Samsung's Second US Foundry Hub 'Taylor'
Many Production Advantages Due to Foundry Proximity
Competing with TSMC and Intel... Expanding Local Engagement
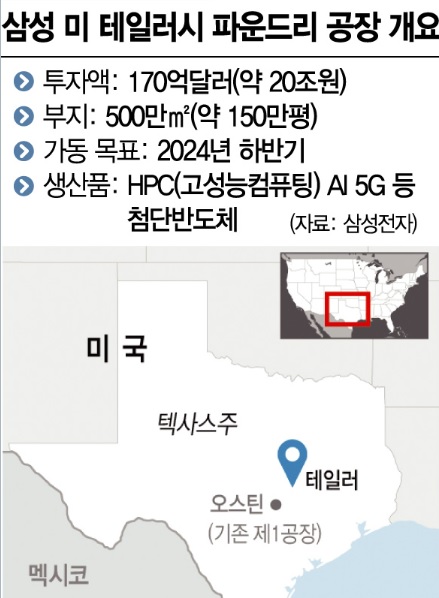
[Asia Economy Reporter Kim Pyeonghwa] Samsung Electronics is investing $17 billion (approximately 21.386 trillion KRW) to build a foundry (semiconductor contract manufacturing) plant in Taylor, Texas, USA. This is to secure local customers. Samsung will have to compete fiercely with TSMC and Intel here.
On January 31, during the conference call regarding the fourth quarter results of last year, Samsung Electronics stated, "The Taylor fab in the US is scheduled to mass-produce 4-nanometer chips in the second half of 2024 as originally planned." They also added, "We will continue investments focused on expanding capacity in Taylor, USA, and Pyeongtaek to meet demand for advanced process technologies."
The Taylor plant is Samsung Electronics' second foundry plant in the United States. Covering 5 million square meters, it is about four times larger than the existing Austin foundry plant. Samsung aims to complete construction this year and start mass production next year. Advanced semiconductors will be manufactured here using the 4-nanometer (nm; 1 nm is one billionth of a meter) process. These semiconductors will be used in various fields such as 5th generation mobile communication (5G), artificial intelligence (AI), and high-performance computing (HPC).
 The area around the site where the Samsung Electronics Taylor factory will be built (left) and Samsung Electronics President Kyung Kye-hyun receiving a Samsung Expressway sign as a gift /
The area around the site where the Samsung Electronics Taylor factory will be built (left) and Samsung Electronics President Kyung Kye-hyun receiving a Samsung Expressway sign as a gift / [Photo by Samsung Electronics website · President Kyung's Instagram account]
Samsung Electronics views the Taylor plant as playing a significant role in expanding its foundry business. Foundry companies manufacture semiconductors according to customer orders. Having a plant near the customer makes business communication easier. It helps build customer trust and improve product quality. This means it can be advantageous in securing local customers. The US hosts many large fabless companies such as Nvidia, AMD, and Qualcomm. Market research firm IC Insights reported that as of 2021, the US held a 68% share of the global fabless market.
Especially in the current situation, having plants on a regional basis can be a competitive advantage. The US introduced the Chips and Science Act (CSA) last year to increase domestic semiconductor production. This law offers tax benefits and subsidies to companies that establish production facilities locally. Market research firm TrendForce analyzed, "Governments worldwide understand the importance of local manufacturing," and added, "Foundry companies need to consider other countries' subsidy policies and local customer demands more."
Of course, there are many challenges as well as benefits. Samsung must compete locally with Taiwan's TSMC, the number one player in the foundry market. TSMC recently increased its investment for building two foundry plants in Phoenix, Arizona, from $12 billion (approximately 15.096 trillion KRW) to $40 billion (approximately 50.32 trillion KRW). The first plant plans to introduce the 4 nm process next year to produce advanced semiconductors. The roadmap is the same as the Taylor plant.
TSMC already has major US fabless companies such as Apple, Nvidia, and AMD as large customers. Increasing local production will strengthen collaboration with these customers. In fact, Apple CEO Tim Cook attended the equipment installation ceremony at the Phoenix plant in December last year. He said, "Apple plans to purchase processors made at the Arizona plant going forward."
Intel, which is building plants in Ohio and Arizona and expanding its foundry business, is also a variable. Intel plans to produce products using the 3 nm process at its foundry plant this year and apply the 2 nm process from the second half of next year. It will be difficult for Intel to achieve immediate results. However, if it successfully secures customers, it could become another competitor for Samsung Electronics.
Samsung Electronics is implementing a strategy to respond quickly to customer orders locally. Samsung is building Line 1 in Taylor and will soon construct Line 2. Line 2 will operate as Shell First. Shell First means pre-building the cleanroom, the space where semiconductor chips are produced. This allows immediate production in the cleanroom once customer orders are received. Samsung is also increasing engagement with the local community. It donates an average of over $300,000 (approximately 377.1 million KRW) annually to the Taylor community. It also operates internships in cooperation with local educational institutions.
In the mid to long term, Samsung must secure technological competitiveness. The goal is to increase yield (the ratio of good products among finished products) in fine processes. Samsung Electronics President Kyung Kye-hyun (Head of the DS Division) said at a meeting with employees on the 1st, "We must catch up with TSMC's performance and yield." Samsung plans to introduce the second-generation 3 nm process and mass-produce products in 2024.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
!["The Woman Who Threw Herself into the Water Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag"...A Grotesque Success Story That Shakes the Korean Psyche [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















