[Asia Economy Reporter Donghyun Choi] The Ministry of SMEs and Startups announced on the 7th that last year’s exports by small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) reached $117.5 billion (approximately 148 trillion KRW), a 1.7% increase compared to the previous year. Despite challenging external conditions such as global economic slowdown, rising raw material prices, and supply chain instability, SME exports surpassed $110 billion for the second consecutive year.
The number of exporting SMEs was 92,578, slightly up from 92,114 in the previous year. Exports increased in all segments except for companies with export amounts between $5 million and less than $10 million. Companies with exports exceeding $100 million grew the most, rising 12.3% from 57 in 2021 to 64 in 2022.
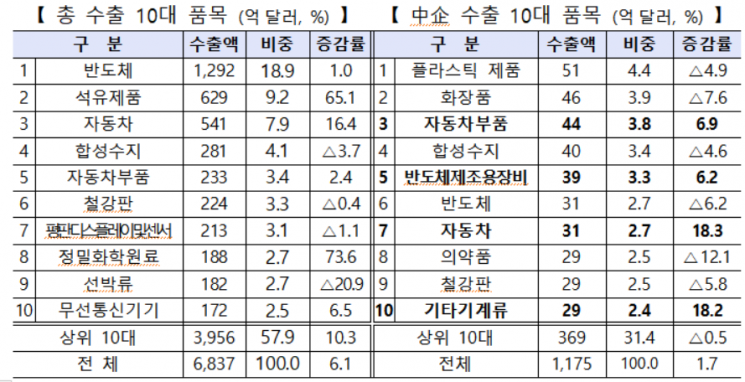
Top export items for SMEs included plastic products, cosmetics, automotive parts, synthetic resins, and semiconductor manufacturing equipment, all recording high export values. The concentration of the top 10 SME export items was 31.4%, lower than the 57.9% concentration of the top 10 export items for the entire country.
Among the top 10 items, exports of automobiles (18.3%) and other machinery (18.2%) recorded double-digit growth. Exports of automotive parts (6.9%) and semiconductor manufacturing equipment (6.2%) also showed favorable trends.
Items with notable year-on-year increases included automobiles ($480 million), other machinery ($440 million), and industrial electrical equipment ($410 million). Automobile exports increased for the second consecutive year due to rising exports of used cars to Russia and neighboring countries.
Other machinery entered the top 10 SME export items last year, driven by strong markets for finished cars and electric vehicles, with increased exports of car parts and electric vehicle battery manufacturing equipment to China, the U.S., and Hungary, and display manufacturing equipment exports to Vietnam.
Industrial electrical equipment also recorded growth for the second consecutive year, with increased exports of automotive electrical components, electric vehicle chargers, and electronic product power supplies to the U.S., China, and Mexico, reflecting rising demand for finished cars and electric vehicles.
On the other hand, the top two SME export items, plastic products (-4.9%) and cosmetics (-7.6%), saw declines compared to the previous year due to reduced demand from China, the largest export market, amid the global economic slowdown.
Among the top 10 export countries, exports to five countries? the U.S., Japan, Taiwan, India, and Mexico?all increased. Except for Japan, the other four countries recorded their highest-ever export figures.
The U.S. (16.5%) saw increased exports of automotive parts due to a strong finished car market. Exports of machinery such as electronic application devices, mechanical components, and industrial electrical equipment also grew by double digits, influenced by manufacturing promotion policies. India (10.6%) experienced increased exports of automotive parts due to local automobile plant expansions and strong machinery exports driven by the Indian government’s expanded infrastructure investments, marking two consecutive years of export growth.
Mexico (10.0%), a North American automotive production hub, saw significant growth in exports of automotive parts, industrial electrical equipment, and molds related to automobile manufacturing. Taiwan (5.7%) experienced nearly an 18-fold increase in exports of COVID-19 diagnostic kits and maintained steady exports of semiconductor manufacturing equipment.
Conversely, China (-8.2%) and Hong Kong (-15.9%) saw overall declines in major item exports due to production and consumption slowdowns caused by strict COVID-19 lockdown policies and delayed economic recovery, resulting in a year-on-year decrease in total exports.
The concentration of the top 10 SME export countries was 67.6%, lower than the 70.4% concentration for the country’s total exports. The proportion of SMEs exporting to a single country was 55.5%, while those diversifying exports to two or more countries accounted for 44.5%, similar to the previous year. The main export destinations for single-country exporting SMEs were China, Japan, and the U.S., in that order.
Last year, online exports by SMEs reached $710 million, an 8.5% increase from the previous year. Exports increased mainly to the U.S. and Southeast Asian countries. SMEs accounted for 78.4% of the total online export value of $910 million, up from 76.7% the previous year, showing SMEs’ strong presence in the online export sector.
Items such as audio equipment (38%) and computers (101.2%) showed strong performance. Exports were active to countries with high Korean Wave influence and developed online malls, including the U.S., Japan, China, Singapore, and Malaysia. The number of SMEs engaged in online exports increased by 21.6% to 3,818.
Choi Won-young, Director of Global Growth Policy at the Ministry of SMEs and Startups, stated, “Although SME exports increased for the second consecutive year in 2022, export declines have continued since the second half due to the global economic recession, and difficult conditions are expected to persist in 2023.”
He added, “The Ministry of SMEs and Startups announced the ‘SME Export Support Plan’ on January 26 to revitalize SME exports and discover new growth engines. We will actively support the implementation of this plan to ensure that exporting SMEs can grow as key players in Korea’s exports.”
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.