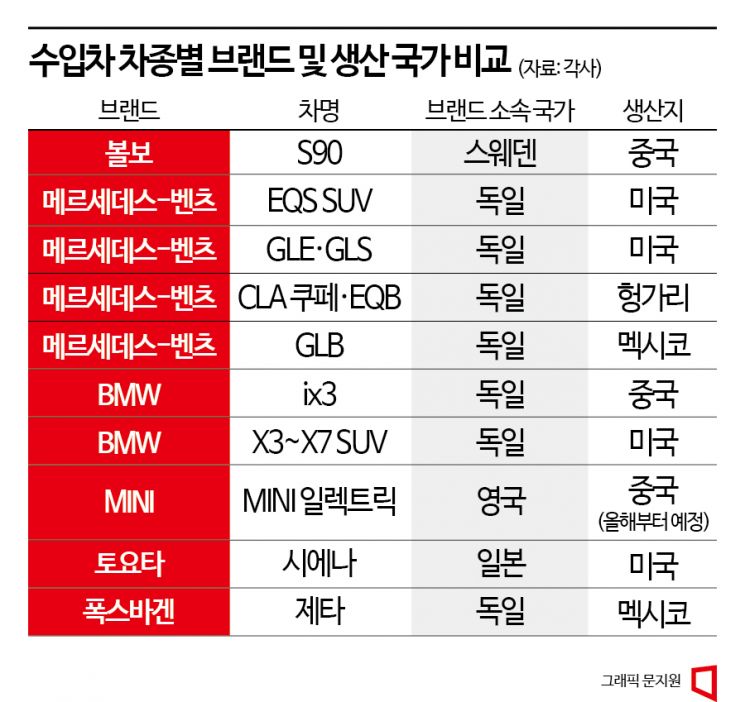
Volvo Ranks 4th in Imported Cars Thanks to Popularity of China-Made S90
Focus on Quality Over Production Location...Consumer Perception Also Changing
Cost Reduction Targeted Through Regional Supply Chain Restructuring
[Asia Economy Reporter Suyeon Woo] The Swedish complete car brand Volvo's large sedan S90 is an imported car from China. When Volvo Korea announced in 2018 that it would launch the China-made S90, import car companies could not hide their skepticism about whether 'Made in China' would really work in the Korean market.
Five years after its launch, the consensus among import car companies has shifted from where it was made to how good the product is. Before the China-produced S90 was officially delivered domestically, Volvo was ranked among the top 10 import car brands in Korea by sales volume. However, that ranking gradually began to rise. It was 6th in 2019, 5th in 2020, and entered the top 4 in 2021. Last year, 4,361 units of the S90 were sold. The S90 accounted for 30% of Volvo Korea's annual sales. The quality silenced the controversy over the place of production.
Behind the success of the S90 is Volvo's rigorous global quality management system. Volvo created a global standard quality assurance system to maintain the same vehicle quality for cars produced in China and Sweden. It strictly controls everything from the materials of parts to the final vehicle inspection after assembly. The manufacturing method (VCMS) also promotes the unification of global factories. Best practices in manufacturing management are collected from each factory and uniformly applied to factories worldwide.
In the past, Korean consumers reacted sensitively to the place of production. This was because they believed that brand and country-of-origin premiums were reflected in vehicle prices. Overseas car brands have worked hard to change this perception. In the process of reorganizing global supply chains focused on efficiency, insisting only on domestic production could risk losing competitiveness.
Companies have strengthened production management systems and classified production sites by region and vehicle type. For example, they establish production bases in mainland China, the world's largest automobile consumer market, to save logistics and labor costs, or concentrate SUV production in factories in the U.S. or Mexico to respond to the U.S. market where sport utility vehicles (SUVs) sell well. To survive fierce competition, they have no choice but to reduce costs.
The Mercedes-Benz EQS SUV, launched domestically on the 31st of last month, is also a product of supply chain reorganization to strengthen competitiveness. The EQS SUV is exclusively produced at the Mercedes-Benz plant in Tuscaloosa, USA. Simply put, it is not a German car but an American-made car. The U.S. plant is responsible not only for large SUVs like the GLE and GLS but also for electric SUV models such as the EQS SUV and EQE SUV. Since the 2000s, the U.S. plant has firmly established itself as Mercedes-Benz's SUV production base.
At this plant, it is possible to connect in real time to the network of all Mercedes-Benz passenger car factories worldwide. This means that Germany can monitor and control the data and process management mode of the U.S. plant. Analysis through big data and improvements in production processes are also possible.
The BMW Group produces the compact electric SUV ix3 at its Shenyang plant in China and imports it, and from this year, it is moving the electric vehicle production line of the premium small car brand MINI to China. A BMW official said, "The quality of vehicles produced at BMW plants worldwide is all the same," adding, "Even if the production site changes, we make products so that the brand premium is not diluted."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![From Bar Hostess to Organ Seller to High Society... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Counterfeit" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















