 Trends in Patent Applications by Applicant Nationality Related to 'Post-Quantum Cryptography'. Provided by the Korean Intellectual Property Office
Trends in Patent Applications by Applicant Nationality Related to 'Post-Quantum Cryptography'. Provided by the Korean Intellectual Property Office
[Asia Economy (Daejeon) Reporter Jeong Il-woong] The competition among countries worldwide to dominate next-generation cryptographic technologies is fierce.
Currently, the representative next-generation cryptographic technologies are 'Quantum Cryptography' and 'Post-Quantum Cryptography.'
These cryptographic technologies are being developed in response to concerns that quantum computers could undermine the cryptographic systems used in modern information and communication sectors.
As countries around the world focus on developing these cryptographic technologies, the related market size is also expected to gradually expand.
In fact, the economic value of post-quantum cryptographic technology is projected to reach 27 trillion KRW by 2026.
This figure is predicted by synthesizing data from STATISTA (2021) on the global cybersecurity market size and the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), accounting for 11% of the total security market size (247 trillion KRW).
Reflecting the competitive landscape in technology development and the market expansion outlook, patent applications related to post-quantum cryptography have also been steadily increasing.
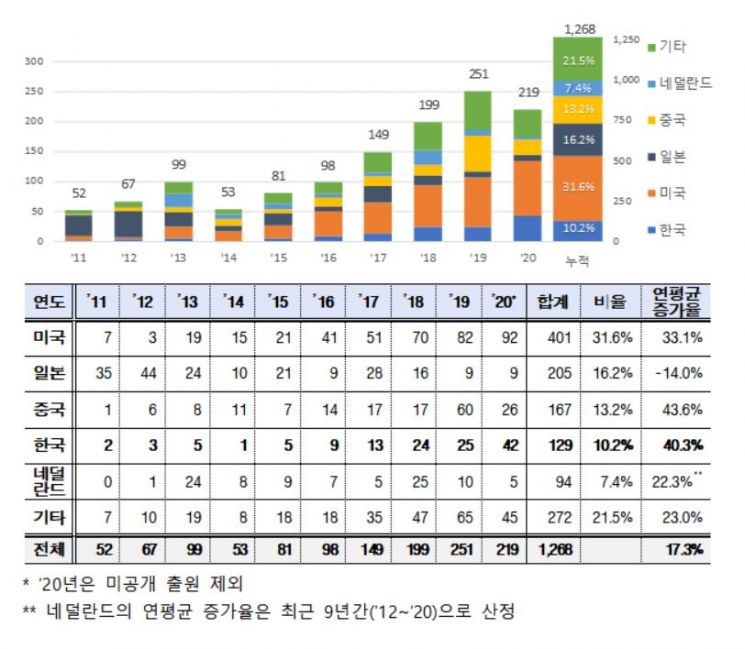
According to the Korean Intellectual Property Office, worldwide patent applications related to post-quantum cryptography have grown at an average annual rate of 17.3% since 2011, increasing 4.2 times from 52 applications in 2011 to 219 in 2020 over ten years.
By country, the share of patent applications related to post-quantum cryptography is highest in the United States at 31.6%, followed by Japan (16.2%), China (13.2%), and South Korea (10.2%).
However, in terms of changes in patent application numbers by country over the past decade, Japan's applications have somewhat decreased, whereas China and South Korea have shown annual growth rates of 43.6% and 40.3%, respectively, presenting a contrast.
Post-quantum cryptography is classified into five types based on the underlying mathematical problems: lattice, hash, multivariate, code, and elliptic curve, with lattice-based cryptography accounting for the largest share at 32.0%.
South Korea's number of patent applications in the lattice-based technology field (2011?2020) is 69, which is fewer than the United States (90) and Japan (76). However, in the last five years, South Korea's applications totaled 59 (ranked 2nd), showing a close gap with the United States' 62 (ranked 1st), which is noteworthy.
Also, when examining by applicant type, globally, post-quantum cryptographic technology development is led mainly by companies (80%), whereas in South Korea, universities (38.8%) and research institutes (10.1%) have higher proportions, indicating government-led technology development.
Park Jae-il, Director of the Artificial Intelligence Big Data Examination Division at the Korean Intellectual Property Office, stated, "Cryptographic technology is a field where ideas can compete with global corporations, and it is encouraging that domestic companies and researchers are performing well. With the emergence of disruptive technology like quantum computing opening the 'next-generation cryptographic technology market,' a nationwide effort is needed to secure core technologies to prepare for cyber security threats and to capture the market."
*Quantum cryptography refers to a cryptographic method that uses physical quantum states employed in quantum computers rather than digital information like current cryptographic systems.
*Post-quantum cryptography refers to cryptographic algorithms that significantly increase the complexity of mathematical problems so that they cannot be solved even by quantum computers.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















