caused the number of casualties to continue rising. Turkish Vice President Fuat Oktay announced on the 7th that at least 2,379 people have died and 14,483 have been injured so far due to the earthquake. In Syria, the death toll has reached at least 810.
Turkey has long been considered a region prone to earthquakes. Earthquakes occur along faults created by the movement or overlapping of tectonic plates, and Turkey is located at the meeting point of the Anatolian Plate, Eurasian Plate, African Plate, and Arabian Plate. The Anatolian Plate, where Turkey is situated, is continuously pushed by the Eurasian Plate to the northeast and the Arabian Plate to the southwest, causing frequent earthquakes.
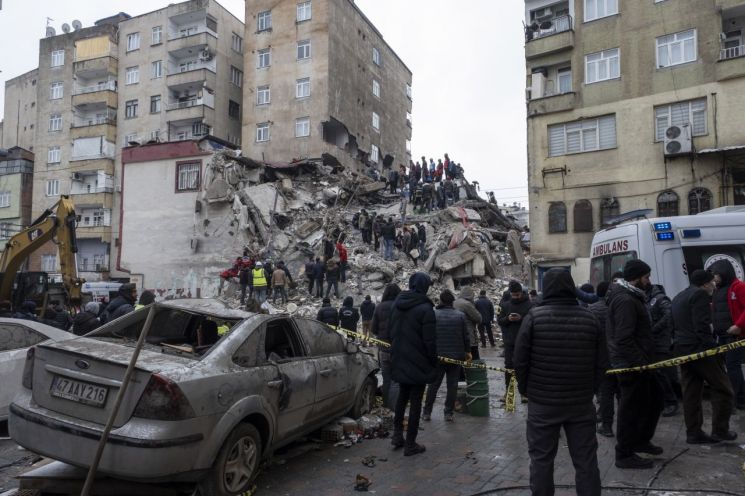 On the 6th (local time), a magnitude 7.8 earthquake struck southeastern Turkey. Rescue workers are saving residents trapped under the rubble of collapsed buildings in Diyarbakır, one of the affected areas. Photo by EPA·Yonhap News
On the 6th (local time), a magnitude 7.8 earthquake struck southeastern Turkey. Rescue workers are saving residents trapped under the rubble of collapsed buildings in Diyarbakır, one of the affected areas. Photo by EPA·Yonhap News
In fact, most earthquakes on Earth occur at plate boundaries, known as plate boundary earthquakes. Like Turkey, Japan is located at the intersection of four tectonic plates (the Eurasian Plate, Philippine Plate, Pacific Plate, and North American Plate). Because it is situated on plate boundaries, Japan has experienced frequent large and small earthquakes in the past and is expected to face major earthquakes in the future as well.
Especially, Turkey is located on one of the most active fault zones in the world, resulting in frequent strong earthquakes. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), seven earthquakes of magnitude 7.0 or higher have occurred in Turkey over the past 25 years.
The scale of damage caused by earthquakes is also significant. On December 27, 1939, a magnitude 7.8 earthquake struck Erzincan in northeastern Turkey near the North Anatolian Fault, killing approximately 33,000 people. This is considered the worst earthquake in Turkish history. On August 17, 1999, a powerful magnitude 7.6 earthquake occurred in western ?zmit. At that time, more than 17,000 people died and over 50,000 were injured.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















