Japan's Rapidus Details 2nm Plan
Intel Targets 2nm in Second Half of Next Year
TSMC Leads with Yield
[Asia Economy Reporter Kim Pyeonghwa] Japan and the United States have announced plans to accelerate development in the global foundry (semiconductor contract manufacturing) market and introduce 2-nanometer (nm; 1 nm is one billionth of a meter) technology. Taiwan, with its leading company TSMC, is expanding its market dominance through superior yield rates (the ratio of good products among total production). South Korea's foundries are currently in a time race with the U.S. and Japan in the process node competition but lag behind Taiwan in yield.
U.S. and Japan Boost Foundry Industry, Targeting 2nm
The Korea Institute for Industrial Economics and Trade recently released issue No. 28 of its 'Future Strategic Industry Brief,' which includes forecasts for new industries. It highlighted the entry of the U.S. and Japan into the foundry sector as a key new industry issue to watch this year.
Japan has recently shown a strong will to develop its foundry industry. Although its semiconductor materials and equipment industries are advanced, its manufacturing technology remains at an early stage, which it aims to supplement.
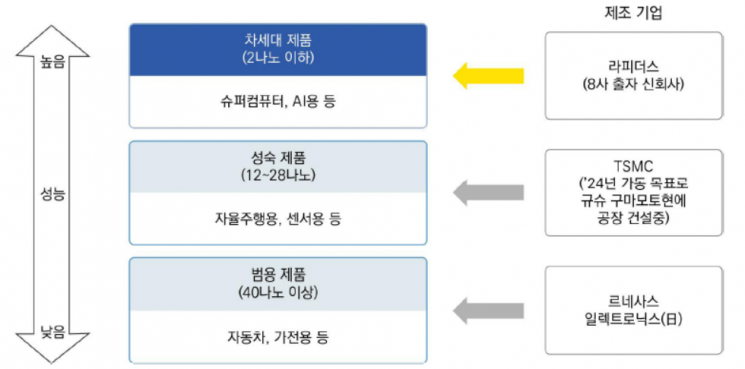 Japan's Next-Generation Semiconductor Manufacturing Capability Acquisition Plan / [Image Source=Korea Institute for Industrial Economics & Trade Future Strategy Industry Brief]
Japan's Next-Generation Semiconductor Manufacturing Capability Acquisition Plan / [Image Source=Korea Institute for Industrial Economics & Trade Future Strategy Industry Brief]
Japan's most advanced process is handled by 'Rapidus,' which appeared in November last year. Rapidus is a corporation jointly established by eight Japanese companies, including Toyota Motor, Sony, and Kioxia, with an investment of 7 billion yen. It plans to operate a prototype line for the 2 nm process by the first half of 2025. Mass production of 2 nm advanced semiconductors is expected to be possible in the late 2020s. The production plant site will be decided by March.
The semiconductor industry believes that Rapidus will find it difficult to showcase 2 nm process technology in a short period. Even leading companies like TSMC and Samsung Electronics only entered the 3 nm technology competition last year. However, Rapidus's decision to jointly develop 2 nm semiconductors with U.S. IBM has raised the level of technological cooperation, which is a variable factor. Its focus on supplying customized semiconductors domestically to secure a certain demand is also expected to increase its influence. The Japanese government is providing Rapidus with a subsidy of 70 billion yen.
In the U.S., Intel's efforts to grow the foundry industry stand out. Intel, which had focused on semiconductor design, announced in 2021 that it would nurture foundry as a core business. It plans to introduce 3 nm technology this year and 2 nm technology from the second half of next year. It is also actively investing to increase production capacity, including building a factory in Arizona.
The U.S. government has introduced the Chips and Science Act (CSA), which provides a 25% tax credit and subsidies to companies building semiconductor factories locally. Various support measures have been introduced to strengthen domestic semiconductor manufacturing capabilities. Administrative support is also generously provided when foreign companies establish foundry plants locally.
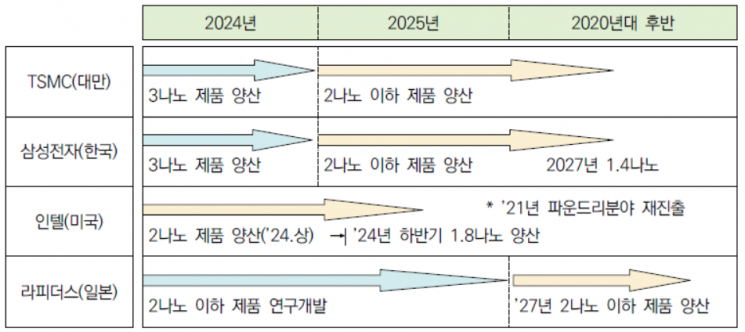 Semiconductor Development and Mass Production Plans by Major Foundry Companies / [Image Source=Korea Institute for Industrial Economics & Trade Future Strategy Industry Brief]
Semiconductor Development and Mass Production Plans by Major Foundry Companies / [Image Source=Korea Institute for Industrial Economics & Trade Future Strategy Industry Brief]
Taiwan Boasts High Yield... New Competitive Landscape in Foundry
If Japan and the U.S. succeed in their challenges, the competitive landscape of the foundry market is expected to change. The Korea Institute for Industrial Economics and Trade predicts that by 2025, Taiwan, South Korea, and the U.S. will compete in the foundry market. Japan is expected to join the competition by 2027.
Taiwan, the market leader, emphasizes its advanced yield as a competitive advantage. Taiwan's TSMC is known to have an 80% yield rate for its 5 nm process. TSMC has stated that its latest 3 nm process has a yield similar to that of 5 nm. Although some in the industry argue that the actual 3 nm yield may be lower, TSMC is evaluated to have increased its influence with superior yield in advanced processes compared to Samsung Electronics.
The Korea Institute for Industrial Economics and Trade advised that South Korea needs to enhance its competitiveness by strengthening system semiconductor capabilities, including foundries. It recommended fostering fabless (semiconductor design) companies and preparing growth strategies for foundries through industry-academia cooperation. Kim Jong-gi, senior research fellow at the institute, explained, "In the mid to long term, it is necessary to closely prepare for China's rise in the system semiconductor sector."
Market research firm Counterpoint Research reported that in the third quarter of last year, Taiwan's TSMC held the top position in the global foundry market with a 59% share. Samsung Electronics (12%) and Taiwan's UMC (7%) followed. Both TSMC and Samsung Electronics are aiming for mass production of 2 nm processes by 2025. Both companies plan to apply gate-all-around (GAA) transistor technology, which is an advancement over the existing FinFET, at 2 nm.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
















